* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Europe
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
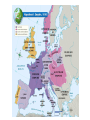
Europe Early Countries Histories Western European Countries • England – Anglo Saxons • Came around 450 AD (From Germany) • Formed numerous kingdoms in England..ruled by Sheriffs • Invaded some by Vikings from Denmark (combined Dane and Anglo Cultures)…around 800 AD • Edward the Confessor (King died)…distant relative was William of Normandy (in France). William claimed the English throne (William the Conqueror). He ruled form 1066-1087 Early England • England – William’s Legacy • Henry II (William’s Grandson) – Strengthened the Royal Authority of Kings by creating a special Army that protected the King • Thomas Beckett (Archbishop of Canterbury) – Once had been good friends with Henry II – Disagreed with Henry’s attempt to prosecute certain members of the church • Beckett was murdered by Henry’s men • Eleanor of Aquitaine: From France, Henry II’s wife – Helped strengthen ties between France and England • Henry’s rule increased the power of the King Early England • England cont.. – Magna Carta: Written document • Protected the liberties of nobles and gave limited rights to the ordinary people of England • Created because King John was threatened by a rebellion from the nobles – Common Laws • Laws based on customs and judges decisions, rather then written codes. • Became common throughout England Early England • England conflicts – Hundred Year’s War (1337-1453) • Edward III (England) claimed land in France after death of French King • England won many battles but eventually lost the war • New Things: – Long Bow’s, gun powder, cannons (Eliminated the Knights) – England’s King lost power to Parliament – War of Roses (1455-1485) • Civil War in England • House of Lancaster defeated the House of York English Rulers • England cont… – House of Tudor (Began with Henry Tudor of Lancaster) • • • • New rulers of England after the War of Roses Henry VII: Made England prosperous Henry VIII: Established the Anglican Church (against Pope) Mary I: First Queen, was a devoted Catholic (unlike her Dad)….got the nickname Bloody Mary because of how ruthless she was trying to destroy the Anglican Church. • Elizabeth I: Mary’s Half Sister…took charge once Mary died in 1558 (She was Protestant) English Rulers • England cont.. – Reign of Elizabeth I • Never married because she did not want to weaken England • Mary Queen of Scots: Heir and closest relative of Elizabeth – Mary (Catholic) and Phillip II of Spain tried to plot against Elizabeth – She found out and cut off Mary’s Head • Spanish Armada – Spain attempted to invade England with an Armada…a bunch of ships – England’s Navy defeated the Armada and Spain never really threatened England again England and Religion • England – Religious Problems • Puritans: Wanted to change the Anglican Church even more…get rid of all things Catholic. • Elizabeth fined everyone who was not Anglican • English Parliament: Gentry (landowners) and Burgesses (business people). – James I • King James I took over after Elizabeth. (was from Scotland) • King James version of the Bible • James didn’t do much to help improve country England and Civil War • England – Civil War • Charles: James’ son…believed Kings were better than everyone else. Married a French Catholic Princess • Charles did not give the Parliament any rights • Charles dealt with revolts in Scotland and Ireland..didn’t have any money to fund a good army to stop those revolts. • Argument between Charles and Parliament over who should be in charge of the Army led to a Civil War • Charles was defeated by Oliver Cromwell (Puritan), England became a commonwealth and Charles was beheaded. Becoming Great Britain • Steps towards becoming Great Britain • Cromwell’s rule was ineffective, England turned back to having a King. (Navigation Acts) • Charles II came back to England, lifted some Puritan restrictions and went to war with the Dutch..winning New Amsterdam (New York) • Tories and Whigs: 2 political parties that were developing in English Parliament. (did not want a Catholic ruler) • Charles II died, his Catholic brother James II won the throne Becoming Great Britain • Steps towards becoming Great Britain • Parliament did not like James II b/c he was Catholic. • They convinced his oldest daughter, Mary (who had married a Dutch Protestant Prince named William of Orange) to rebel against her father. • Glorious Revolution: James II left and William and Mary took the throne. • Thomas Hobbes vs. John Locke – Hobbes: People live in anarchy and are selfish – Locke: People gave up some rights to be ruled…still had right to live, enjoy liberty, and have property • Habeas Corpus: Protected individuals against unfair treatment after they had been arrested Becoming Great Britain • Steps towards becoming Great Britain • English Bill of Rights: Parliament chose who would rule the country and protected the rights of citizens • Act of Settlement: Kept Catholics from English throne • Significance: England would still have a king BUT the real power is with Parliament • Act of Union • England and Scotland united to become Great Britain • Strengthened both areas; helped compete w/ France • Ireland would be added in 1801 (not liked by Ireland) Great Britain • Great Britain • Queen Anne (1702-1714) had 17 children, she lived longer than all of them • Both King George I and II were born in Germany and really had no idea what was going on. • Prime Minister: Leader of Great Britain’s Parliament • Limited Constitutional Monarchy: King/Queen was the head of the state but powers were limited by constitution. France • Early France – William the Conqueror: Frenchman who connected France and England – 100 Years War • France became divided between House of Burgundy and House of Orleans • Joan of Arc: Helped Charles VII of Orleans win the crown and kick out the English – After the War • Louis XI: United France , nobles kept power, people remained poor Early France • Early France Monarchy • Henry IV: Huguenot (minority protestant), eased religious tension. • Louis XIII: Son, ruled but was very weak. • Cardinal Richelieu: Helped Louis XIII strengthen the crown and country. Was harsh on regional kings and Huguenots. • 30 Years War: Protestant Rebellions to Holy Roman Emperor. Richelieu kept France out of the fighting until the end. When it was over, France had won land and other areas lost power. France • Early France Monarch – Louis XIV: • Starting in 1643, he ruled France for 72 years. • Believed that the Kings were “divine” and made a huge compound at Versailles. • Jean-Baptiste Colbert: Adviser, wanted France to expand all over the world. • Increase military to 400,000 soldiers. Wanted to expand to the Rhine River. Other countries joined together to stop this from happening. • Last war was over Louis grandson being named King of Spain. France lost war, Phillip could be King of Spain but countries could never unite. French Revolution • Start of the French Revolution • 97% of people belong to the Third Estate fell into the middle or lower class in France. • Families got larger, people needed more money to survive (wasn’t happening) • Louis XV: ruled for 20 year..peaceful but country was still in more debt due to Louis XIV • Louis XVI: married Marie Antoinette (Austrian), debts continued to grow (thanks to helping America). • The people of the Third Estate got sick of not being represented and formed their own form of government which is when the revolution started. French Revolution • French Revolution • • • • • National Assembly: Name of Third Estate Government National Guard: Name of Third Estate Army Mass riots and looting all over Paris The Old Regime (nobles, etc) left France Constitution of 1791 – Limited the power of King, 3 Branches (executive, leg, judicial) – Louis XVI did not like it, tried to leave France but was caught – Things did not go smooth, not everyone bought in, people were poor, no executive power – Conservatives, Radicals, Moderates • Other monarchies wanted to help Louis XVI – Invaded by Austria and Prussia French Revolution • End of Monarchy • • • • • • Louis XVI had plotted against his own people (they knew it) Legislative Branch suspended the power of King Louis XVI was behead by the guillotine (Shocked Europe) France finally defeated Austria and Prussia Felt threatened by other countries: conscription Reign of Terror – “complete destroy both internal and external enemies” – A lot of people (even the ones who started the violence) ended up being executed. Napoleon • Napoleon Bonaparte • Young general who took control of France’s Army • Led France in Wars from 1796-1815 • He defeated most of the powerful countries in Europe and established a vast empire. He did struggle against the British and Russia • He led a coup against the French government and Napoleon took over as dictator. • He did some good things for the government of France – Organized all French Law – Established the Bank of France Napoleon • Napoleon cont.. • Napoleon named the Emperor of France • France continued to fight with Great Britain and Napoleon continued to win battles on land • Eventually Napoleon controlled much of Europe (Spain to Russia)…introduced modern military techniques and got rid of feudalism • Spain was able to overthrow France’s rule • Napoleon became mad at Russia, ordered 600,000 soldiers to invade. • Czar Alexander allowed French troops to take Moscow..Alexander burnt the city and watched the French troops suffer without shelter during the winter Napoleon • Napoleon • He decided to retreat in October…huge mistake • 2/3 of the troops did not make it out of Russia alive • Other armies were excited to finally get a shot to beat the weakened French Army • Battle of Waterloo: Final defeat of Napoleon and the French Army. Post Napoleon • Post Napoleon France • Louis Philippe became King in 1830, did not have a lot of power. • He issued a decree that restricted the ability of citizens to speak freely. Led to riots and Philippe leaving the throne. • Louis-Napoleon: Nephew of Napoleon – Won an election in 1848, tried to build support but was only able to serve for 1 term due to constitution. – He organized a military coup on the National Assembly. – Renamed Napoleon III, served for ten years and did both good (modernization) and bad (exiled critics) France Wars • Post Napoleon France – Crimean War • Russia and France disputed lands in the Middle East • France, GB and Ottoman Empire formed an alliance against Russia. France won glory but really nothing else • Florence Nightingale and battlefield nurse – Franco Prussian War • France