* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prenatal Development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
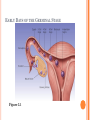
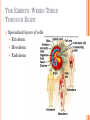
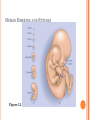
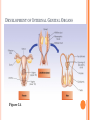
CONCEPTION AND PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OT 500 : Child Behavior and Development Spring 2016 Figure 2.9 WHAT PROCESS BRINGS TOGETHER THE GENES FROM EACH PARENT? Only one sperm enters the zona pellucida Sperm secrete enzyme hyaluronidase to allow penetration of the zona pellucida When one sperm enters, the zona pellucida thickens, locking out other sperm Chromosomes from sperm and egg combine to form 23 new pairs MISCARRIAGE Spontaneous abortion Before 20 weeks pregnancy Usually due to mutation/ problem with chromosomal pairing Estimated over 50% of fertilized eggs die, often before a woman is aware of pregnancy At 4 -5 weeks pregnancy, miscarriage rate is 20% Can be related to stress, environmental toxins, and maternal health issues and more common in older women, and women who have had prior miscarriage INFERTILITY Fertility problems among men Low sperm count Deformed sperm Low sperm motility Diseases Direct trauma to testes Autoimmune responses Causes Genetic factors, environmental poisons, diabetes, STI’s, overheating testes, pressure to testes, aging and effects of drugs INFERTILITY Major fertility problems among women Irregular or failure to ovulate Fertility drugs are used to cause women to ovulate Declining hormone levels due to aging Infections Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Endometriosis Obstruct fallopian tubes Barriers or disorders in passageways (i.e. Fallopian tubes) OTHER WAYS OF BECOMING PARENTS Surrogate Mothers Surrogate “substitutes” bring babies to term for another woman Adoption Greater diversity of adopted children and adoptive parents Consideration of adopted children needs OTHER WAYS OF BECOMING PARENTS HOW ARE COUPLES HELPED TO HAVE CHILDREN? Artificial Insemination Sperm injected into mother’s uterus In Vitro Fertilization Ova and sperm are fertilized, then implanted in mother’s uterus Donor IVF Ovum harvested from donor woman; fertilized in vitro and implanted in recipient’s uterus Embryonic transplant PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT 3 Phases Germinal Stage: Period from conception to implantation (approximately 2 weeks) Embryonic Stage: Period from implantation to the 2nd month Fetal Stage: Period from the beginning of the third month until birth THE GERMINAL STAGE Zygote repeatedly divides but does not gain in mass as it moves, taking about 3-4 days to reach the uterus Within 3 days, the mass of dividing cells is about 32 cells, and is called a Blastocyst The blastocyst shoes cell differentiation Inner layer or part of blastocyst is called the embryonic disk (becomes embryo and fetus) Outer part of the blastocyst is called the trophoblast (protects and nourishes); blood cells, umbilical cord, placenta EARLY DAYS OF THE GERMINAL STAGE Figure 3.1 HOW DOES THE DIVIDING MASS OF CELLS OBTAIN NOURISHMENT DURING THE GERMINAL STAGE? Prior to implantation, the dividing cells are nourished by the yolk of the original egg Once implanted, nourishment is obtained from the mother FAILED PREGNANCY Miscarriage (spontaneous abortion) Usually stems from abnormalities in development Approximately one-third of all pregnancies result in miscarriage THE EMBRYONIC STAGE WHAT HAPPENS DURING THE EMBRYONIC STAGE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT? Begins with implantation (3rd week) through 8th week Major organ systems differentiate Developmental trends Cephalocaudal – head takes precedence over lower parts of the body Proximodistal outward – central axis of body WHAT HAPPENS DURING THE EMBRYONIC STAGE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT? Embryonic disk Ectoderm (outer layer) develops into nervous system, sensory organs, nails, hair, teeth, and skin; Neural tube develops into brain and spinal cord Endoderm (inner layer) forms the digestive and respiratory systems, liver, and pancreas Mesoderm (middle layer) develops into the excretory, reproductive and circulatory system, muscles, skeleton, and inner layer of skin THE EMBRYO: WEEKS THREE THROUGH EIGHT Specialized layers of cells Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm HUMAN EMBRYOS AND FETUSES Figure 3.2 WHEN DOES THE HEART BEGIN TO BEAT? Heart begins to beat (4rd week); when you were about ¼ inch long!!! Arm buds and leg buds appear (4th week) Eyes, ears, nose and mouth