* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deployment of Broad Band WMAN using Wi
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
National Broadband Plan (United States) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
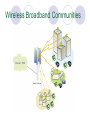
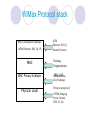
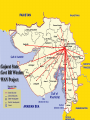
Deployment of Broad Band WMAN using Wi-max Standards Dr. (Mrs.)Nupur Prakash Professor, School of Information Technology GGS Indraprastha University, Delhi, INDIA Wireless Networks Facilitate Freedom from wires All pervasive computing Access to network resources anywhere anytime Higher productivity and connectivity Mobile Network Architecture & Standards Wireless Networks WPAN WLAN WMAN Standardization IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.16 WMAN WLAN WPAN Features of Wireless Networks WPAN WLAN WMAN Protocol 802.15 802.11 802.16 Standards Frequency Range Bluetooth, Wi-fi IrDA, UWD 2.4 to 2.483 5.15 to Ghz 5.35Ghz Speed .1- 4 Mbps Cell radius 1-10 ms Modulation FHSS Wi-Max 10 Ghz to 66 Ghz 1-54 Mbps 2-70 Mbps 1-500 ms OFDM, DSSS 1km-50km QPSK WiMax Technology WiMax (Worldwide Interoperability for microwave access) A technology based on an evolving standard for point-to-multipoint wireless networking Medium range wireless data communication standard (IEEE 802.16) Solution for Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN) BWA (Broadband Wireless Access) Solution What is WiMax? Operates on frequencies between 10-66GHz 1 to 10 mile range (10 miles assuming rural areas with little blockages). 70MB/second transfer rate Image copyright Intel (2004) Broadband Fixed wireless access architecture Supports P-MP configuration Hub uses broad coverage antenna mounted on towers or tall building and transmits to a group of subscribers Subscriber uses highly directional antenna pointed towards the hub Broadband wireless access system architecture using WiMAX Standards WiMax Forum WiMax was Founded in Jan 03’ No Profit organization comprised of wireless access system manufacturers component suppliers software developers and carriers. Promotes conformance, compliance and interoperability WiMax Forum certified product WiMAX Forum Initial Founding Members (2003) WiMAX Members * Fujitsu Hughes Network Systems Intel Alcatel Reliance Infocom China Motion Telecom Alvarion Proxim Siemens * OFDM Forum France Telecom Tata Teleservices PCCW Atheros British Telecom Qwest Aperto Networks ZTE Partial List WiMAX Standard for WMAN The IEEE 802.16 standard defines a powerful OFDM and NLOS technology for wireless metropolitan area network (WMAN) provides broadband wireless connectivity to Fixed, Portable and Nomadic users. can be used to backhaul LANs to the Internet provides inter-campus connectivity and a wireless alternative to cable, DSL, T1’s or even fiber or cable WiMax Features provides up to 50-kilometers of service area range allows users to get broadband connectivity without needing direct LOS with the base station single base station simultaneously supports hundreds of businesses with T1/E1-type connectivity thousands of homes with DSL-type connectivity Benefits of Broadband Wireless Access Very cost effective to deploy to rural communities and businesses, where terrain or situation do not allow traditional cabling or satellite connectivity Resolve traditional “Last Mile” customers reach issues and enhance broadband services to rural, low density communities. broadband in-fill for DSL black-spots adding capacity to mobile & line networks Broadband and Internet access in underserved, developing communities. IEEE 802.16 Versions 802.16a uses the licensed and license-exempt frequencies from 2 to 11Ghz Supports Mesh-Network 802.16b Increases spectrum to 5 and 6GHz Provide QoS (for real-time voice and video service) 802.16c Represents a 10 to 66GHz system profile 802.16d Improvement and fixes for 802.16a 802.16e Addresses on Mobile Enable high-speed signal handoffs necessary for communications with users moving at vehicular speeds The family of 802.16 standard Deployment of Wi-Max Wi-Max deployment is planned in three phases. Phase one: Hubs with outdoor antennas that target known subscribers in a fixed location leading to quick inexpensive solution without laying cable. Phase two: will roll out indoor antennas making installation simpler at user sites leading to simple, low cost installation of fixed wireless access. Phase three: will launch IEEE 802.16e Wi-Max certified hardware available in portable solutions supporting roaming of users within a service area. WiMax compatible PDAs and laptops are expected to be launched by 2007 Image copyright Intel (2004) Image copyright Intel (2004) Image copyright Intel (2004) Infrastructure required for WMAN using Wi-Max Base Stations Subscriber’s Module Send/Receive Antenna Receiver/Transmitter Router connected to Server via cable or 802.11 hot-spot The backhaul unit Wireless Broadband Communities WiMax Protocol stack MAC Convergence Sublayer (ATM, Ethernet. 