* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 9 Study Guide Unit 8 Unit 8 - Circle Geometry Pythagorean
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
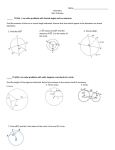
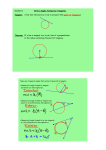
Math 9 Study Guide Unit 8 Unit 8 - Circle Geometry Pythagorean Theorem a2 + b2 = c2 (where c is always the hypotenuse) Properties of Tangents to a Circle A line that intersects a circle at only one point is a TANGENT to the circle. The point where the tangent intersects the circle is the POINT OF TANGENCY. Line AB is a tangent to the circle with centre O. Point P is the point of tangency. Properties of Chords in a Circle Chord: a line segment that joins 2 points inside a circle Diameter: a chord through the centre of a circle Math 9 Study Guide Unit 8 Properties of Angles in a Circle Arc: section of the circumference of a circle Minor Arc: shorter section Major Arc: longer section Central Angle: angle formed by joining endpoints of an arc to the center of a circle. The sum of all the central angles in a circle is 3600 Inscribed Angle: angle(s) formed by joining the endpoints of an arc to any point on the circle. The inscribed and central angles in this circle are subtended by the same minor arc. In the circle below the inscribed angle (ACB) and central angle (AOB) are subtended by the minor arc AB.