* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 1 power
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
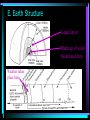
Unit 1 Measuring the Earth In this unit you will learn about the size, shape and features of the earth. You will also learn how to read maps, from the simple to the complex. A. Models – things that help explain events 1. ___________uses observations of sight to provide Physical us with explanations example: globe Laboratory models used to simulate 2. ____________natural events example: Stream table 3. _____________images of something in Mental your mind that you are trying to understand A. Models – things that help explain events 4. _____________formulas and equations that Mathematical explain certain properties of a material or system 5. ______________uses graphs to simplify Graphic certain relationships B. Spherical Earth – evidence to prove it. 1. The Mast of a ship was the first part to appear over the horizon and the last part to disappear. 2. Change in the altitude of the North Star (Polaris) and other celestial objects when you travel north or south. The altitude of Polaris equals the latitude! Polaris • Only star in the night sky that does not move, because Earth’s axis points directly at it • Also called the “north star” or the “pole star” • Very last star in the handle of the Little Dipper • Can only be seen in the Northern Hemisphere • Altitude = Latitude of Observer • Can be found using the Big Dipper B. Spherical Earth – evidence to prove it. 3. Shadow of Earth during a lunar eclipse is always the arc (part) of a circle. 4. Not a perfect sphere,( ) an Oblate Spheroid object at the equator will weigh slightly less than an object at one of the poles because the Earth has a slight bulge at the equator. 5. Space photos. Views from space Earth Shape PowerPoint C. Earth’s Dimensions Circumference at Equator 40,076 km Circumference at Poles 40,008 km Diameter at Equator 12,756 km Diameter at Poles 12,714 km Land 29 % of surface Water 71 % of surface FYI – Moving at 55 mph it would take you one month to circle the earth. E. Earth Structure 1. Lithosphere- Crust and top of mantle, solid and rocky Hydrosphere 2. _______________-thin layer of water resting on the lithosphere. -covers about 70% of the Earth’s surface. Atmosphere 3.________________-a relatively thin shell of gases, held to Earth by gravity. 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% mostly Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Helium and Water Vapor E. Earth Structure Liquid layer Made up of solid Nickel and Iron Weather takes place here F. Coordinate System - Latitude System of imaginary lines that help determine the location of a point on the Earth’s surface. 1.Latitude -distance in degrees__________________________________. north or south of the equator -latitude numbers are followed by an N if they’re north of the equator and an S if they’re south of the equator. -equator 0° -North Pole 90°N -South pole 90°S 43.3091°N or 43°18’45”N -Attica F. Coordinate System - Latitude _______________-lines that measure latitude. Parallels -they are parallel to the equator (horizontal). -degrees of latitude are about 111.1 kilometers from each other. Same for all lines of latitude. _____________-(North Star)- The angle of altitude of Polaris Polaris in a given location in the northern hemisphere is equal to the latitude of that location. Very important don’t forget! F. Coordinate System - Longitude 2. Longitude -distance in degrees east or west of Prime Meridian -longitude numbers are followed by an E if they’re east of the Prime Meridian and a W if they’re west of the prime meridian. -Prime Meridian- line that passes through Greenwich, England and connects the North and South Poles. - 0 degrees longitude. F. Coordinate System - Longitude -____________-imaginary Meridians semicircles that connect the poles and measure longitude -the distance between them is greatest at the equator and they come together at the poles -180 meridian-line on the opposite side of the Earth as the Prime Meridian. -in the middle of the Pacific Ocean -______________________-roughly follows the 180 International Date Line meridian but does go around some land areas. -where the date changes. F. Coordinate System – Longitude and Time chronometer-very accurate clock that keeps time at the Prime Meridian (Greenwich Mean Time- G.M.T.) and the solar time (time by the sun) at any other meridian. questions: 1. How many are there degrees in a circle? 360° 2. How many hours are there in a day? 24 hours 3. How many degrees would the Earth rotate in one hour? 360° 15°/hr. 24 hours = F. Coordinate System – Longitude and Time facts: 1.In the Western Hemisphere, local time is earlier than Greenwich time. 2.In the Eastern Hemisphere, local time is later than Greenwich time. questions: 1.If it is 12:00 noon where you live and the chronometer reads 5:00 PM Greenwich Time: a. How many hours are the times apart? 5 hours b. What is your degree longitude? 5 hrs. X 15°/hr. = 75° c. Are you in the Eastern or Western Hemisphere? Western G. Fields and Field maps ___________Isolines lines connecting points of equal value on a map. __________Isobars lines that join points of equal barometric pressure on a weather map. Isotherms lines of equal temperature. __________Contour Lines _________ __-lines joining points of equal elevation. G. Fields – Contour Maps contour map- (topographic map) - Two dimensional model which shows the elevation of various points on the Earth’s surface. Contour lines isolines that connect points of equal _____________elevation above sea level. Contour Interval _________________difference in value between two contour lines. What is the contour interval of this map? 20 feet G. Fields – Contour Maps - Depressions depressions- pits holes or low areas in the Earth. - shown on contour maps as a hachured line. - first hachure has the ____________value as the same lowest _____________contour line near it. -any hachured lines inside the first decrease in elevation by the contour interval . Both lines are 100 feet Elevation of this line is 80 feet G. Fields – Contour Maps - Direction Direction- most maps have an arrow to indicate north, if not they are usually oriented with north at the top. -latitude and longitude are usually on maps as well. -degrees are divided into 60 minutes and minutes are divided into 60 seconds. What is the latitude and longitude of the center of Jones Swamp? 41° 43’ 15” N 72° 17’ 45” W G. Fields – Contour Maps – Map Scale Map scale ratios-many maps have ratios printed on them. -An example is 1:10,000 which means every one inch on the map equals 10,000 real inches. This works for any unit. One centimeter equals 10,000 cm. scale-distance scale -line that shows what length the distances on maps are equal to. Called a graphic scale. question- What is the distance from the period in Bert Mtn. to the apostrophe in Bob’s Creek? 3.5 miles G. Fields – Contour Maps - Profiles Profile Procedure 1. Place a piece of paper along the area where you are drawing the profile. 2. Place a mark where each line touches the paper and label it with the elevation. 3. Take the strip of paper and place it on the bottom of the graph. 4. Plot the elevations on the graph and connect the points with a line. G. Fields – Contour Maps - Slope map slope- (gradient) -determined by comparing the rate of change in elevation between two points gradient = Change in field value Distance questions 1. What is the elevation of the period in Bert Mtn.? 200 ft. 2. What is the elevation of the apostrophe in Bob’s Creek? 120 ft. 3. What is the distance between them? 3.5 miles G. Fields – Contour Maps - Slope 4. What is the gradient? gradient = 200 ft. – 120 ft. 3.5 miles 80 ft. 3.5 miles Gradient = 22.9 ft/mile 5. If the contour lines are close together , what is it like there? Steep 6. If the Contour lines are far apart, what is it like there? Gentle or gradual G. Fields – Contour Maps – Stream Flow - streams always flow downhill - contour lines always bend upstream when they cross a stream. questions1. Which direction is Bob’s creek flowing? West 2. Which direction is Denbrook flowing? South