* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Role of Imaging in Sinusitis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
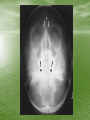
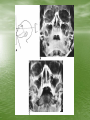
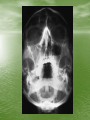
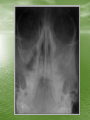
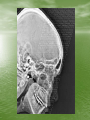
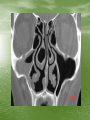
The Role of Imaging in Sinusitis Dr Mohamed El Safwany, MD. Intended learning outcome • The student should learn at the end of this lecture role of imaging in sinusitis. Pediatric Population • The nasal sinuses are not developed at birth • The maxillary and ethmoid sinuses begin to develop first and the frontal sinuses are the last to appear between 5-7 yrs of age • They become progressively aerated and may not be completely developed until up to 10 yrs of age • A normal radiograph in a young child can be • • confused with sinusitis or other sinus disease due to opacification This sometimes occurs when radiographs are ordered for other reasons such as trauma Therefore, routine sinus radiographs are not very useful in young children to make the diagnosis of sinusitis Older Children and Adults • In general, sinusitis is a clinical diagnosis and imaging should be reserved for cases that are unresponsive to treatment, when complications are suspected, or when the diagnosis is questionable • The typical imaging used for detecting sinus disease are plain films and axial and coronal CT scans Plain Films • The typical sinus series consists of 4 views • The Water’s view can be useful in detecting • • • maxillary sinusitis Caldwell’s view is used to evaluate the frontal sinus The submentovertex view looks at the sphenoid sinus and also the anterior and posterior walls of the frontal sinus The lateral view shows the frontal, maxillary, and sphenoid sinuses • Plain films are not very specific for sinusitis because opacity can be difficult to distinguish from other pathology such as tumors • Signs on a plain film that suggest sinusitis include opacification, air-fluid level, or 6mm or more of mucosal thickening CT Scan • CT scan is considered the gold standard for sinus • • imaging and the coronal view is typically the image of choice. Axial views are needed to complement the coronal views when severe disease is suspected in the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses. Signs suggestive of sinusitis on CT include opacification, air-fluid level, sinus wall displacement, and/or mucosal thickening of 4mm or more Since CT scans can show much more anatomical detail of the sinuses, they are especially useful when clinicians are concerned about complications or extension of disease from sinusitis • CT scans are often used to evaluate a patient • • before surgical intervention for chronic sinus disease Surgeons use it mainly to document the presence of disease and to look for any anatomical abnormalities that could increase the risk of complications during surgery For surgical evaluation, the CT scan should be obtained after treatment with broad spectrum antibiotics and at least 4 weeks of topical nasal steroids otherwise it is difficult to assess the meaning of a positive scan Text Book • David Sutton’s Radiology • Clark’s Radiographic positioning and techniques Assignment • Two students will be selected for assignment. Question • Define role of CT in sinusitis? • Thank You