* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECE/CS 4984: Lecture 11
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
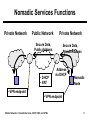
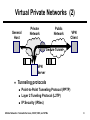
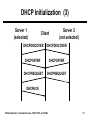
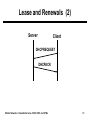
Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems Lecture 10 Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs Lecture Objectives ● Describe the role of nomadic services in mobile ● ● ● ● ● networking Describe the objectives and operation of IP virtual private networks (VPNs) Describe the objectives and operation of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Describe the objectives and operation of network address translation (NAT) Describe firewall and packet filter functions, especially as related to NAT Provide some high-level background in web services, especially for a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 2 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 3 Nomadic Services ● Nomadic services support hosts that attach to different networks, but where host reconfiguration is acceptable ■ Compare to mobile services where hosts can move to a different network without reconfiguring ● Functions ■ Changing the host’s IP address to that of the current network to which it is attached DHCP ■ Limited number of public Internet addresses available in the current network (or any network) NAT ■ Lack of trust of the current network (or any network) VPN ● A wireless “hot spot” usually combines DHCP, NAT, and firewall functions Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 4 Nomadic Services Functions Private Network Public Network Private Network Secure Data, Public Address • DHCP • NAT • VPN endpoint Secure Data, Private Address Address via DHCP Nomadic Node • VPN endpoint Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 5 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 6 Virtual Private Networks (1) ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ■ Enable end-to-end security (authentication and, optionally, privacy) for a single (mobile) host connecting to a private network over untrusted (public) intermediate networks ■ Enable security for private network-to-network communication over untrusted intermediate networks ■ Support quality-of-service and other attributes of a service level agreement over a shared network for network-tonetwork connectivity Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 7 Virtual Private Networks (2) General Host Private Network Public Network VPN Client Secure Tunnel VPN Server ● Tunneling protocols ■ Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) ■ Layer 2 Tuneling Protocol (L2TP) ■ IP Security (IPSec) Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 8 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol ● PPTP is an extension of the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to support tunneling ● Can carry IP and non-IP packets Layer 2 IP GRE Header Header Header Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs PPP Packet 9 Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol ● Resulted from the IETF’s merger of PPTP and the Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2FP) ● Can carry IP and non-IP packets over IP and other networks PPP Frames L2TP Data Messages (unreliable) L2TP Data Channel (unreliable) L2TP Control Messages L2TP Control Channel (unreliable) Packet Transport (UDP, FR, ATM, etc.) Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 10 IP Security ● IPSec has two main components ■ Authentication Header (AH) ■ Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) ● Two modes ■ Transport mode ■ Tunnel mode Tunnel Mode IP AH Inner IP Header (or ESP) Header IP Payload Original IP Datagram Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 11 VPN References K. Hamzeh, G. Pall, W. Verthein, J. Taarud, W. Little, G. Zorn, “Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol,” RFC 2637, July 1999. W. Townsley, A. Valencia, A. Rubens, G. Pall, G. Zorn, B. Palter, “Layer Two Tunneling Protocol ‘L2TP’,” RFC 2661, Aug. 1999. S. Kent, R. Atkinson, “Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol,” RFC 2401, Nov. 1998. D. Fowler, Virtual Private Networks, Morgan-Kaufmann Publishers, 1999. Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 12 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 13 DHCP ● DHCP provides all necessary configuration information to allow a stationary node to become a viable Internet host ● Applications ■ To simplify system administration in traditional networks ■ To improve utilization of IP address space ■ To allow mobile hosts to obtain collocated care-of addresses on foreign networks R. Droms, “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,” RFC 2131, March 1997. C. E. Perkins, Mobile IP: Design Principles and Practices, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1998 (Chapter 9). Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 14 DHCP: Client-Server Model (1) ● DHCP adheres to a client-server model ■ Client requests service ■ Server provides response ● Request and reply must be sent without the benefit of the client being an Internet host DHCP Client 1 DHCP Server DHCP Client 2 request reply Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 15 DHCP: Client-Server Model (2) ● Client broadcasts request to network ■ Broadcast received by server or relay ■ If a relay is used, it forwards request with other information to the server ● Server responds with configuration information ● Client acknowledges receipt ● Server reserves IP address (for some lease time) and notifies client that address is reserved ● Client must renew the lease Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 16 DHCP Initialization (1) ● Client broadcasts a discover message (DHCPDISCOVER) ■ Sent via UDP to port 67 ■ Received by one or more DHCP servers (or relays) ● Responding servers … ■ Determine configuration ■ Send an offer message (DHCPOFFER) to the client ● Client selects a configuration that it wants ■ Sends a request message (DHCPREQUEST) to the selected server ■ Sends the same request message to servers not selected so