* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Regional differentiation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
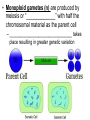
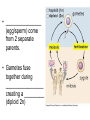
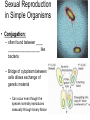
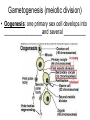
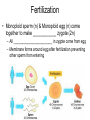
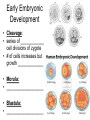
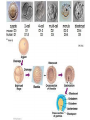
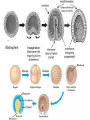
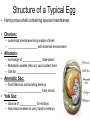
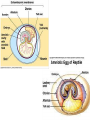
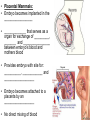
Sexual Reproduction Why Sex?: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gRpEt61XM4M&safe=active • Monoploid gametes (n) are produced by meiosis or “_____________” with half the chromosomal material as the parent cell – ________________________________ takes place resulting in greater genetic variation • ________________ (egg/sperm) come from 2 separate parents. • Gametes fuse together during _________________ creating a _________ (diploid 2n) • Advantages of Sexual Reproduction: – Offspring genetically _________from parents – This variation means that even if changes in environment occur some offspring may survive (__________________) Sexual Reproduction in Simple Organisms • Conjugation: – often found between ____ ___________________ like bacteria – Bridge of cytoplasm between cells allows exchange of genetic material • Can occur even though the species normally reproduces asexually through binary fission Sexual Reproduction in Animals • Usually involves two different sexes • Gametes develop in specialized organs (_____________) • Ovaries produce eggs (n) (ova) – Usually larger, round and ______________ – Often contain stored food in the form of yolk • Testes produce sperm (n) – Usually motile – Has a head (containing DNA), middle (containing Mitochondria) and tail (flagellum) – Head has _____________________, helps penetrate egg Gametogenesis (meiotic division) • Oogenesis: one primary sex cell develops into _________________and several __________ Gametogenesis (meiotic division) • Spermatogenesis: one primary sex cell develops into _________________ • Hermaphrodites – Have _________________________ – Usually found in animals that _____________ and it may be hard to locate mates – Two animals meet and fertilize each other • Ex: earthworm Fertilization • Monoploid sperm (n) & Monoploid egg (n) come together to make ____________ zygote (2n) – All _______________________ in zygote come from egg – Membrane forms around egg after fertilization preventing other sperm from entering External Fertilization • _______________ outside body of female. • Requires ______________ for sperm to swim to egg – Often occurs with aquatic animals • ___________ numbers of eggs and sperm are released to increase chance of fertilization • Timing of release controlled by hormones and sexual signaling – Ex: _______________& _______ Internal Fertilization http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bRKdTAzPBv0&safe=active http://www.united-academics.org/magazine/earth-environment/topten-weirdest-animal-penises/ • Fusion of gametes occurs within moist __________ environment of female’s reproductive tract • Occurs in ________________________________ – terrestrial vertebrates – Allowed for a way for animals to evolve to live on land! • Requires specialized sex organ to carry sperm from males body to females (____________) • Seminal fluid (semen) provides _______________ for sperm to swim Internal Fertilization • After fertilization the embryo is either: – enclosed in a ____________ and is ejected to develop outside of females body (oviparous) • ex: chicken egg – remains and develops in a special __________ of females body • ex: human uterus • Advantages of Internal Fertilization: – Gametes not _____________ in environment where they could be destroyed – Chances of fertilization _____________ – Don’t need __________________________ • they require a huge amount of energy to make! • Still have ________________ of sperm released to guarantee fertilization takes place • Parthenogenisis – Development of an _______________ into an adult animal without fusion with sperm – Ex: many insects including bees, wasps, ants, also some lizards • In bees an unfertilized egg will become a male drone and fertilized eggs become female workers or queens Early Embryonic Development • Cleavage: • series of ____________ cell divisions of zygote • # of cells increases but growth _____________ • Morula: • ___________________ • Blastula: • ___________________ • Gastrulation: – Cells of blastula _____________________ forming gastrula – Opening is called the blastopore • This later becomes the opening to digestive system • Three cell layers form: – ______________, _________________ & ______________ Growth & Differentiation of Cells • Three cell layers of gastrula differentiate into different tissues of body (___________________) • • • • • • Ectoderm (outer layer) _______________________________________ Mesoderm (middle layer) _______________________________________ Endoderm (inner layer) _______________________________________ Differentiation • Differentiation occurs because: – different sections of DNA called genes _____________________ in different cells, controlling what type of cell it will become – _____________________________ between adjoining cells can also influence cell type and development http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/overview-of-animal-reproduction-anddevelopment.html Development & Growth of Embryo • Development is the process by which the embryo becomes the organism. • An embryo needs: – protection from elements – a way to get __________________ – regulate temperature – get rid of it’s __________________ External Development • In Water: – nourishment comes from ______________, gets oxygen from water, wastes diffuse into water – Requires little or no ____________________ • Some animals guard eggs or fan water currents to provide more oxygen • On Land – Need large egg with yolk (nourishment) protected by a shell • A self sustained watery environment – ____________________ allows oxygen in and carbon dioxide out • Ex: Reptiles, Birds and Monotremes (Ex: platypus) Structure of a Typical Egg • Hard porous shell containing special membranes • Chorion: – outermost membrane lining inside of shell – _____________________ with external environment • Allantois: – exchange of ______________ take place – Metabolic wastes (like uric acid )collect here – Site for ____________________________ • Amniotic Sac: – fluid filled sac surrounding embryo – ________________________ from shock • Yolk Sac: – Source of ____________ for embryo – Has blood vessels to carry food to embryo Internal Development • Mammals: • Internal fertilization • Embryo develops in ________ or ______________ • When born offspring receives nourishment from mother from __________________ • Only _______________ are produced at a time • Placental Mammals: • Embryo becomes implanted in the _________________ • _____________ that serves as a organ for exchange of _________, _______ and ________________ between embryo’s blood and mothers blood • Provides embryo with site for: __________, ____________ and __________________ • Embryo becomes attached to a placenta by an __________________ • No direct mixing of blood • Non Placental Mammals – Pouched: • Marsupials (like Kangaroo) – Egg Laying: • _____________ (Echidna), _____________________ – Embryos are born _______________________. Must complete development in a pouch. – No _____________________ of young in uterus – Crawls into pouch, attaches ________________ to complete development Baby Echidna: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZXEC1Qx4cJg&safe=active Kangaroo Giving Birth http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2lCKc8tURtc&safe=active Try These Questions • What is the function of the placenta? • Why do fish produce more eggs than birds? • What advantage is it to have an egg shell on dry land? • How do the eggs that develop in water obtain nourishment and oxygen? • What happens during gastrulation?