* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - The Physics Doctor
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
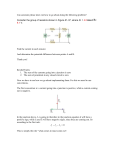
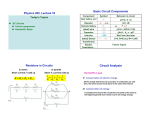
A –Level Physics: Electrical Quantities: Kirchhoff’s Laws Objectives: Additional skills gained: • Deriving equations • Accurate definition of quantities Starter: Write an evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of a ski slope model of an electric circuit including discussion of: • Representation of the charge carriers • Analogies of electrical energy • Ski lift as a cell • Snowpark obstacles as components • Differing speeds by different skiers • How each quantity is represented You have 15mins ONLY Extension: Draw a diagram of the model with annotations Gustav Kirchhoff • Gustav Kirchhoff was a German physicist who worked in the middle of the 19th century • He made many significant contributions to science, specifically in the fields of spectroscopy, thermodynamics and electricity • There are two main circuit rules that bear his name: • The junction rule • The closed loop rule Junction Rule This rule states that the algebraic sum of all the currents entering a junction is equal to zero ΣI=0 In order to conserve electrical charge (law of conservation of charge), the sum of all currents arriving at a point (a junction), must be equal to those leaving it! If a current is arriving we give it a positive value and if it is leaving we give it a negative value Junction Rule- In action Let’s look at the figure below and consider our point of interest (or junction) as the resistor. There is 0.8A of current flowing into the resistor (I4) and 0.8A flowing out (I5). Remember if it flows away from a point then we consider the value as a negative, so it is -0.8A going away. The current in + current out = 0 I4 + I5 = 0 0.8A + -0.8A =0 So it proves the rule! Prove the rule again for the junction indicated in pink Closed Loop Rule In order for energy to be conserved in any loop of a circuit (not necessarily the whole circuit), the sum of EMFs must equal the sum of the potential differences around a loop. Σε= ΣV Note: The potential differences are a result of ohms law calculations based upon the current and the resistance. For this reason, the P.d. may have a negative or positive value dependent on the direction of the current Closed Loop Rule So in the figure below let’s look at the large loop consisting of a cell, a fixed resistor and a variable resistor. Starting at the cell and moving clockwise, we can see the only EMF is the cell so that gives us a total EMF of 3.0V. We can tell that V3 must equal 0.85V as the p.d for any component in parallel is the same (and V4) is parallel. Continuing we know that the next in the loop is the variable resistor which has a p.d of 2.15V Closed Loop Rule As the current is flowing the same way through all components, we can consider them all to have a positive value. So thus far: Σε= ΣV V1= V3+ V2 3.0V = 0.85V + 2.15V 3.0V = 3.0V The rule is proven! Closed Loop Rule Now let’s consider another loop. This time between A and B, including the bulb! Try to prove the rule for this loop. Remember, you consider it completely separate from the rest of the circuit There are no EMFs here in this loop so the total p.ds must = 0! Starting a point A and going clockwise, the p.d through the bulb is 0.85V (V3). Continuing back to A, the p.d. through the resistor is going against the flow of current so is considered negative, so -0.85V (V3) Σε= So: ΣV 0= V3+ V2 0V= 0.85V + -0.85V 0V = 0V Proven! Closed Loop Rule- Practice 15 mins fig D Simple rules Use the printouts to make basic notes on the following: 1. Current and Voltages in series circuits 2. Current and Voltages in parallel circuits 3. Resistance in series and parallel circuits Draw the summary table on page 93 (sheet), in your books as this will be an easy key to check each time. Make it obvious and neat in your notes Answer the questions on page 93 20mins Levelled Practice Questions You have been handed practice questions for Kirchhoff’s laws (and linked calculations). Normal= C grade Higher= B grade Extension= High A grade These must be completed by next monday