they can release reserved IP address Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 17 DHCP Initialization (2) ● Selected server … ■ Commits configuration ■ Replies with an acknowledge message (DHCPACK) to complete initialization Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 18 DHCP Initialization (3) Server 1 (selected) Client Server 2 (not selected) DHCPDISCOVER DHCPDISCOVER DHCPOFFER DHCPOFFER DHCPREQUEST DHCPREQUEST DHCPACK Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 19 Lease and Renewals (1) ● Server grants use of the IP address for a limited time, the lease time ● Client should renew the lease about after about twothirds of the lease time has expired ● Lease renewal … ■ Client sends DHCPREQUEST message to the original selected server via unicast ■ Server responds with DHCPACK message ■ If no response from the server, client must start again with DHCP initialization Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 20 Lease and Renewals (2) Server Client DHCPREQUEST DHCPACK Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 21 Graceful Shutdown ● Client can perform a graceful shutdown by sending a DHCP release message (DHCPRELEASE) to the server ■ Allows server to release reserved IP address ● Often, clients just shutdown and IP address is released after the lease time expires Server Client DHCPRELEASE Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 22 DHCP Options ● DHCP servers can provide optional information beyond the assigned IP address ■ Default router ■ Subnet mask ■ Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers ■ Service Location Protocol (SLP) servers ■ Domain Name System (DNS) servers ■ Local domain name ■ Host name ● Request in discover or request message ● Response in offer or acknowledge message ■ Type, Length, Value (TLV) option Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 23 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 24 Network Address Translation ● NAT “mangles” a packet’s addressing headers as it passes through a router to change either the source or destination address ● Most common form of NAT: Network and port address translation ■ A.k.a. IP Masquerading – Linux ■ A.k.a. Port Address Translation (PAT) – Cisco Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 25 What is Masquerading? ● One-to-many translation ● The process of routing Internet-bound traffic from a private network through a gateway router that modifies the traffic to look like its own ● On the return, the router, demultiplexes the traffic back to the appropriate hosts by source/destination port/address pairs (remembered from transmission) Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 26 Example Configuration Internal Network – 192.168.1.xxx .2 External Network Host1 eth0 – 192.168.1.254 .3 Host2 Router eth1 – 12.34.56.78 Host3 .4 ● Trace a packet from Host1 to google.com ■ IP address: 216.239.39.101 Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 27 Packet Trace ● Packet sent to HTTP server at google.com Interface Src IP Dest IP Src Prt Dest Prt Host1:eth0 192.168.1.2 216.239.39.101 4356 80 Router:eth0 192.168.1.2 216.239.39.101 4356 80 12.34.56.78 216.239.39.101 65013* 80 12.34.56.78 216.239.39.101 65013* 80 NAT Router:eth1 … routing Google.com *Note: Masquerading changes the source port as well as source address for assured demultiplexing. Value depends on implementation. Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 28 Packet Trace (2) ● Returning packet Interface Google.com Src IP Dest IP Src Prt Dest Prt 216.239.39.101 12.34.56.78 80 65013 216.239.39.101 12.34.56.78 80 65013 Router:eth0 216.239.39.101 192.168.1.2 80 4356 Host1:eth0 216.239.39.101 192.168.1.2 80 4356 …routing Router:eth1 NAT Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 29 Implementation of Masquerading ● Linux – built into kernel firewall ■ Resident for years ■ ipfwadm, ipchains, iptables ● Windows – Internet Connection Sharing ■ Partially with Microsoft Windows 98SE and Windows ME (only share certain interfaces) ■ Full implementation in Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP (share any interface) Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 30 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 31 Firewalls ● Routers with “attitude” ● Process packets based on rules ● Rules based on any packet characteristics or attributes ■ Source and destination addresses and ports (e.g., source port 1234 from host 10.0.3.23) ■ Protocol flags (e.g., TCP SYN, TCP ACK) ■ Protocol types (e.g., ICMP, UDP) ■ Connection status (e.g., new or established) Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 32 Firewall Services Application-specific proxy, Application-specific filter Application Presentation Gateway, User Filter Port map, Port filter, Address map, Address filter Address map, Address filter, Protocol filter Address filter, Protocol filter Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 33 Types of Firewalls (1) ● Two types ■ Stateful ■ Stateless ● Stateless ■ Simple, less secure than stateful ■ Makes decisions based on individual packet information ■ Does not maintain any connection status ■ Example: ○ Allow all traffic inbound with destination port 80 ○ Deny all traffic from 192.168.1.0/24 on the external interface Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 34 Types of Firewalls (2) ● Stateful ■ All the attributes of a stateless firewall plus … ■ Connection status (context for decisions) ○ Watches traffic for SYN, ACK, and FIN packets ○ Knows connection status (established, initiating) ■ More complex, better security ■ Example: ○ Deny all ICMP Echo Reply packets not associated with an Echo Request ○ Deny all TCP sessions not initiated from the inside network Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 35 Firewall Implementations ● Implementations ■ Hardware and software ● Hardware (network devices) ■ Cisco PIX, Sonicwall, Watchguard Firebox ● Software (applications) ■ Windows – ZoneAlarm, Norton Personal Firewall, BlackICE ■ Unix and variants – ipfw, ipchains, iptables, ipf Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 36 iptables (1) ● Linux firewall (and more) ● Present with the 2.4 series kernel ● Part of the netfilter project ■ http://www.netfilter.org/ ● Consists of two parts ■ Firewall code in the kernel ■ User space “iptables” executable to manipulate kernel code Oskar Andreasson, Iptables Tutorial 1.1.19, http://iptables-tutorial.frozentux.net/. Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 37 iptables (2) ● Three parts ■ Rules ■ Chains ■ Tables Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 38 iptables (3) ● Rule ■ Lowest-level (most basic) entity in firewalling ■ A single tuple of what to do (action) and packets to which to apply the action (filter) ■ Filter – identifies packets to which the rule applies ○ Addresses, ports, status ■ Action – what to do with the packet (stream) ○ Accept, reject (drop, but reply with ICMP error message), drop, redirect, masquerade, go to another chain, and more Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 39 iptables (4) ● Chains ■ An ordered list of rules ■ Traversed in order ■ The first matching rule in the chain is selected ■ Important predefined chains in FILTER table ○ INPUT – all incoming packets go here ○ FORWARD – packets to be routed ○ OUTPUT – all outgoing packets go here Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 40 iptables (5) ● Tables ■ Separate different types of operations ■ Three built-in tables ○ FILTER – general filtering ○ NAT – dealing with network address translation ○ MANGLE – other packet changes ■ Each contain multiple chains Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 41 iptables (6) ● Incoming packet traversal Example: Typical Firewall Functions Network Example: Setting DSCP Mangle PREROUTING Routing Decision Local Mangle INPUT Filter INPUT Application Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs Example: Typical Firewall Functions Example: Redirecting Nat PREROUTING Non-Local Mangle FORWARD Filter FORWARD *to output* 42 iptables (7) ● Outgoing packet traversal Application Routing Decision Example: IP Masquerading Mangle OUTPUT Nat OUTPUT Example: Typical Firewall Functions Filter OUTPUT Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs Network *from non-local input* Nat POSTROUTING Mangle POSTROUTING 43 iptables (8) ● Rule placement ■ Rule type specifies table ○ Address translation and IP masquerading map to the NAT table ○ Simple packet filtering maps to the filter table ■ Rule stage specifies chain ○ Prerouting versus postrouting ○ Traffic from local application versus forwarded traffic Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 44 Firewall Comments ● “Good” firewall rules are difficult to write ■ Must consider all possible traffic ■ Only allow what should pass ● Stateful firewalls are more secure (and more complex) than stateless firewalls ● Stepping forward ■ Intrusion Detection System (IDS) – “smarter” stateful firewall Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 45 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 46 Web-Based Authentication ● Consider a wireless LAN “hot spot” service ● This will require consideration and use of… ■ DHCP ■ Firewalling ■ Authentication ■ IP masquerading (NAT) ● Authentication is commonly done using a web-based scheme − here is one approach… ■ The first attempt to access any web page is redirected to an authentication page for the service ■ A script or program must perform authentication and updates the configuration to allow access, if appropriate Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 47 HTML ● HyperText Markup Language (HTML) ■ Web page “language” (content) ■ Currently in version 4.01 ■ Maintained by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) ○ http://www.w3c.org ■ Uses “tags”: <begin_tag>text</end_tag> ■ Formatting language ○ Take data and add formatting, pictures, input, and/or links Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 48 HTML (2) ● Many extensions and add-ons ■ Responsible for rich web content ● Tags interpreted by web browser; no server processing involved ● May be edited by hand or with a WYSWYG editor ■ By hand: notepad, emacs, vi ■ WYSWYG: MS Frontpage, Dreamweaver Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 49 Web Programming (1) URL, param Web Browser (2) CGI HTTP Server (5) HTML, text, … Gateway Program (4) HTML, text, … Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs (3) Process ● Common Gateway Interface (CGI) ■ A way for web servers to interact with standard programs to generate dynamic web content ■ Input typically HTML form data ■ Output dynamic content (web pages) ■ Can be written using C++, Perl, Fortran, or PHP ■ Can do many functions with the appropriate library 50 Web Programming (2) ● Model ■ Client request ■ Server reference ■ Server processing (CGI, SSI, PHP) ■ Request sent to client ■ Browser processing (JavaScript, HTML, CSS) Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 51 No Experience? ● PHP suggested for those with no experience with web programming ● PHP code is embedded in HTML code ■ No compilation ■ Quick editing ● Familiar syntax ■ Borrows syntax “look and feel” from Java, Perl, and C++ Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 52 Agenda ● Nomadic services ● Virtual private networks (VPNs) ● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ● Network address translation (NAT) ● Firewalls and packet filtering ● HTML and web programming ● Brief comments on a wireless “hot spot” service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 53 A Test Network Configuration “Public” Internet Public Private Private Network ● DHCP server ● Firewall ● IP masquerading ● Web-based authentication Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 54 Summary ● Nomadic services enable Internet access ■ Security, addressing, filtering ● VPNs provide authentication and privacy for nomadic ● ● ● ● users and protect private networks DHCP allows nomadic users to obtain an IP address and other configuration information NAT conserves addresses in private networks, allowing support for nomadic hosts Firewalls and packet filtering provide security and enable access control HTML and web programming can be used to authenticate nomadic users for a hot spot service Mobile Networks: Nomadic Services, DHCP, NAT, and VPNs 55