* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Excretory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
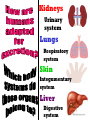
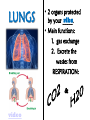
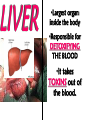
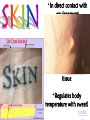
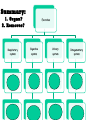
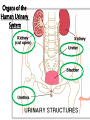
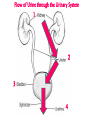
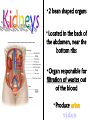
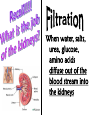
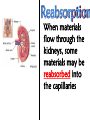
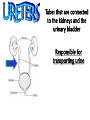
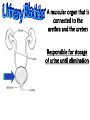
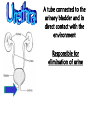
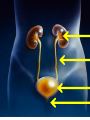
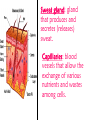
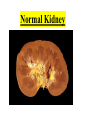
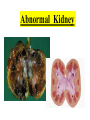
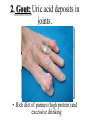
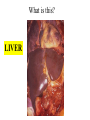
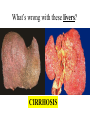
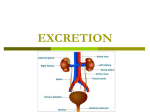
Excretion Why is the process of excretion necessary? 1. Name this process. Copy 2. Name the end products (hint there are three). 3. Why are these end products? video The process of releasing cellular wastes from an organism. • water • perspiration •urine •carbon dioxide Why is excretion necessary for our cells survival? a.) they must continually intake and output water….maintain water balance b.) export molecules or the cell gets bigger and bigger c.) dispose of waste products that are toxic (cell metabolism) video Kidneys Urinary system Lungs Respiratory system Skin Integumentary system Liver Digestive system What is the DIFFERNCE ….. Excretion or Egestion? EXCRETION material NOT used within the cell. removal of cellular waste (Nitrogenous waste) EGESTION material NOT used in digestive system. removal of undigested waste Solid wastes (feces) ANY COMPOUND OR MIXTURE THAT CONTAINS NITROGEN. 1. AMMONIA 2. UREA 3. URIC ACID LUNGS • 2 organs protected ribs by your _____. • Main functions: 1. gas exchange 2. Excrete the wastes from RESPIRATION: & video •Largest organ inside the body •Responsible for DETOXIFYING THE BLOOD •It takes TOXINS out of the blood. •In direct contact with environment •Acts as a barrier •Is the largest organ of the human body epithelial •Made of __________ tissue •Regulates body temperature with sweat! vide Do Now: Explain this cartoon using as many scientific terms/phrases as possible. Excretion How are humans adapted for excretion? PART 2 Do Now: summary Summary: 1. Organ? 2. Removes? Excretion Respiratory system Digestive Urinary system system Integumentary system Lungs Liver Kidneys Skin Carbon dioxide Produces Urea Produces Urine Perspiration Organs of the Human Urinary System Flow of Urine through the Urinary System 1 2 3 4 •2 bean shaped organs •Located in the back of the abdomen, near the bottom ribs •Organ responsible for filtration of wastes out of the blood •Produce urine video When water, salts, urea, glucose, amino acids diffuse out of the blood stream into the kidneys When materials flow through the kidneys, some materials may be reabsorbed into the capillaries To replace any substances that need to be in the bloodstream Examples Glucose, water, Amino acids a.) water b.) urea c.) salts Is a nitrogenous compound that is the end product of protein digestion From the liver Tubes that are connected to the kidneys and the urinary bladder Responsible for transporting urine A muscular organ that is connected to the urethra and the ureters Responsible for storage of urine until elimination A tube connected to the urinary bladder and in direct contact with the environment Responsible for elimination of urine •Act as a physical barrier from the outside environment •Regulate body temperature •Excretion of perspiration •Similar to the Cell membrane ____________________ of a unicellular organism Sweat gland: gland that produces and secretes (releases) sweat. Capillaries: blood vessels that allow the exchange of various nutrients and wastes among cells. Excretion How does the excretory system malfunction? handout. Normal Kidney Abnormal Kidney 1. Jaundice: Metabolic waste of bile are reabsorbed by blood, while bile is not secreted properly. Causing a yellowing of the skin and eyes. 2. Gout: Uric acid deposits in joints. • Rich diet of purines (high protein) and excessive drinking 2. Kidney Stones: Various substances crystallize out of urine into urinary tract or kidney and do not pass through urethra. 3. Kidney Failure: Inability of kidney to filtrate and absorb nutrients properly. Excess waste and fluids build up in the body- death occurs if not treated. • Dialysis acts as an artificial kidney. There are two types of treatment: hemodialysis and peritoneal (sac around the abdominal organs) dialysis. • About 90 percent of dialysis patients receive hemodialysis: the blood is circulated outside the body and cleaned inside a machine before returning to the patient. What is this? LIVER What’s wrong with these livers? CIRRHOSIS 4. CIRRHOSIS: is scarring of the liver and poor liver function as a result of chronic liver disease. Causes: excessive DRINKING of ALCOHOL LAB