* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MahadyGeographyStandardsforgeolit.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
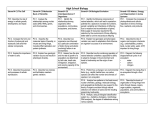
New Geography Standards: Hantavirus: Grade Six Strand One: American History Concept 1 Research Skills for History PO 2 Interpret historical data displayed in graphs, tables, and charts PO 4 Formulate questions that can be answered by historical study and research Grade Six Strand Two: World History Concept 1 Research Skills for History PO 2 Interpret historical data displayed in graphs, tables, and charts PO 4 Formulate questions that can be answered by historical study and research Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 1 The World in Spatial Terms PO 2 Identify purposes and differences of maps, globes, aerial photographs, charts, and satellite images PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions. Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 3 Physical Systems PO 1 Identify the physical processes that influence the formation and location of resources Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 5 Environment and Society PO 2 Describe the intended and unintended consequences of human modification (e.g., irrigation, aqueducts, canals) on the environment PO 3 Explain how changes in the natural environment can increase or diminish its capacity to support human activities (e.g., flooding of the Nile, industrial pollution, hydropower) PO 4 Identify the way humans adapt to natural hazards in order to remain safe (i.e., lightning, flash floods, dust storms, tornadoes, hurricanes, floods, and earthquakes) Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 6 Geographic Applications PO 1 Describe ways geographic features and conditions influenced historical events in different periods of time, places, and regions (e.g., the location of settlements: near waterways; on high terrain; with adequate fresh water; on good land for farming; in temperate climates Grade Seven Strand One: American History Concept 1 Research Skills for History PO 2 Interpret historical data displayed in graphs, tables, and charts PO 4 Formulate questions that can be answered by historical study and research Grade Seven Strand Two: World History Concept 1 Research Skills for History PO 2 Interpret historical data displayed in graphs, tables, and charts PO 4 Formulate questions that can be answered by historical study and research Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 1 The World in Spatial Terms PO 2 Identify purposes and differences of maps, globes, aerial photographs, charts, and satellite images PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions. PO 6 Explain key geographic concepts (importance of location, migration, adaptation to/modifications of the environment, what is a region, characteristics of cultures) Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 5 Environment and Society PO 2 Describe the consequences of natural hazards (e.g., Dust Bowl, hurricanes, droughts, earthquakes) Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 6 Geographic Applications PO 3 Use geographic knowledge and skills (e.g., recognizing patters, mapping, graphing) when discussing current events Grade Eight Strand One: American History Concept 1 Research Skills for History PO 2 Interpret historical data displayed in graphs, tables, and charts PO 4 Formulate questions that can be answered by historical study and research Grade Eight Strand Two: World History Concept 1 Research Skills for History PO 2 Interpret historical data displayed in graphs, tables, and charts PO 4 Formulate questions that can be answered by historical study and research Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 1 The World in Spatial Terms PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information. Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 5 Environment and Society PO 3 Explain how changes in the natural environment can increase or diminish its capacity to support human activities (e.g., global warming, pollution, mining, natural disasters, water table). PO 6 Explain how societies and governments plan for and respond to natural disasters (e.g., evacuation routes, changing farming techniques, warning systems). From Around the Corner to Around the World Grade Six Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1 Construct charts, graphs, and narratives using historical data Grade Six Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1 Construct charts, graphs, and narratives using historical data Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1 Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions. Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 3 Describe the interactions of people in different places and regions Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 4 Identify the factors that influence the location, distribution, and interrelationships of economic activities over time in different regions (e.g., river/coastal civilizations, trade, Industrial Revolution) PO 6 Describe how changes in technology, transportation, communication, and resources affect the location of economic activities in places and world regions (e.g., Industrial Revolution, Imperialism) Grade Six Strand Five: Economics Concept 2: Macroeconomics PO 2 Describe how investment in physical capital leads to economic growth (e.g., factories, machinery, and new technology) Grade Seven Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1 Construct charts, graphs, and narratives using historical data Grade Seven Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1 Construct charts, graphs, and narratives using historical data Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1 Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 4 Locate physical and cultural features throughout the world. (e.g., continents, cities, countries, significant waterways, mountain ranges, climate zones, major water bodies, landforms). PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions. Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 3 Compare the historical and contemporary interactions among people in different places and regions. Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 3 Identify the effects of human migration (e.g., imperialism, quota system, changing of political boundaries, multiculturalism). PO 7 Identify the factors that influence the location, distribution, and interrelationships of economic activities in different places and world regions Grade Seven Strand Five: Economics Concept 2: Macroeconomics PO 2 Describe how investment in physical capital leads to economic growth (e.g., factories, machinery, and new technology) Grade Eight Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1 Construct charts, graphs, and narratives using historical data Grade Eight Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 1 Construct charts, graphs, and narratives using historical data Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1 Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 4 Locate physical and cultural features throughout the world. (e.g., continents, cities, countries, significant waterways, mountain ranges, climate zones, major water bodies, landforms). Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 4 Identify the ways human and physical features influence a perception of place (e.g., the role of media, word of mouth, advertising, images) Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 4 Identify the factors that influence the location, distribution, and interrelationships of economic activities in different regions (e.g., breakup of USSR, unification of Germany, cheap labor forces, outsourcing of services, oil industry). PO 7 Describe how changes in technology, transportation, communication, and resources affect economic development. Grade Eight Strand Five: Economics Concept 2: Macroeconomics PO 6 Describe how investment in real capital leads to economic growth (e.g., factories, medical advancements, and new technology) PO 7 Describe how competition affects supply and demand from the vantage point of the consumer and producer (e.g., Microsoft/Apple, Wal-Mart/Target). PO 8 Identify how market prices provide incentives to buyers and sellers. Grand Canyon: So What’s the Attraction Grade Six Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Six Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 4 Locate physical and human features in the United States and in regions of the world on a map (e.g., continents, significant waterways, mountain ranges, cities, countries). Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 1 Identify regions using a variety of criteria (e.g., climate, landforms, culture, vegetation). Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 4 Identify the factors that influence the location, distribution, and interrelationships of economic activities over time in different regions (e.g., river/coastal civilizations, trade, Industrial Revolution) Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 5: Environment and Society PO 1 Describe ways that human dependence on natural resources influences economic development, settlement, trade, and migration Grade Six Strand Five: Economics Concept 2: Macroeconomics PO 2 Describe how investment in physical capital leads to economic growth (e.g., factories, machinery, and new technology) Grade Seven Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Seven Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 4 Locate physical and human features in the United States and in regions of the world on a map (e.g., continents, significant waterways, mountain ranges, cities, countries). Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 4 Identify the factors that influence the location, distribution, and interrelationships of economic activities in different places and world regions Grade Seven Strand Five: Economics Concept 2: Macroeconomics PO 2 Describe how investment in physical capital leads to economic growth (e.g., factories, machinery, and new technology) Grade Eight Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Eight Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 4 Locate physical and human features throughout the world. (e.g., continents, cities, countries, bodies of water, landforms, mountain ranges, climate zones). Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 4 Identify the ways human and physical features influence a perception of place (e.g., the role of media, word of mouth, advertising, images). Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 6: Geographic Applications PO 2 Describe ways geographic features and conditions influenced historical circumstances in different periods of time (e.g., jungle warfare in Vietnam, desert warfare in Iraq) Grade Eight Strand Five: Economics Concept 2: Macroeconomics PO 6 Describe how investment in real capital leads to economic growth (e.g., factories, medical advancements, and new technology) Welcome to My World Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 3 Describe the interactions of people in different places and regions PO 5 Describe the physical and human characteristics of places and regions of a Middle Eastern country. Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 5 Identify cultural norms that influence different social, political, and economic activities of men and women. Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 1 Describe the human and physical characteristics of places and regions. PO 3 Compare the historical and contemporary interactions among people in different places and regions. Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 1 Discuss the implications of the demographic structure of places and regions. PO 6 Describe the distributions and patterns of cultural characteristics (e.g., religions, language, standard of living) over time. Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1. Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information. PO 4. Locate physical and cultural features throughout the world. (e.g., continents, cities, countries, bodies of water, landforms, mountain ranges, climate zones). Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 3. Describe the distributions of cultures throughout the world. PO 6. Describe the aspects of culture related to beliefs and understandings that influence the economic, social, and political activities of men and women. (e.g., literacy, occupations, clothing, property rights). Is there a Map in that Story? Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1 Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1 Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 4 Analyze why people choose to live where they do (e.g., natural resources, farmland, water, mild climate, family, employment). Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 1 Construct maps, charts, and graphs to display geographic information PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information Get on the Track: African American Migration Grade Six Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Six Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 2: Places and Regions PO 2 Describe the factors that cause regions and places to change Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 2 Describe the environmental, economic, cultural, and political effects of human migrations and cultural diffusion on places and regions PO 3 Analyze the causes and effects of settlement patterns Grade Six Strand Five: Economics Concept 1: Foundations of Economics PO2 Determine how scarcity, opportunity costs, and trade-offs influence decision-making Grade Seven Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Seven Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 1 Discuss the implications of the demographic structure of places and regions PO 2 Identify the push and pull factors that cause human migrations (e.g., need for raw materials, African-American enslavement, employment opportunities, impact of war, religious freedom, political freedom). PO 3 Identify the effects of human migration (e.g., imperialism, quota system, changing of political boundaries, multiculturalism). PO 4 Analyze why people choose to live where they do (e.g., natural resources, farmland, water, mild climate, family, employment). Grade Seven Strand Five: Economics Concept 1: Foundations of Economics PO2 Analyze how scarcity, opportunity costs, and trade-offs influence decision-making Grade Eight Strand One: American History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Eight Strand Two: World History Concept 1: Research Skills for History PO 7 Analyze cause and effect relationships between and among individuals and events Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 4: Human Systems PO 1 Identify the push and pull factors that drive human migrations (e.g., wars, economic conditions, human rights conditions, famines, political strife/wars, natural disasters, changes in technology). PO 2 Describe the effects of human migrations on places and regions (e.g., economic, environmental, cultural, political). Grade Eight Strand Five: Economics Concept 1: Foundations of Economics PO2 Analyze how scarcity, opportunity costs, and trade-offs influence decision-making What A Map Grade Six Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 2 Identify purposes and differences of maps, globes, aerial photographs, charts, and satellite images. PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions. Grade Seven Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 2 Identify purposes and differences of maps, globes, aerial photographs, charts, and satellite images. PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions. Grade Eight Strand Four: Geography Concept 1: The World in Spatial Terms PO 2 Identify purposes and differences of maps, globes, aerial photographs, charts, and satellite images. PO 3 Interpret maps, charts, and geographic databases using geographic information PO 5 Interpret thematic maps, graphs, charts, and databases depicting various aspects of the United States and world regions.