* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploring the network
Low-voltage differential signaling wikipedia , lookup
Parallel port wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Registered jack wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
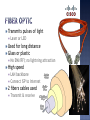
Chapter 4 Intro to Routing & Switching Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the purpose of the physical layer Identify characteristics of copper cabling Make a UTP cable Describe fiber optic cabling & its advantages Describe wireless media Select the appropriate media to connect devices Describe the data link layer, its purpose & structure of a frame Compare logical & physical topologies Describe media access control What data? does the data link layer do to help send What does the physical layer do to help send the data? What does the physical layer do to help receive data? What does the data link layer do to help receive data? 4.1.1 Connect wired or wirelessly Switch, WAP, or ISR How NIC How do you connect to a wired network? do you connect to a wireless network? WLAN NIC What are disadvantages of wireless? Distance from WAP (can use extender) Sharing of wireless signal (more=slower) 4.1.2 Copper Electrical pulses Fiber Light Wireless Radio waves All follow standards so they can communicate together ISO (RJ-45), EIA/TIA (568B), IEEE (802.3, 802.11), and others Identify network devices & cabling 4.1.3 Physical components Cabling, NICs, connectors, ports/interfaces Encoding Pattern of voltage for 1’s & 0’s Differentiates data from control bit info The patterns indicate start & end of frame Signaling It’s what represents a 0 or 1/like Morse code Volts/no volts; short pulse of light/long; type of radio wave Random timing between signals (Asynchronous) or set time (clock) between signals (synchronous) Speed/capacity a media can handle Like size of a hose Bigger hose= more water through it Measure of transfer of bits over a time Varies on amount & type of traffic, latency (delay) Can only be as fast as the slowest link The measure of usable data transferred over a given period of time. Throughput - traffic overhead Example: Ethernet is 100Mbps Throughput is 85Mbps If traffic overhead is 15Mbps, then goodput is 70Mbps What’s the difference? Type of copper cabling Bandwidth it can handle Type of connectors used Wiring order & colors Max distance GCIT’s Ethernet is 1000Mbps. It’s throughput is 800Mbps. If overhead is 10Mbps, what is the goodput? 790Mbps Why are encoding methods (patterns for the bits) used by the physical layer? So the code can be recognized Distinguishes data from control bits Tells where frame starts and ends An asynchronous signal means what? No clock signal sent Morse code & the timing between the bits is known as what? Signaling The speed or capacity of your media is what? Bandwidth The actual amount of bits/data that can actually pass over a period of time is what? Throughput The more bandwidth you have, the more __________________ you should have. Throughput 4.2.1 Inexpensive & easy to install Look up a box of Cat 5e 500ft spool Electrical pulses Distance limit (attenuation) Interference from EMI/RFI, crosstalk To avoid problems, select the right cable for the right situation UTP, STP, Coaxial Most common RJ-45 connectors 8 wires, 4 twisted pairs Twisting prevents crosstalk Color coded Better EMI/RFI protection More expensive to buy & install RJ-45 8 wires, 4 twisted pair wrapped in foil Used in very early Ethernet & now for TV Wireless antenna connections Cable Internet Shielding Thicker cable BNC or F-connector Flammable Electrical hazard; attracts lightning What in the ceiling could “mess up” the electrical signal in an UTP cable? Lights, electrical boxes/equipment Radio waves cause what kind of interference? RFI An electrical motor near a UTP cable causes what kind of interference? EMI Signals from one cable jump into another. What problem is this? Crosstalk Excessively long cable runs cause what problem? Attenuation, signal gets weaker What is the solution to prevent crosstalk? Twisting of the pairs Which STP & coaxial What cables have shielding? RJ45 kind of connector is on UTP & STP? 4.2.1 What does the twisting do? No shielding so it relies on cancellation Wires are paired for this & twisted a certain distance apart RJ45 connector Cat 3, 5/5e, 6 Based on bandwidth rates Straight-through We’re going to make them Crossover We’re going to make them Rollover (Cisco’s) Connect to console port 568B to reverse TIA/EIA 568A & 568B 568B to 568B Connect unlike devices Computer to Hub/Switch Switch to router port On the PC NIC Pins 1 & 2 transmit Pins 3 & 6 receive Straight-through 568B to 568B White-Orange Orange White-Green Blue White-Blue Green White-Brown Brown 568A to 568B Like Devices Switch/hub port to switch/hub port Router port to router port PC to router port PC to PC Crossover 568B to 568A Change Oranges & Greens on ONE SIDE! White-Green Green White-Orange Blue White-Blue Orange White-Brown Brown What is the 568B color order? Wor/Or, WGr/Bl, WBl/Gr, WBr/Br For speeds of 1000Mbps or more, what Category cable should be used? Cat 6 What Goes between same devices? Crossover Goes from PC to switch? cable… Straight through Goes from serial to console port? Rollover What colors do you change for a crossover cable? Oranges & greens What 1&2 What pairs transmit? pairs receive? 