* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reading Strategies
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
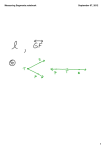
Name ________________________________________ Date __________________ Class__________________ LESSON 1-2 Reading Strategies Understanding Vocabulary Consider the following terms: congruent segments—segments of the same length These segments are not congruent. midpoint—point at the exact center of a segment bisect—dividing into two congruent parts segment bisector—any ray, segment, or line that intersects a segment at its midpoint Use the figure for Exercises 1–3. 1. Name the congruent segments in this figure. ________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Name the midpoint of BC . _____________________ 3. Name the segment bisector of BC . __________________ Use the figure for Exercises 4–6. 4. Name the congruent segments in this figure. ________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the midpoint of ZY . ____________________ 6. Name the segment bisector of ZY . __________________ Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. 1-18 Holt McDougal Geometry Reading Strategies Reteach 1. 4 cm 2. 1.5 cm 3. 3 cm 4. 2 5. 6 6. 41 7. 21 8. 135 9. 22 1. AB,CD; BC, AD; AC, BD; DE, BE,CE, and AE 2. Point E 3. AD 4. XY ≅ XZ; ZP ≅ PY 5. Point P 6. XP 10. 1-3 MEASURING AND CONSTRUCTING 11. 12. 13. NP or PN . 14. 4 ANGLES Practice A 15. 12, 12, 24 Challenge 1. Possible drawing: 1. vertex JJJG JJJG 2. PQ and PR 3. ∠QPR and ∠RPQ 4. point S 5. protractor 6. 90°; right 7. 60°; acute 8. 180°; straight 9. 10. 125° 2. Check students’ work. Practice B 2 of the distance from 3 each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. 3. The centroid is 4. EN = 2 cm, EX = 3 cm, 1. 2 of 3 cm is 2 3 2 EX; FN = 2 cm, 3 2 FY = 3 cm, therefore FN = FY; GN = 2 3 2 cm, GW = 3 cm, therefore GN = GW 3 cm, therefore EN = 2. ∠A, ∠C, ∠ABC, ∠ABD, ∠ADB, ∠ADC, ∠CBD, and ∠CDB Problem Solving 3 1. 24 ft 4 4. 120°; obtuse 5. 30°; acute 6. 14° 7. 123° 8. 44° 9. 3°15′05″ 2. 23 ft 10. 79.958° Practice C 1. ∠BAE 3. 18 ft 2. ∠BAC, ∠DAE, ∠CAD 4. 9.7 cm and 38.8 cm 5. B 3. 90°; right 3. ∠BAD and ∠CAE 6. F 4. a straight angle 7. D 5. First, Keisha can draw a straight angle (180°). She can then bisect the straight angle to make two right angles (90°). Keisha can then bisect one of the right angles to make a 45° angle. Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. A3 Holt McDougal Geometry