* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Course Outline - Lake Land College
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
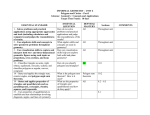
2-3-2015 DATE Math/Science REQUIRED COURSE ELECTIVE COURSE X DIVISION NEW COURSE REVISION LAKE LAND COLLEGE Course Information Form COURSE NUMBER SEM CR HRS 3 COURSE PCS # MAT009 TITLE Geometry LT HRS 3 LAB HRS SOE HRS (Assigned by Administration) PREREQUISITES: ECH 3 MAT005 or Placement by Math Assessment Catalog Description (40 Word Limit): This course is an introductory course in plane geometry for students with less than one year of high school geometry. Topics included, but not limited to, are: lines, angles, proofs, triangles Pythagorean theorem, circles, various geometrical formulas and coordinate geometry. CONTENT OUTLINE LECTURE HOURS Problem Solving Approaches in Geometry 3 Geometric Shapes and Measurements 5 Perimeter, Area and Volume 8 Reasoning and Triangle Congruence 6 Parallel Lines and Quadrilaterals 8 Similarity 6 Circles and their properties 5 Coordinate Geometry 4 LAB HOURS _ _ Total EVALUATION: Quizzes Lab Work Textbook: Title Author X Exams 45 X Projects Oral Pres. Comp.Final X Papers Other College Geometry: A Problem-Solving Approach with Applications Musser, Trimpe and Maurer Publisher Pearson/Prentice Hall Volume/Edition 2nd Edition Copyright Date 2008 Major Course Segment Hours Problem Solving Approaches Learning Outcome At the end of this segment each Sketch a picture, guess & check, variables 1 student will approach an unknown Finding patterns & making tables 1 problem utilizing one or many of Solve a simpler problem 1 the listed approaches. Geometric Shapes, Line and Angle Measurement At the end of this segment each Lines and Angles 1 student will understand state- Definitions and Postulates 2 ments, postulates, definitions and Angles, Polygons and Circles theorems in relation to lines and Three-dimensional shapes 1 angles. In addition, the student Dimensions 1 will be able to identify (& measure) different kinds of angles, polygons and geometric shapes and convert dimensions. Perimeter, Area and Volume Perimeter and Area Formulas for Circles, After completing this segment, the 1 student will be able to find the Triangles and Rectangles Perimeter and Area Formulas for polygons perimeters and areas of triangles, 2 quadrilaterals, polygons and circles. Students will solve right triangles Pythagorean’s Theorem using Pythagorean’s theorem. 2 When the students complete this Surface Area and Volume Formulas for Prisms 3 section, they will be able to compute and Pyramids, Cones and Cylinders the surface areas and volumes for and Spheres prisms, pyramids, cones, cylinders and spheres. Reasoning & Triangle Congruence At the conclusion of this segment, Geometric Proofs and Conditional Reasoning 1 create basic formal proofs. Congruence Conditions for Triangles 3 The student will be able to prove SAS, ASA, AAS, SSS Solving problems using congruence triangles congruent, identify and 2 know properties of different kinds of triangles and utilize these properties to solve problems. Major Course Segment Hours Parallel Lines Learning Outcome After completing this section, the Parallel Postulate, Special Angles and Introduction 2 to Indirect Proofs student will understand parallel lines and related angles and have Theorems involving Parallel Lines 2 an understanding of indirect proof. Measure of Interior and Exterior Angles Quadrilaterals The student, after completing Introduction to Different Quadrilaterals and Their 1 Properties this section, will be able to identify and know the different kinds of Definitions and Properties of Parallelograms, 3 quadrilaterals and their properties. Rectangles, Squares Rhombi, Trapezoids Similarity At the conclusion of this segment, the Ratio and Proportion 1 Introduction to Similarity, Proportionally of 2 Corresponding Sides & Equal angles Applications with Similar Polygons student will understand properties of similarity pertaining to triangles and 1 polygons. In addition, the student will be able to solve problems involving Right Triangle Trigonometric Ratios 2 Circles trig ratios with right triangles. On completion of this section, the Circle properties, related segments & angles 1 student will know about circles and Arcs, Central Angles, Chords 2 the relationships between the related Tangents, Secants, Inscribed Angles 2 angles, segments and lines. Coordinate Geometry On completion of this segment, a Introduction to the Rectangular Coordinate System and Midpoint & Distance Formulas student will understand the rectangular 1 coordinate system and be able to graph points and lines. In addition, the Slopes and Linear Equations 2 student will be familiar with different forms of equations of lines and be Equations of Circles Mat 009 – Geometry 1 able to determine circle equations. Course Outcomes: At the successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Understand and apply basic concepts of lines, segments, rays and angles. Identify and apply triangle properties in simple proofs Recognize and apply relationships among the angles created by parallel lines and transversals. Students should then apply these concepts to polygons. Apply relationships found in circles between chords, arcs, angles, radii, and diameters to analyze problems.