* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.1 Using Technology
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Jodrell Bank Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical seeing wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
History of gamma-ray burst research wikipedia , lookup
European Southern Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
History of the telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
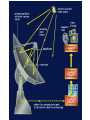
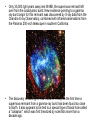
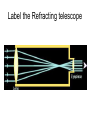
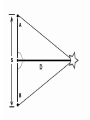
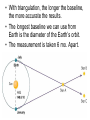
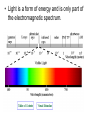
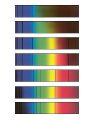
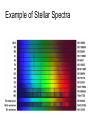
3.1 Using Technology Crab Nebula (Image from HST) 3.2 Using Technology to See Beyond the Visible Gamma imaging of Earth Optical Telescopes • 1608 Dutch optician Hans Lippershey makes one of first telescopes. • Galileo is first person credited for using it to look at stars. • Optical telescopes simply gather and focus light from distant stars so we can see it. • BUT Optical telescopes are only useful for viewing objects that emit light. • Stars and galaxies emit more than just visible light. • They also emit radio waves, infrared (heat) waves, and x-rays.. • These are all forms of electromagnetic energy. • All forms of EMR travel at the speed of light (300 000 Km/s) but have different wavelengths and frequencies. • Wavelength: The measurement from one point on a wave to the same point on the next wave. • Usually crest to crest, or trough to trough. • We measure wavelength in micrometers (µm) • 1 µm = one millionth of a meter • Frequency: the number of waves per second (usually measured in Hz). • Since all electromagnetic energy travels at the same speed, as wavelength increases, the frequency decreases. • This is an inverse relationship. • Light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio Telescopes • Radio telescopes gather radio waves from distant stars, nebula, galaxies, and planets. – Radio waves are not affected by weather – They are not distorted by time of day, clouds, pollution, or the atmosphere. – They can detect information not detected by optical telescopes – They can map and detect neutral hydrogen to determine the shapes of galaxies. Very Large Array (VLA), National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a group of 27 bowl-shaped radio antennas. Each antenna is 25 metres (82 feet) across. When used together, they make one very powerful radio telescope. Radio Interferometry • Multiple radio telescopes combined for greater resolving power. • The greater the distance between telescopes the greater the accuracy. • The more telescopes used, the greater the accuracy. • A group of telescopes used together is called an array. VLA (Very Large Array) in New Mexico • Gamma-rays and x-rays are also being used to study our universe. NASA’s Chandra X-Ray Observatory • In this composite image of spiral galaxy M106 Radio data from the Very Large Array appears as blue, X-ray data from Chandra is coded red, and infrared data from the Spitzer Space Telescope appears green. The anomalous arms appear as purple and blue emission. • Only 35,000 light years away lies W49B, the supernova remnant left over from the cataclysmic burst. New evidence pointing to a gamma ray burst origin for this remnant was discovered by X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, combined with infrared observations from the Palomar 200-inch telescope in southern California. • The discovery is exciting for two reasons. It may be the first time a supernova remnant from a gamma-ray burst has been found so close to Earth. It also appears to be tied to a special type of black hole called a "collapsar," which was first theorized by scientists more than a decade ago. Space Probes • Unmanned satellites or remote controlled landers. • Probes have been sent to all planets but Pluto. The only other object in the solar system to be physically explored by man, except for Earth, is the moon. This was first accomplished by the Apollo 11 Mission in 1969. • Space Probes Sounds of Jupiter There are two types of Optical Telescopes: 1. Refracting telescopes: – Use 2 lenses – Limited to 1m diameter Yerkes telescope in Wisconsin is Largest refracting telescope in the word Label the Refracting telescope 2. Reflecting Telescopes: – Use concave mirrors – One of the largest reflecting mirrors in the world is in Russia and has a diameter of 6m. – Segmented mirrors are used to make even more powerful reflecting telescopes. Keck observatory on Mauna Kea, Hawaii The 10 m segmented mirror of the Keck Telescope Interferometry • Using a combination of telescopes together to obtain more detailed images of distant objects The European Southern Observatory Hubble Space Telescope • A reflecting telescope orbiting 600 Km above the Earth. • 13m in length and 4.4m in diameter • 1 trip around the Earth takes 95min. • HST has discovered many galaxies not visible from Earth. • New discoveries are constantly being made. • See Hubble ppt in MS Data • Hubble's Top 10 Photos • Hubble--The-amazing-space-photographsuniverse 3.3 Using Technology to Interpret Space Measuring Distance • Triangulation – By measuring the angles between a baseline and the target object (such as a tree or tower) you can determine the distance to that object. – You must know the length of one side of the triangle (baseline) and the measures of the two angles at each end of the baseline. – See P. 447 • Parallax – The apparent shift in position of an object when the object is viewed from two different places. – Astronomers use a star’s apparent shift in position relative to the background stars to determine what angles to use when triangulating the stars distance from Earth. • With triangulation, the longer the baseline, the more accurate the results. • The longest baseline we can use from Earth is the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. • The measurement is taken 6 mo. Apart. Determining a Star’s Composition • White light is a combination of all colours and can be separated into its component colours (visible spectrum). • Light is a form of energy and is only part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Shorter wavelength Longer wavelength • When light from a star is refracted distinct dark bands in a distinct sequences and thicknesses appear in their spectra. • Each element in a star absorbs light at different wavelengths creating its own “signature” spectra. • By analyzing the spectra of refracted light from a star with an instrument called a spectroscope astronomers can determine the composition of the star. Example of Stellar Spectra Determining a Star’s Direction • The Doppler Effect – Sound waves become compressed in front of a moving object and stretched behind it. – This makes the pitch higher as the object moves towards you and lower as it moves away from you. Doppler Effect at the Race Track Video • Like sound, light also travels in waves and is affected by the Doppler effect. • Changes in the wavelength of light can be used to measure how fast and in what direction a light emitting object is moving. • The dark spectrum lines of an approaching star will be shifted to the blue side of the spectrum as the wavelengths of light are being compressed. • For a star moving away from the Earth the dark lines will be shifted to the red side of the spectrum as the light waves are being stretched. • The Doppler effect is used in radar guns by the police to measure the speed of vehicles, as well as by weather networks to predict storms