802.1Q, IP) ATM Ethernet, 802.1Q Internet Protocol MAC Packing, Fragmentation MAC Privacy Sublayer ARQ, QoS Authentication, Key Exchange Physical Layer Privacy(encryption) OFDM, Ranging Power Control, DFS, Tx, Rx Physical Layer Point-to-multipoint architecture, BS transmits a TDM signal, with individual subscriber stations allocated time slots serially. burst single-carrier modulation (OFDM) with adaptive burst profiling transmission parameters, including the modulation and coding schemes, adjusted individually to each subscriber station (SS) on a frame-by-frame basis. Channel bandwidths of 20 or 25 MHz (typical U.S. allocation) or 28 MHz (typical European allocation) are specified Frame Structure and PDU Each MAC packet consists of the three components, A MAC header, which contains frame control information. A variable length frame body, which contains information specific to the frame type. A frame check sequence (FCS), which contains an IEEE 32-bit cyclic redundancy code (CRC). Security Mechanism The IEEE 802.16 protocol supports security mechanism for terminal authentication and privacy. Each connection is mapped to a Security Association (SA) that specifies the encryption algorithm to be used the data authentication algorithm to be used and the algorithm for exchanging the data encryption keys. Security Implementation Authentication is based on the use of PKI technology-based X.509 digital certificates. Each Subscriber Station (SS) contains both a manufacturer-issued factory-installed X.509 digital certificate and the certificate of the manufacturer. Privacy Sublayer uses privacy protocol that is based on the privacy key exchange management (PKM) protocol PKM protocol uses X.509 digital certificates with RSA public key encryption for SS authentication and authorization key exchange. Wireless Roaming The 802.16e task group is working on developing a specification to enable 802.16 mobile clients PDAs using embedded chips or laptops using 802.16e enabled cards These clients will be able to handoff between 802.16 base stations, enabling users to roam between service areas. Hand-off Procedure Roaming and hand offs between heterogeneous 802 networks is being studied ‘Hand off’ procedures would allow mobile devices to switch the connection from one base station to another from one 802 network type to another (such as from 802.11 to 802.16) from wired 802.x to 802.16, connections. Seam less Roaming As the mobile client (a notebook or a PDA user) moves within WMAN it remains connected via Ethernet or 802.11 when docked and stays connected with 802.16 when roaming the city or suburbs The goal is to standardize handoffs between heterogeneous networks and support seam less roaming. The mobile devices thus become interoperable as they move from one network type to another. Broadband Wireless Access 802.16e Expected players Backed by 140 companies in the WiMax Forum (www.wimaxforum.org) Intel is producing chips and currently managing 50 test sites around the country Covad (currently a big DSL provider) is considering using WiMax for last mile connections. Adoption of Broadband Wireless at Ahmedabad Rural District, INDIA District Inds. Center Dist. Court Krushi Bhavan Multistoried Bldg. Superintendent Of Police Office Civil Hospital Jal Bhavan Sales Tax Karai CP Office Circuit House GMDC Ahd.Diet Collector Blk.12 High Court RTO Jail Gujarat State Govt BB Wireless WAN Project WiMAX’s Path to future Broadband Mobility Internet Telephone Network IP Based Access Network Satellite Network Wi-Fi Base Station 802.16-2004 Base Station Pedestrian Speeds, 11Mbps, Lightweight, Limited Coverage Vehicular Speeds, 20 Mbps, Power Source, Heavy, Limited Coverage, Specialized Applications T I ME 802.16d/e Base Station Vehicular Speeds, 20 Mbps, Lightweight, Full Coverage Thank You