* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Manufacturing of electrical machines – 1. Lecture
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
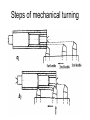
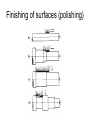
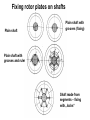
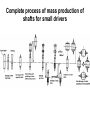
Shafts for rotating machines Sorting of rotating el. machines • According power • Ac. principle – Small < 10 kW – middle-class up to 1 MW – big (not correctly specified) – – – – DC asynchronous synchronous Alternative, ECM etc. • Ac. application - traction, - crane, slow/fast rotating - compressors, - explosion-proof, etc.) Sorting of non-rotating machines (especially chokes, transformers, elmag. chucks) • Ac. power and • Ac. design, assembly • Acc. application voltage – power plants – air (transformers) – low-power, up to – traction – oil based 10 kW – ovens/furnaces – special (auto– middleclass, up to transformers, – electrochemical 1 MW regulating tr., etc.) – Etc. – big Modern trend – increase of operating temperature (class „F“) very popular (190°C) Characterization of production flow Piece production – product = big machines or technology element – layout designed according technological requirements – special production machines and templates are used – exacting preparation of production and high requirements on the staff – qualifications! Mass-production – product = small machines – layout according production flow! – Often single-usage technology equipment (machines) – just for one operation – using of „lines“ layout – more automation – lower requirements of staff qualification Manufacturing of shaft Issue: strength, precision of mechanical turning, dimensions acc. standards Initial material: • rolled- steel rod up to 150 mm • steel rod calibrated up to 70 mm (for mass-production) • forged ingot, heated and hammered Note: Quality of material is checked, some off-takes are done and analyzed Hammered shaft – production procedure • casting (founding) – ingots with double mass • hammering – at circa 700 °C • pre-heating (possible) • annealing - 700 - 800 °C (also „tempering), changing of hardness and mechanical properties • axis hole – off-taking of samples, analysis, also space for winding or cooling Tests of mechanical parameters.: visual, DC current, ultrasonic, etc. Mechanical turning of shafts • • • • Rolling – between two rollers, presses Splitting – scissors, sawmill, flame-cutting Clamping – centering by axis-hole Mechanical turning: – Rough turning (big tolerance) – Finishing of surface (précising) – pads for bearings Issues: using of more tools, troubles with clamping and accuracy. Today popular clamping with magnetic chucks or induction heating. Cutting of grooves – sometimes by turning, more often by milltool. Steps of mechanical turning Finishing of surfaces (polishing) Sorting of shafts • smooth (plain) shafts – small machines • graded shafts (terrace) profile • shaft with flange – just for rolling-bench • special design – shaft made from segments • special surface – grooving – for small machines Fixing rotor plates on shafts Plain shaft Plain shaft with grooves (fixing) Plain shaft with grooves and ruler Shaft made from segments – fixing with „locks“ Complete process of mass production of shafts for small drivers Balancing of shaft • vertical rotors – hydro („lens“ or lentils design) • horizontal rotors – AC generators, synchronous rotors (rulers design) • principle: – static balancing – dynamic balancing • typical dimensions of rotors: – hydro generator: up to 6 meters height, diameter 6-10 meters, – synchronous generators: 10-12 meters length, diameter up to 1 meter (limited with the solidity of used steel). Note: some parts of the rotors have nearly the supersonic velocity!