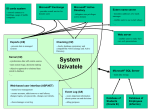
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9781111309770_PPT_ch01
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Windows wikipedia , lookup
Windows Mobile wikipedia , lookup
Windows Phone wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT startup process wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Windows Vista wikipedia , lookup
Windows Phone 8.1 wikipedia , lookup