* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
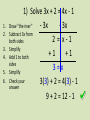
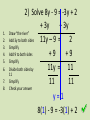
Warm Up • Write down objective and homework in agenda • Lay out homework (Multi-Step Equations wkst) • Homework (Kuta Identity & No Solution wkst) Unit 1 Common Core Standards • • • • • • • • • • • 8.EE.7 Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = a, or a = b results (where a and b are different numbers). b. Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms. 8.G.6 Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. 8.G.7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in realworld and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 8.G.8 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. A-CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear and quadratic functions, and simple rational and exponential functions. Note: At this level, focus on linear and exponential functions. A-CED.4 Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations. For example, rearrange Ohm's law V = IR to highlight resistance R. Note: At this level, limit to formulas that are linear in the variable of interest, or to formulas involving squared or cubed variables. Unit 1 Common Core Standards • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • A-REI.1 Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method. A-REI.11 Explain why the x-coordinates of the points where the graphs of the equations y = f(x) and y = g(x) intersect are the solutions of the equation f(x) = g(x); find the solutions approximately, e.g., using technology to graph the functions, make tables of values, or find successive approximations. Include cases where f(x) and/or g(x) are linear, polynomial, rational, absolute value, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Note: At this level, focus on linear and exponential functions. A-REI.3 Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. A-SSE.1 Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context. a. Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients. b. Interpret complicated expressions by viewing one or more of their parts as a single entity. For example, interpret P(1+r)n as the product of P and a factor not depending on P. Note: At this level, limit to linear expressions, exponential expressions with integer exponents and quadratic expressions. G-GMD.1 Give an informal argument for the formulas for the circumference of a circle, area of a circle, volume of a cylinder, pyramid, and cone. Use dissection arguments, Cavalieri's principle, and informal limit arguments. Note: Informal limit arguments are not the intent at this level. G-GMD.3 Use volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres to solve problems.* Note: At this level, formulas for pyramids, cones and spheres will be given. G-GPE.7 Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using the distance formula. Unit 1 Common Core Standards • • • • • • • • • N-Q.1 Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays. N-Q.3 Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities. N-RN.1 Explain how the definition of the meaning of rational exponents follows from extending the properties of integer exponents to those values, allowing for a notation for radicals in terms of rational exponents. For example, we define 51/3 to be the cube root of 5 because we want (51/3)3 = 5(1/3)3 to hold, so (5 1/3)3 must equal 5. N-RN.2 Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational exponents using the properties of exponents. Note: At this level, focus on fractional exponents with a numerator of 1. MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP.4 Model with mathematics. MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. Warm Up • Two more than a certain number is 15 less than twice the number. Find the number. • Solve for each variable. • -3v-5+12=17v-22 • x+2=x-2 Warm Up • Two more than a certain number is 15 less than twice the number. Find the number. – X + 2 = 2x – 15, x = -13 • Solve for each variable. • -3v-5+12=17v-13, v = 1 • 4x+2=x-2, x = -4/3 Vocabulary • Identities An equation that is true for every value. "Infinite Solutions" • No Solution An equation that is never true, no matter what value you place in for the variable. "No Solutions" 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1) Solve 3x + 2 = 4x - 1 Draw “the river” - 3x - 3x Subtract 3x from 2 = x-1 both sides Simplify + 1 + 1 Add 1 to both sides 3 = x Simplify Check your 3(3) + 2 = 4(3) 1 answer 9 + 2 = 12 - 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 2) Solve 8y - 9 = -3y + 2 + 3y + 3y Draw “the river” 11y – 9 = 2 Add 3y to both sides Simplify +9 +9 Add 9 to both sides Simplify 11y = 11 Divide both sides by 11 Simplify 11 11 Check your answer y=1 8(1) - 9 = -3(1) + 2 Solve 6) 2x + 5 = 2x - 3 1. Draw “the river” 2. Subtract 2x from both sides 3. Simplify -2x -2x 5 = -3 This is never true! No solutions Solve 7) 3(x + 1) - 5 = 3x - 2 1. 2. 3. 4. Draw “the river” Distribute Combine like terms Subtract 3x from both sides 5. Simplify 3x + 3 – 5 = 3x - 2 3x - 2 = 3x – 2 -3x -3x -2 = -2 This is always true! Infinite solutions or identity Be Careful! • When the solution is ZERO: Zero can be an answer! Don’t get it confused with no solution! • Example: 2x + 3 = 3 • You try: a + 5 = -5a + 5 What is the value of x if 3 - 4x = 18 + x? 1. -3 2. 3. 1 3 Identity 4. No Solution Answer Now What is the value of x if 3(x + 4) = 2(x - 1)? 1. 2. 3. 4. -14 -13 13 14 Answer Now What is the value of x if -3 + 12x = 12x - 3? 1. 2. 3. 4. 0 4 No solutions Infinite solutions Answer Now You Try! • • • • • 4x + 2 = -2x – 8 5x + 4 = 5(x + 3) - 11 8x + 3 = 3x + 2 6(x-1) = 2x + 6 4(x – 7) = 4x + 3 - 8 You Try! - Answers • • • • • 4x + 2 = -2x – 8 5x + 4 = 5(x + 3) - 11 8x + 3 = 3x + 2 6(x-1) = 2x + 6 4(x – 7) = 4x + 3 - 8 • • • • • X = -5/3 Identity (all solutions) X = -1/5 X=3 No Solution Extra Help! • http://teachers.henrico.k12.va.us/math/hcpsa lgebra1/Documents/examviewweb/ev3-4.htm • http://www.phschool.com/webcodes10/index .cfm?fuseaction=home.gotoWebCode&wcpref ix=ata&wcsuffix=0303 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KFBykIQO 8rU&feature=plcp