* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.1 Proving Patterns with Lines and Angles
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
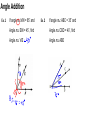
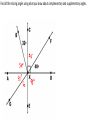
5.1 Proving Patterns with Lines and Angles Angles A shape, formed by two lines or rays splitting from a common point (the vertex). Angle Addition Ex. 1 If angle m∠VIN = 85˚ and Ex. 2 If angle m∠ ABC = 35˚ and Angle m∠ EIN = 45˚, find Angle m∠ CBD = 40˚, find Angle m∠ VIE Angle m∠ ABD Angle Bisector A line or ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles 27. Vertical Angles Two angles whose sides form opposite rays. Vertical Angles have the same measurement and are congruent. Linear Pair 28. angles that form a straight line. Two adjacent Linear Pairs always add to be 180° Find all the missing angles using what you know about complementary and supplementary angles. Find the value of the variable and YZ if Y is between X and Z. XY = 7a, YZ = 5a, XZ = 6a + 24