* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.7 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
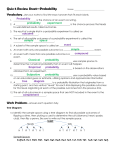
8.7 – Probability Probability Probability = the likelihood that an event will occur Outcomes = possible results of an event Probability formula: P(event) = # favorable outcomes # possible outcomes All probabilities range from zero (impossible) to one (guaranteed). Ex: Find the probability of rolling 2 dice and receiving a total of 5. There are a total of 6 outcomes on each die, so the total amount of outcomes for 2 dice is 6•6= 36 It may help to write outcomes in a sample space… S (1,1), (1, 2), (1,3), (1, 4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,1)...(6,6) Of those outcomes, how many add to 5? (1, 4), (2, 3), (3, 2), (4, 1) So the probability is 4/36, which reduces to 1/9 Ex: In the Illinois Lotto, you pick 6 numbers from 1 to 52. To win, you must have all 6 numbers in any order. What is the probability of winning the jackpot? Since the order of the 6 numbers doesn’t matter, the number of favorable outcomes (amount of winning combos)is 1. For the total outcomes is a combination, 6 numbers out of 52 are picked, and order doesn’t matter: 52 So the final answer is 20,358,520 1 20358520 6 Find the probability that the sum of 2 rolled dice is 8. 1. 1/36 2. 1/9 3. ½ 4. 5/36 5. 2/9 Find the probability that the sum of 3 rolled dice is 17. 1. 1/72 2. 1/216 3. 17/216 4. 5/216 5. 1/108 In a bag of 3 green marbles, 2 blue marbles, and 5 red marbles, what is the prob. of picking a green or a blue marble? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1/2 3/50 1/15 3/10 1/3 In a bag of 3 green marbles, 2 blue marbles, and 5 red marbles, what is the prob. of picking a green or a blue, then a red, without replacement? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1/3 1/24 3/100 1/4 5/18 If A and B are events in the same sample space, then the probability of A or B occurring is given by: P( A B) P( A) P( B) P( A B) P(A U B) is the probability of A or B occurring and is called A “union” B P( A B) is the probability of A and B occurring simultaneously and is called A “intersection” B Ex: One card is selected randomly from a standard 52-card deck. What is the probability that it is a heart or a jack? There are 13 hearts in a deck and 4 jacks, and 1 jack of hearts P ( h J ) P (h) P ( J ) P ( h J ) 13 4 1 16 4 52 52 52 52 13 If A represents the desirable outcomes in a sample space, its complement, or A’, represents the undesirable outcomes in the sample space. P(A’) = 1 – P(A) Ex: The probability of Mr. Werner touching the net of a basketball hoop is 4%. What is the probability that he doesn’t touch the net? 100% - 4% = 96% Find the probability of drawing a 10 or a 6 from a standard deck. 0% 0% 0% 0% 15 /5 2 0% 04 /1 3 5. 07 /5 2 4. 02 /1 3 3. 0. .. 2. 1/169 2/13 7/52 4/13 15/52 0 1. Find the probability of drawing a diamond or a non-ace from a standard deck. 0% 0% 0% 0% 1/ 4 0% 0. .. 5. 1 4. 10 /1 3 3. 04 /1 3 2. 49/52 4/13 10/13 15/13 1/4 49 /5 2 1.