* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grand Rounds - University of Louisville Ophthalmology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
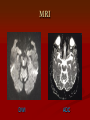
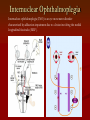
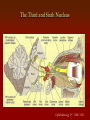
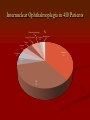
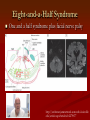
Grand Rounds Conference Jinghua Chen, MD, PhD University of Louisville Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences July 17, 2015 History CC: Double vision for three days. HPI: 56 year old African American male presented to PCC with double vision for 3 days. Three days ago he woke up in the morning with right eye deviated to the right side. He denied vision change, numbness, weakness, tingling or speech problems. Past Medical History POH: None PMH: Hypertension, Type 2 diabetes on insulin Allergy: NKDA FH: Non contributory Medication: Aspirin 81 mg, amlodipine 10 mg, and Humalog 20 units with meals (? compliance) SH: Smokes 1 pack per day and drinks 6 packs of beer up to 3 times a week. Exam OD OS BCVA: 20/20 20/20 Pupils: 43 43 No APD OU IOP: 13 11 EOM Limited adduction OD(-4) CVF: Full OU Anterior segment: Mild Cataract OU DFE: Normal OU Eye Movement Exam Video MRI DWI ADC Assessment Impression: 56 year old African American male presented to PCC with double vision for 3 days. Exam shows adduction deficit in OD. Differential Stroke Diagnosis of Causes: Demyelination Other Trauma Infection Tumor Hemorrhage Vasculitis Diagnosis: Right internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) Management The patient was admitted to Stroke Service Diagnosis: Right midbrain acute ischemic stroke in the posterior brainstem CTA and TEE were negative Plavix and IV fluids were started in the ER. Follow up Visit after Two Weeks Patient states doing better. Improved VA: adduction of OD (-2) and diplopia. 20/20 OU Follow up Video Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) is an eye movement disorder characterized by adduction impairment due to a lesion involving the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF). History 1859 Foville’s landmark study of pontine gaze palsy The CN VI nucleus- gaze center Yoked eye muscles A crossed pathway connecting the pons and midbrain to coordinate horizontal gaze 1873 medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) was identified as the connecting pathway 1921 Lhermitte named INO The Third and Sixth Nucleus Ophthalmology 2nd . 2004: 1324 Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia in 410 Patients •Infarction 38% •Multiple sclerosis 34% •Unusual causes 28% •Medications: Adalimumab-anti-TNFα Arch Neurol. 2005;62(5):714-717. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.5.714 Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia in 410 Patients % Infection 4% Brainstem hemorrhage 3% Vasculitis Miscellaneous Surgery/Procedure 2% 2% 3% Tumor 4% Infarction 38% Herniation 5% Trauma 5% MS 34% Unilateral INO Decreased saccadic velocity in adducting eye Abducting nystagmus of the fellow eye Convergence may be spared or disrupted Skew deviation INO is named for the side of limited adduction Bilateral INO One-and-a-Half Syndrome A horizontal gaze palsy and ipsilateral INO Eight-and-a-Half Syndrome One and a half syndrome plus facial nerve palsy http://archneur.jamanetwork.com.echo.louisville. edu/article.aspx?articleid=2279877 Prognosis of Ischemic Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia. 78.8% demonstrated resolution of diplopia in primary position with an average time to resolution of 2.25 months. The presence of associated neurologic symptoms (vertigo, ataxia, dysarthria, facial palsy, pyramidal tract signs) correlated with a worse prognosis for resolution of diplopia. Ophthalmology. 2002 Sep;109(9):1676-8. References BSCS 2014-2015 Book 5, Neuro-Ophthalmology: 209-211 James R. Keane. Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia: Unusual Causes in 114 of 410 Patients . Arch Neurol. 2005;62(5):714-717. Shanzer S Neuro-ophthalmology in 19th century Paris: pioneering work on conjugate gaze. In: Rose FC, ed. Neuroscience Across the Centuries. London, England: Smith-Gordon & Co Ltd; 1989:151-156 Freeman W Paralysis of associated lateral movements of the eyes: a symptom of intrapontile lesion. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 1922;7454- 487 Michael Strupp, Katharina Hüfner, etc. Central Oculomotor Disturbances and Nystagmus. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011 Mar; 108(12): 197–204. Bocos-Portillo J, Ojeda JR, etc. Eight-and-a-Half Syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2015 May 11. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0255. Drury J, Hickman SJ. Internuclear ophthalmoplegia associated with anti-TNFα medication. Strabismus. 2015 Mar;23(1):30-2. Eggenberger E, Golnik K, etc. Prognosis of ischemic internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Ophthalmology. 2002 Sep;109(9):1676-8.