* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CVP Measurement - Wellington ICU
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
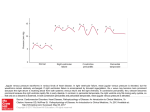
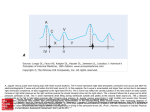
CVP Measurement 25/11/10 - pressure in the central veins (IJ, SC or Femoral) typically referred to as the blood pressure at junction of vena cavae & RA normal 0-6mmHg recorded at the end of expiration measured by transducing the waveform of a central venous line represents the driving force for filling the right atrium & ventricle. electronic transducer placed & zeroed at the level of the RA. measurement may reflect vascular compliance and changes in volume status a = atrial contraction c = closing and bulging of the tricuspid valve x = atrial relaxation v = passive filling of atrium y = opening of the tricuspid valve DETERMINANTS OF CVP CVP = MSFP – RAP/Resistance to venous return - intravascular fluid volume right and left ventricular function pulmonary vascular resistance venous capacitance intrathoracic/pleural pressure ventricular compliance and arterial pressure right atrial pressure mean systemic filling pressure HELPFUL IN DIAGNOSIS OF: - right ventricular infarction - PE - ARDS Jeremy Fernando (2010) - cor pulmonale - tamponade CVP WAVEFORM ANALYSIS Dominant a wave – PHT, TS, PS Canon a wave – complete heart block, VT with AV dissociation Dominant v wave – TR Absent x descent – AF Exaggerated x descent – pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis Sharp y descent – severe TR, constrictive pericarditis Slow y descent – TR, atrial myxoma Prominent x and y descent – RV infarction FACTORS DETERMINING ACCURACY (1) Placement of device tip (RA, RV, femoral vein) (2) Levelling – the position on the patient that you want to be zero (usually level of RA) (3) Zeroing – zero means atmospheric pressure (4) Calibration – comparing zero and a level above to a gold standard (mercury sphygmomanometer) (5) Damping – assess by a fast flush test, preferred co-efficient around 0.7) (6) Frequency response of the system (intrinsic + additional tubing) -> may significantly alter damping (preferred shorter stiffer tubing) (7) Running averages rather than single spontaneous readings Jeremy Fernando (2010)