3&6 4.2.3 Transmits pulses of light Laser or LED Used for long distance Glass or plastic No EMI/RFI; no lightning attraction High 2 speed LAN backbone Connect ISP to Internet fibers cables used Transmit & receive Multimode LED Many paths of light Used in LANs/Campuses 2000 meters Less $, used more Single Laser light Single path of light Connects backbone/NOCs Mode 3000 meters More $, faster speed Issue Bandwidth Distance Immunity to EMI/RFI Immunity to Electrical Hazards Media/Connector cost Installation Skill/Cost Safety Precautions UTP Fiber Optic Which cable is more expensive, copper or fiber? Fiber Which cable allows data to travel further, copper or fiber? Fiber Why are two strands of fiber used for communication? Light can only travel in one direction at a time. This will allow for full-duplex. What signal travel on a single-mode cable? Laser Which cable would be used to go further distances? Single mode Why would you use fiber between buildings rather than copper? Fiber does not attract lightning 4.2.4 Many devices use wireless Cordless Phones 2.4GHz Interference Microwave Ovens Interference Range Solid Walls a problem Not as fast as, or reliable as, wired Security Wireless is east to access & can be intercepted Authentication & Encryption now used Specifies data speed, range, RF spectrum IEEE standards, Wi-Fi 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n Wi-Fi Alliance tests devices from manufacturer Will work with other devices w/ same logo 1999 2.4GHz 11Mbps 150ft range indoors 300 ft range outdoors 1999 5GHz Unused at that time Less congestion 54Mbps (faster than B) NOT compatible with b/g/n 75ft-150ft range Originally too expensive Now hard to find 2003 2.4GHz 54Mbps 150ft range indoors 300 ft range outdoors Compatible with 802.11b 2.4Ghz 100-600Mbps Up to 750ft range Backwards compatible b/g Access Point (AP) Connects wireless devices to wired network Wireless NIC adapter Gives wireless to a host Standard 802.11a 802.11b 802.11g 802.11n 802.11ac Maximum Speed Frequency Backwards compatible Maybe??? Doesn’t really show wireless You’d like to add wireless with speeds up to 1.3Gbps. Which spec should you buy? 802.11ac What is the max speed of G? 54Mbps What connects wireless devices to a wired network? AP What wireless spec is no compatible with others? 802.11a What could interfere with a wireless signal? Cordless phones, microwaves, solid walls What are 2 other concerns with wireless networks? Security and distance 802.11b, g, and n all operate on what frequency? 2.4GHz 4.3.1 TCP/IP Data equivalent? link layer jobs: Takes layer 3 packets & encapsulates into frames Controls access to the media/encapsulates for the media being used MAC addressing LLC Closer to layer 3 Identifies what layer 3 protocol is being used MAC Closer to layer 1; rules for accessing media MAC address Ready for convert to any type of bits/media Encapsulates data into a frame Adds frame header & trailer Signifies beginning and end of packet What layer of the OSI generates the electrical signals? Physical layer What layer decides the best path? Network layer What layer handles the encapsulation for the proper media going to be used? Data link layer What are the 2 sublayers of the Data Link layer? LLC & MAC What signifies the beginning & end of a frame? Header & trailer Which sublayer identifies the network protocol being used? LLC 4.4.1 Rules of the rode way Depends on: Topology Media sharing Point-to-point WAN connection (between 2 routers) Shared connection (LAN) Full duplex Half duplex Either all complete for the line or take turns CSMA/CD (ETHERNET) Listen for silence, transmit Collision= all backoff random time, listen for silence, retransmit CSMA/CA (WIRELESS) This is MAC (Media Access Control) at Layer 2 Listen for silence, notify all you are sending, gets clearance to send, transmits Token Passing (OLD for Token Ring/FDDI) Wait for your turn/have the token Logical ring topology Ethernet’s collision detection system is known as what? CSMA/CD Describe CSMA/CD. 802.11 wireless networks use what for avoiding collisions? CSMA/CA What is the main difference between CSMA/CA & CD? CA notifies all that you are sending 4.4.4 How is the FCS helpful in a frame? Determines if there are errors What Start frame & MAC addresses The is in the frame header? data in a frame can be how many bytes? 46-1500 bytes Complete Take the study guide handout the quiz on netacad.com Jeopardy review In this chapter, you learned: Devices Chapter 4 Intro to Routing & Switching