suffered many defeats to the Prussians. • France had to give lands to Prussia. – Republic • Became an official Republic in 1875. Germany and Italy • German and Italian Early History • Otto I: Similar to Charlemagne. H was able to unite the German tribes and parts of Northern Italy. (936 AD) • Named the area the Holy Roman Empire which it would still be called for around 900 years. • Germany and Italy have a common bond. • Henry III: (1046-1056) held the strongest rule of any of the kings. He put the church second. • This would be a constant debate: Who had more power, the king or pope? Germany and Italy • German and Italian Early History – Struggles between Popes and Rulers • Henry IV (took over at 5) fought with Pope Gregory VII • Main issue was who could appoint bishops • Gregory urged the nobles to get rid of Henry and Henry begged for forgiveness • This limited the power that the kings had over the church – Fredrick Barbarossa (Red Beard) • Ruled from 1152-1190, wanted to control Northern Italian Cities. This failed. – Innocent III • 1198-1216….greatly strengthened the church • He felt that all Kings were weak and below him Germany and Italy • Early Germany and Italy • Emperors were never able to fully unite Germany and Italy and they really very little power. • Each area remained divided into small and independent cities and feudal states. (Princes and Knights had pwr). • Hapsburgs: Named Emperor (not a lot of power) – Used marriages and smart military moves to conquer much of Central Europe (Netherlands, Luxemburg, Austria, Spain, Italy) – Became one of the most powerful families of Europe but could not ever unite all of the old Holy Roman Empire German Isolation • German Isolation • By the 1740’s, the Holy Roman Empire was a mess of different peoples (languages, religions, etc) • Made it difficult for anyone to rule effectively • Hollenzollerns were a rival family in Northern Germany that began to unite some of the areas around Baltic Sea • Frederick William I: 3 generation made the Prussian Army stronger, eventually into the strongest Army in Europe during the 1700s. • Frederick William II: Fredrick the Great, despite seeming uninterested in his youth, became a great leader of Prussia (Northern Germany) German Isolation • German Isolation • Prussia was able to invade parts of the Austria controlled by the Hapsburgs • Seven Years War – – – – War that involved almost all the European countries Prussia/GB vs France/Austria/Russia Part of the French and Indian War No clear winner, Russia and Prussia actually became friends • Improvements – Fredrick the Great spent the next twenty years fixing Prussian economic and social situation German Unification • German Unification • Prussia was invaded by Napoleon in the early 1800s • By 1815, they had fought back against him and created the German Confederation (Prussia, Saxony, Lower Rhine River Valley). • The Holy Roman Empire was abolished by Napoleon and not restored. • First step was to abolish tariffs between different states on Prussia and Germany • Still acted independent politically German Unification • German Unification • William I became the King of Prussia. He appointed Otto von Bismarck to be the head of the cabinet. • Both of them opposed democracy • Bismarck: Wanted to find away to weaken Austria’s influence on some of the German States • Prussia and Austria went to war with Denmark to win two smaller states (Holstein and Schleswig) that were made up mostly of German people. • Prussia then dominated Austria in 7 weeks, shocking the rest of the world. The Northern German states united with Prussia to for the North German Confederation German Unification • German Unification • Bismarck needed to get the Southern German states to join the Northern German Confederation • Bismarck sent a fake letter to the French, made the French mad and they declared war on Germany. • This is what caused the Southern German states to unite with the Northern German Confederation. • Created a new German Empire that included all German states except Austria. • Kaiser: Name given to the German Emperor Italian Unification • Italian Unification • Italy remained divided into multiple states by 1800 • By 1948, people began to lead revolts in throughout Italy • Revolts were unsuccessful because liberals and nationalist could not get along • King Victor Emmanuel II and Camillo Benso di Cavour took control of the government of Sardinia. • Both of them liked how Great Britain was set up. • Biggest threat was Austria, convinced the French to help them get rid of Austrians in Northern Italian States. Italian Unification • Italian Unification • • • • The war with Italy united Tuscany, Modena, and Parma The French backed out and unification was put on hold Two Sicilies: Made up the Southern Half of Italy Giusepee Garibaldi: Leader of a movement to unite the Southern half of Italy. • Garibaldi and King Emmanuel met in 1860…compromised to unify Italy. • By 1870, Italy had become unified but still had problems being a divided nation. Spain • Spain – Islam • Conquered by the Moors in 711 • General Tariq • Would rule parts of Spain until the 1400’s – Ferdinand and Isabella • Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castile united Spain in 1479. • Captured Granada (last Muslim strong hold) in 1492 • Kicked anyone out who was not Catholic.