* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Name___________________________________
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
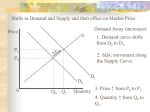
Exam Name___________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) During a recession, ________ jobs are destroyed than created and during an expansion ________ jobs are created than destroyed. A) more; fewer B) more; more C) fewer; fewer D) fewer; more 1) Answer: B 2) In the above figure, a recession begins at point ________ and an expansion begins at point ________. A) b; c B) b; a C) d; c D) a; b 2) Answer: D 3) The circular flow diagram indicates that A) households sell goods and services to the government. B) firms buy goods and services from households. C) households sell the services of factors of production to firms. D) firms buy the services of factors of production from the government. 3) Answer: C 4) The chain-weighted output index method of measuring real GDP is based on A) averaging the market value of the expenditures over a two year period and then comparing with a base period. B) using current prices rather than base year prices C) using the prices of two adjacent years to calculate the growth rate of real GDP. D) averaging the nominal and real measures of GDP to come up with a more accurate figure. Answer: C 1 4) 5) Suppose the population of Tiny Town is 100 people and the working age population is 70. If 10 of these people are unemployed, the unemployment rate in Tiny Town is A) 10/80 × 100. B) 10/70 × 100. C) 10 percent. D) There is not enough information provided to calculate the unemployment rate. 5) Answer: D 6) Which of the following means that the CPI overstates the actual inflation rate? A) outlet substitution bias B) new goods bias C) quality change bias D) All of the above cause the CPI to overstate inflation 6) Answer: D 7) If a worker is temporarily laid off because the economy is in a recession, A) structural unemployment increases. B) frictional unemployment increases. C) the size of the labor force rises. D) cyclical unemployment increases. 7) Answer: D 8) Which is the proper order for the business cycle? A) peak, expansion, trough, recession C) peak, recession, trough, expansion B) peak, recession, expansion, trough D) peak, trough, expansion, recession 8) Answer: C 9) Consumption expenditure increases if A) current and future disposable income rise. B) current and future disposable income fall. C) current disposable income falls. D) future disposable income falls. 9) Answer: A 10) A fall in the real interest rate A) shifts the investment demand curve leftward. B) creates a movement upward along the investment demand curve. C) shifts the investment demand curve rightward. D) creates a movement downward along the investment demand curve. 10) Answer: D 11) A firm has a marginal product that is less than the real wage rate. To maximize profit, the firm will ________. A) produce more output B) hire less labor C) hire more labor D) shift its labor demand curve rightward 11) Answer: B 12) Classical growth theory proposes that real GDP growth is ________ and that real GDP per person will ________ the subsistence level. A) permanent; always be above B) temporary; temporarily be above C) permanent; temporarily be above D) temporary; be above and below Answer: B 2 12) 13) Which of the following is NOT a flow variable? A) the number of DVDs produced per year B) the number of DVDs available at the library C) annual spending on DVD rentals D) the number of DVD players sold per month 13) Answer: B 14) The smallest and most stable source of unemployment is A) job leavers. B) job losers. C) new entrants into the labor force. D) reentrants into the labor force. 14) Answer: A 15) When the quantity of labor demanded exceeds the quantity of labor supplied the real wage rate A) falls to eliminate the labor-market shortage. B) falls to eliminate the labor-market surplus. C) rises to eliminate the labor-market shortage. D) rises to eliminate the labor-market surplus. 15) Answer: C 16) An economy is in a long-run equilibrium. The real interest rate and the target rate of return are 6 percent a year. Then technology advances and the real interest rate rises to 10 percent. Neoclassical growth theory predicts that economic growth will continue ________. A) indefinitely B) until the real interest rate and subsistence wage rate are equal C) only after the real interest rate returns to 6 percent a year D) until the real interest rate falls to 6 percent a year 16) Answer: D 17) In an economy, 43 million people are employed, 3 million are unemployed, and 4 million are not in the labor force. What is the employment-to-population ratio? A) 92 percent B) 93 percent C) 6.5 percent D) 86 percent 17) Answer: A 18) According to new growth theory ________. A) ever-advancing productivity keeps the rate of return below the target rate of return B) knowledge is subject to the law of diminishing returns C) knowledge does not experience diminishing returns D) growth rates and income levels per person around the globe will converge 18) Answer: C 19) GDP can be computed as the sum of A) the total expenditures of consumers and business over a period of time. B) all sales that have taken place in an economy over a period of time. C) the total expenditures of consumption, investment, government purchases of goods and services, and net exports over a period of time. D) the total expenditures of consumption, investment, and government purchases of goods and services over a period of time. Answer: C 3 19) 20) In the illustration above, Figure A shows the ________ and Figure B shows the ________. A) aggregate supply curve; production function B) production possibilities frontier; production function C) labor demand curve; production function D) production function; production possibilities frontier 20) Answer: D 21) Which pieces of information do you need to calculate the MPL? I) the change in real GDP. II) the change in the quantity of money. III) the change in the amount of labor input. A) III only B) I only C) I and III Answer: C 4 21) D) II and III Quantity of labor (hours of work) 0 1 2 3 4 5 Output (units per hour) 0 9 16 21 24 25 22) Based on the previous table, the marginal product of the second hour is A) 9 units. B) 8 units. C) 7 units. D) 16 units. 22) Answer: C 23) The real wage rate will fall if the A) labor demand curve shifts rightward and the labor supply curve does not shift. B) labor demand curve shifts rightward more than the labor supply curve shifts rightward. C) labor supply curve shifts rightward and the labor demand curve does not shift. D) labor supply curve shifts leftward and the labor demand curve does not shift. 23) Answer: C 24) The demand for labor curve slopes downwards because A) output increases as more workers are hired. B) as more workers are hired, the marginal product of labor increases. C) as more workers are hired, the marginal product of labor decreases. D) as more workers are hired, output decreases. 24) Answer: C 25) An advance in technology shifts the production function upward and shifts the labor A) supply curve leftward. B) demand curve rightward. C) demand curve leftward. D) supply curve rightward. 25) Answer: B 26) Investment demand is the relationship between investment and the ________ other things remaining the same. A) price level B) inflation rate C) real interest rate D) nominal interest rate 26) Answer: C 27) As the ________ rises, saving ________ other things remaining the same. A) real interest rate; increases B) inflation rate; increases C) nominal interest rate; increases D) real interest rate; decreases Answer: A 5 27) Real wage rate Quantity of labor Quantity of labor (2000 dollars demanded (billions supplied (billions per hour) of hours per year) of hours per year) 15 70 10 20 60 20 25 50 30 30 40 40 35 30 50 Real GDP (trillions of 2000 dollars per year) 3 9 14 18 21 Quantity of labor (billions of hours per year) 20 30 40 50 60 28) The tables above show the labor market and the production function schedule for the country of Pickett. Potential GDP is ________. A) $14 trillion B) $40 trillion C) $25 trillion D) $6 trillion 28) Answer: A 29) The tables above show the labor market and the production function schedule for the country of Pickett. An increase in population changes the labor supply by 20 billion hours at each real wage rate. Potential GDP ________. A) decreases to $3 trillion B) increases to $50 trillion C) does not change D) increases to $18 trillion 29) Answer: D 30) Growth accounting is designed to measure the amount of economic growth resulting from A) only increased capital and labor. B) technological progress, increased labor, and increased capital. C) only increased labor. D) only technological progress. Answer: B 6 30)