begin to take shape Limbs are elongating, facial features become distinct (8th week) Teeth week) buds, working kidneys and liver (8th DEVELOPMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM By end of first month, the neural tube is producing 400 million neurons/nerve cells per day Neurons form cerebral hemispheres (5th week) Cells in the nervous system begin to release neurotransmitters (2nd month) SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Nondescript sex organs formed (5 to 6 weeks) Internal and external genitals at this stage resemble female structures Müllerian (female) ducts and Wolffian (male) ducts Sex organs begin to differentiate, based on genetic code (7th week) Y chromosome causes testes to differentiate No Y chromosome causes ovaries to differentiate Distinct external genital structures (4 months) BOY OR GIRL? Prenatal sexual development Stage 1 – male and female have similar gonadal streak, Müllerianducts, and Wolffian ducts Stage 2 – physiological differences emerge Stage 3 – external genitals form; testosterone stimulates development of testicles and penis Stage 4 – testosterone inhibits the cycles of the hypothalamus and pituitary, which regulate female ovulation DEVELOPMENT Figure 3.4 OF INTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS SEX HORMONES AND SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Male hormonal influences Testes produce androgens Testosterone differentiates male duct system (Wolffian) DHT (dihydrotestosterone) triggers development of male external genital organs Müllerian inhibiting substance (MIS) SEX HORMONES AND SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION Female hormonal influences Small amounts of androgens are produced Play a role in secondary sexual characteristics in adolescence Important in sex drive of females Wolffian ducts degenerate and Müllerian ducts develop into Fallopian tubes, uterus, and inner part of the vagina HOW DOES THE EMBRYO GET NOURISHMENT FROM THE MOTHER? Amniotic Sac Protects the embryo/fetus within the uterus Sac is surrounded by amniotic fluid Placenta Mass of tissue exchanges nutrients and wastes between embryo/fetus and mother Umbilical Cord Connects the fetus to the placenta DO GERMS OR DRUGS IN THE MOTHER PASS THROUGH THE PLACENTA AND AFFECT THE BABY? Placenta acts as a filter between the bloodstream of the mother and the bloodstream of the embryo/fetus Oxygen and nutrients reach the embryo Carbon dioxide and waste pass to the mother Many germs and drugs may also reach the embryo (alcohol, aspirin, narcotics) Secretes hormones that prepare breasts for nursing, and stimulate contractions that prompt childbirth The EMBRYO IS VERY SUSCEPTIBLE THE FETAL STAGE WHAT HAPPENS DURING THE FETAL STAGE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT? Third End month through birth of first trimester Major organ systems formed Fingers and toes formed Eyes can be distinguished Sex of fetus can be determined visually WHAT HAPPENS DURING THE FETAL STAGE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT? End of second trimester Opens and shuts eyes Sucks thumb Alternates between sleep and wakefulness; mother feels baby moving around 4 months Responds to light and sound At 22 to 25 weeks gestation, about 50% babies born will survive WHAT HAPPENS DURING THE FETAL STAGE OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT? End of third trimester Heart and lungs increasingly able to sustain life Gains in weight and length During 7th month, fetus turns upside-down in uterus Born at end of 7th month – 90% survival rate WHEN DOES THE MOTHER BEGIN TO DETECT FETAL MOVEMENTS? Middle of 4th month – detect first fetal movements End of second trimester Fetus moves vigorously, turns somersaults Begins slow squirming movements Begins sharp jabbing and kicking movements As fetus grows, movements becomes restricted Prenatal activity predicts activity levels after birth ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES ON PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT HOW DOES THE NUTRITION OF THE MOTHER AFFECT PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT? Malnutrition in mother (esp. during last trimester) Low-birth-weight, prematurity, stunted growth, retardation of brain development, cognitive deficiencies, behavioral problems, cardiovascular disease Some effects of fetal malnutrition can be overcome by supportive, care-giving environments Maternal obesity Linked to higher risk of still-birth Increases risk of neural tube defects WHAT SHOULD A PREGNANT WOMAN EAT? Well rounded diet including