* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cor Pulmonale
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
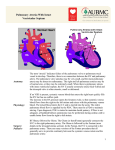
Cor Pulmonale Right heart failure caused by Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension induced by chronic hypoxia secondary to diseases of the lung, its vessels or the thoracic cage. Causes Lung disease Asthma (severe, chronic) Bronchiectasis Pulmonary fibrosis Multiple pulmonary emboli Sickle-cell disease Parasite infestation Kyphosis Scoliosis Thoracoplasty Myasthenia gravis Poliomyelitis Motor neurone disease Sleep apnoea Enlarged adenoids in children Cerebrovascular disease Pulmonary vascular disease Thoracic cage abnormality Neuromuscular disease Hypoventilation Typical presentation CCF +/- infective bronchitis (dyspnoea, cyanosis). More common in Blue-bloaters than pink puffers. Typical symptoms Exertional dyspnoea and fatigue Pulmonary hypertension Chest pain, Syncope, Loud P2, 4th heart sound, Pulmonary flow murmur, Diastolic murmur from pulmonary regurgitation Right heart hypertrophy Right ventricular heave, Dominant R wave in lead V1 on ECG Right heart failure Peripheral oedema, Anorexia, Nausea, Raised JVP from liver and GI engorgement, Ascites, Tender smooth hepatomegaly, Tricuspid regurgitation Functional tricuspid regurge - because right heart enlarges. Pansystolic murmur, v wave in the JVP, pulsatile liver, more rarely ascites and right-sided pleural effusion Tests ABGs Blood/Sputum cultures if infection suspected clinically CXR: Enlarged right atrium and ventricle and prominent pulmonary artery ECG: P pulmonale (peaked P wave), right axis deviation, right ventricular hypertrophy/'strain': tall R in V1, deep S in V6, if severe - inverted T wave in V1-V4 Causes of Pulmonary Hypertension Increased pulmonary vascular resistance - any cause of chronic hypoxia, primary pulmonary hypertension, collagen vascular disease, drugs, toxins: crotolaria, denatured rape-seed oil High pulmonary blood flow - left to right shunts (VSD, ASD, patent ductus arteriosis). Increased pulmonary flow leads to increased resistance causing increased right-sided pressure. Eventually right heart pressure > left heart pressure, shunt reverses causing cyanosis. Called Eisenmenger's syndrome, irreversible. Chronic pulmonary venous hypertension - Chronic LVF or mitral stenosis Management If irreversible, or resistant to treatment - steady decline to cor pulmonale and death Reduce work load of right heart - reduce pulmonary resistance and arterial pressure Treat any underlying condition Treat infective exacerbations vigorously Continuous oxygen therapy (at least 15h/day) reduces hypoxia, lowers pulmonary resistance, increases survival Treat fluid overload with frusemide and appropriate potassium supplements. Venesection may reduce severe polycythaemia Consider heart-lung transplantation