* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 6.3 • Arcs and Angles
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Poincaré conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
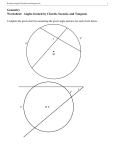
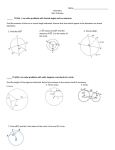
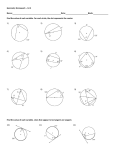
DG4GSP_897_06.qxd 12/20/06 1:32 PM Page 88 Lesson 6.3 • Arcs and Angles Investigation 1: Inscribed Angle Properties In this investigation you’ll discover a relationship between an inscribed angle and the arc it intercepts. Sketch Step 1 In a new sketch, construct circle AB. Step 2 !, where point C is a point on the circle. Construct BC Step 3 !!, where point D is another point on the circle. Construct CD Step 4 Measure !DCB. Step 5 Select, in order, point B, point D, and the circle, and choose Construct ⏐ Arc On Circle. Change its line width to thick. Step 6 m!DCB ! 50.38° arc angle A ! 100.77° D A B C Select the arc and choose Measure ⏐ Arc Angle. Investigate 1. Drag point D (but not past points C or B) and look for a relationship between the arc measure (called Arc Angle in Sketchpad) and the measure of the inscribed angle. Make a conjecture (Inscribed Angle Conjecture). 2. Drag point C. As long as you don’t drag it past points B and D, the measurements don’t change. Is your computer broken? Well, dragging point C doesn’t do anything to the arc. What does that mean for all the inscribed angles that intercept that arc? If you’re not sure, construct !. Write a and measure another inscribed angle that intercepts BD conjecture about inscribed angles that intercept the same arc (Inscribed Angles Intercepting Arcs Conjecture). 3. Construct segment DB and change its line width to dashed. Drag ! passes through the circle’s center. What is the point D until DB measure of !DCB? Now drag point C to see if m!DCB changes. Write a conjecture about angles inscribed in a semicircle (Angles Inscribed in a Semicircle Conjecture). Investigation 2: Cyclic Quadrilaterals Now you’ll apply your previous discoveries to the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle, which is called a cyclic quadrilateral. C D Sketch Step 1 In a new sketch, construct circle AB. Step 2 Use the Segment tool to construct quadrilateral BCDE, where points C, D, and E are also points on the circle. Step 3 A B E Measure the four angles of the quadrilateral. (continued) 88 CHAPTER 6 Discovering Geometry with The Geometer’s Sketchpad ©2008 Key Curriculum Press DG4GSP_897_06.qxd 12/20/06 1:32 PM Page 89 Lesson 6.3 • Arcs and Angles (continued) Investigate 1. Look for relationships between pairs of angles in the quadrilateral. Use the calculator to check any relationships you discover, then write a conjecture (Cyclic Quadrilateral Conjecture). 2. Explain why the Cyclic Quadrilateral Conjecture is true. (What kinds of angles did you measure? What is the sum of the arc measures of the two arcs intercepted by opposite angles in the quadrilateral?) Investigation 3: Arcs by Parallel Lines Now you’ll discover a relationship between arcs formed when parallel lines intersect a circle. Sketch Step 1 In a new sketch, construct circle AB. Step 2 !"#, where point C is a point on the circle. Construct BC (Drag points B and C to make sure the line is attached correctly.) C B A D Step 3 Construct point D on the circle. Step 4 !"#. Construct a line through point D parallel to BC Step 5 Construct point E where the new line intersects the circle. Step 6 Select, in order, point E, point B, and the circle. Choose Construct ⏐ Arc On Circle. Change the line width of this arc to thick. ! the same way. Make sure you select your points in Construct CD Step 7 E counterclockwise order. Investigate 1. Select each arc and measure its arc angle. Drag point C and observe the arcs and their measurements. Make a conjecture about the arcs intercepted by parallel lines (Parallel Lines Intercepted Arcs Conjecture). EXPLORE MORE Given a circle and a point outside the circle, find a method for constructing the two tangents from that point. Describe how you made your construction. (Hint: Start by constructing a segment from the point to the circle’s center. Then construct the midpoint of that segment. You’re on your own from here.) Discovering Geometry with The Geometer’s Sketchpad ©2008 Key Curriculum Press CHAPTER 6 89