* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monopolistic Competition
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
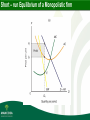
Price Discrimination Price Discrimination: This occurs when firms sell the same product to different consumers at different prices. Price discrimination only occurs when price differences are based on different buyers’ valuations of the same product. If price differences are based on cost differences they are not discriminatory. Two conditions for Price Discrimination : • The firm must be a price maker or price setter. • Consumers or markets must be independent. Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition combines certain features of monopoly and perfect competition. Firms are said to be “competing monopolists”. In a monopolistically competitive market a large number of firms produce similar but slightly different products. Features of Monopolistic Competition • Each firm produces a distinctive, differentiated product. • Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its particular product. • There are a large number of firms in the industry. • There are no barriers to entry or exit. A monopolistically competitive firm has a certain degree of monopoly power, as it is the only producer of the particular brand or variety of the product. Under monopolistic competition, each firm is thus in effect a mini-monopoly. Monopolistic Competition Each monopolistically competitive firm has a certain degree of monopoly power, as it is the only producer of the particular brand or variety of the product. The main difference between monopolistic competition and monopoly lies in the barriers to entry. On the other hand, the essential difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition is found in the nature of the product. Short – run Equilibrium of a Monopolistic firm Short-run equilibrium of a monopolistic competitor is the same as that of a monopolist, except that the demand curve for the product of the monopolistic competitor is significantly more price elastic than that of the monopolist. In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms earn normal profits only, just like the perfectly competitive firm. Short – run Equilibrium of a Monopolistic firm Oligopoly The word oligopoly comes from the Greek words oligoi, meaning “few”, and polein, meaning “sell”. Under oligopoly a few large firms dominate the market. The product may be homogeneous (e.g. steel, cement), but it is mostly heterogeneous (e.g. motorcars, cigarettes, household appliances) The main feature of oligopoly is the high degree of interdependence between the firms. Interdependence refers to the degree to which the actions of one firm affect (or are determined by) the actions of other firms. Oligopoly-Kinked Demand Curve Implications of the kinked demand curve There is unlikely to be permanent price competition under oligopoly; Firms will compete through non-price methods such as advertising, promotions and product development; and Firms may engage in collusive agreements and form cartels The shortcomings of the kinked demand curve model are as follows: The theory is difficult to test effectively because it does not actually explain how the price is initially determined; The model takes no account of non-price competition which is an important feature of the market; and There are other reasons for infrequency of price adjustments such as their cost, lost customer goodwill which may be as equally important as the more specific market pressures. QUIZ A monopoly market has which of the following characteristics? A Firms are price makers B There are a large number of small firms C Quantity and price are set at their socially optimal levels D There are few or no barriers to entry QUIZ Which of the following is a characteristic of monopolistic competition? A All of these answers B There exists a perception of non-price differences between products C Few barriers to entry and exit D Producers have some degree of control over price MARKET STRUCTURES - SUMMARISED