protein, vitamins, minerals, calcium, and calories Folic acid supplements Reduce risk of neural tube defects Mother can expect to gain 25 to 35 pounds during pregnancy Inadequate weight gain increases chance of premature or low-birth-weight baby TERATOGENS AND HEALTH PROBLEMS OF THE MOTHER Teratogens – environmental agents that can harm embryo or fetus Drug ingested by mother Substance produced by mother Heavy metals such as lead and mercury Excessive hormones Radiation Pathogens – bacteria and viruses DOES IT MATTER WHEN, DURING PREGNANCY, A WOMEN IS EXPOSED TO A TERATOGEN? Critical periods of exposure to teratogens Based on development of organs Embryo is more vulnerable than fetus due to major organ systems differentiating CRITICAL PERIODS IN PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT Figure 3.5 SENSITIVE PERIODS IN PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF MATERNAL HEALTH PROBLEMS? Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Syphilis can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, or congenital syphilis Infected mother can be treated with antibiotics before 8th week Infected mother not treated Baby 40-70% chance of being infected in utero Babies with congenital syphilis WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF MATERNAL HEALTH PROBLEMS? Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) HIV/AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) Disables body’s immune system Lethal unless treated About one-quarter of babies born to HIV/AIDSinfected mothers are infected also Many are infected during childbirth HIV is also found in breast milk WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF DRUGS TAKEN BY THE MOTHER? Accutane Prescribed for difficult cases of acne Linked to numerous abnormalities during first trimester Thalidomide Antibiotics Missing or stunted limbs Tetracycline may lead to yellowed teeth and bone abnormalities Hormones Progestin can masculinize external sex organs of female embryo DES can cause cervical and testicular cancer WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF MATERNAL HEALTH PROBLEMS? Influenza (Flu) Rubella (German measles) Impacts mother’s respiratory system Viral infection may cause birth defects Toxemia May cause premature or undersized babies Cause of maternal death Rh Incompatibility Transfer of maternal antibodies that may cause brain damage or death WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF DRUGS TAKEN BY THE MOTHER? Vitamins High doses of vitamins A and D are associated with central nervous system damage, small head size and heart defects Heroin and Methadone Maternal addiction linked to low-birth-weight, prematurity, and toxemia Baby may be born addicted Marijuana Risk of low-birth-weight, immature development of nervous system Predisposes offspring to dependence on opiates, even in adulthood WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF DRUGS TAKEN BY THE MOTHER? Cocaine Maternal use of cocaine increases risk of stillbirth, lowbirth-weight, and birth defects In utero exposure results in problems throughout childhood Alcohol Alcohol passes through placenta and poses risks for death of fetus and neonate, malformations, and growth deficiencies Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) Physical and psychological defects Fetal Alcohol Effect (FAE) FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF DRUGS TAKEN BY THE MOTHER? Caffeine Connected with miscarriage and low-birth-weight Cigarettes Nicotine and carbon monoxide pass through the placenta Nicotine stimulates fetus Carbon monoxide is toxic and decreases oxygen to fetus More likely to deliver smaller babies Long-term effects More likely to be stillborn or die soon after birth Short attention spans, hyperactivity, lower cognitive scores, poor grades Men who smoke are more likely to produce abnormal sperm WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARDS? Prenatal exposure to PCBs Connected with smaller, less responsive babies More likely to develop cognitive deficits Heavy metals (lead, zinc, mercury) Fetal exposure to radiation Threatens cognitive development Risks for neural and skeletal problems Father’s exposure to heavy metals and radiation may also cause abnormalities in baby WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF MATERNAL STRESS? Maternal stress linked to secretion of hormones Adrenaline passes through placenta CNN week of Jan 25/2016: Zika Virus linked to birth defect in newborns..3-4 million cases in the Americas (mostly Brazil); spreading explosively..by mosquitos..can result in microcephaly in newborns