* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lorem Ipsum - jan.ucc.nau.edu
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
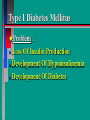
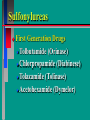
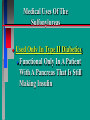
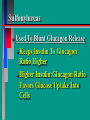
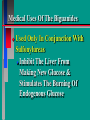
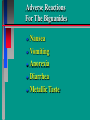
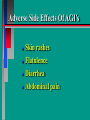
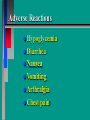
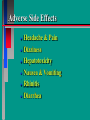
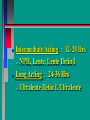
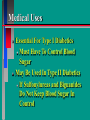
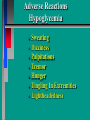
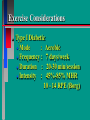
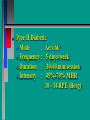
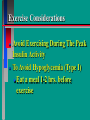
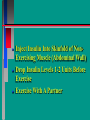
Glucoregulatory Drugs Ways To Control Blood Glucose In Diabetic Patients Classification Of Diabetic Patients Type I Diabetic Patient Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Juvenile Onset Diabetes Type I Diabetes Mellitus Problem : Loss Of Insulin Production Development Of Hypoinsulinemia Development Of Diabetes Type II Diabetic Patient Adult-Onset Diabetes Mellitus Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Problem : No Functional Loss Of The Beta Cell Population Blood Insulin Levels May Be Below Normal, Normal, or Higher Than Normal Exhibit Peripheral Tissue Resistance To Insulin Obesity Drug Choices For The Diabetic Patient Oral Hypoglycemic Agents The Sulfonylureas The Biguanides Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors Others Insulin Porcine Insulin Bovine Insulin Humulin The Sulfonylureas Increase The Availability Of Insulin In Type II Diabetics Sulfonylureas First Generation Drugs Tolbutamide (Orinase) Chlorpropamide (Diabinese) Tolazamide (Tolinase) Acetohexamide (Dymelor) Second Generation Drugs Glipizide (Glucotrol) Glyburide (Micronase, Diabeta) Glimepiride (Amaryl) Sulfonylureas Mechanism Of Action Stimulate Release Of Insulin From Pancreatic Islet Cells In Type II NIDDM Patients Blunt The Release Of Glucagon Increase The Sensitivity of Peripheral Tissues To Insulin Up-Regulation Of Insulin Receptors Improve The Binding Of Insulin To Its Recptor Medical Uses Of The Sulfonylureas Used Only In Type II Diabetics Functional Only In A Patient With A Pancreas That Is Still Making Insulin Sulfonylureas Used To Blunt Glucagon Release Keeps Insulin To Glucagon Ratio Higher Higher Insulin:Glucagon Ratio Favors Glucose Uptake Into Cells The Overall Effect : Blood Glucose Regulation Euglycemia Adverse Side Effects For The Sulfonylureas Hypoglycemia Skin Rashes Nausea Vomiting The Biguanides Metformin (Glucophage) Buformin Biguanides Mechanism Of Action Create An Environment Conducive to Keeping Blood Sugar Low Suppress Gluconeogenesis In The Liver Inhibit The Absorption Of Glucose In The Intestine Stimulate Glycolysis Probably Up-Regulates Insulin Receptors For Improved Clearance of Glucose Medical Uses Of The Biguanides Used Only In Conjunction With Sulfonylureas Inhibit The Liver From Making New Glucose & Stimulates The Burning Of Endogenous Glucose Help To Deplete Blood Levels Of Glucose By Reducing Uptake Of Dietary Glucose The Overall Effect : Blood Glucose Regulation Euglycemia Adverse Reactions For The Biguanides Nausea Vomiting Anorexia Diarrhea Metallic Taste Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors Miglitol ( Glyset) Acarbose (Precose) Mechanism Of Action For AGI’s Delay The Digestion Of Ingested Carbohydrates Results In A Lower Postprandial Blood Glucose The Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors do not increase insulin receptor sensitivity and do not increase blood insulin levels in Type II diabetics. Medical Uses Of AGI’s The Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors are used alone or in combination with Sulfonylureas to improve blood glucose control. The net effect is euglycemia. Adverse Side Effects Of AGI’s Skin rashes Flatulence Diarrhea Abdominal pain Others Repaglinide (Prandin) Troglitazone (Rezulin) Repaglinide Mechanism of Action Stimulates release of insulin Regulates calcium channel function in the beta cell Adverse Reactions Hypoglycemia Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Arthralgia Chest pain Medical Uses Used to regulate blood glucose levels Can be used in combination with Metformin (Glucophage) Troglitazone Troglitazone is a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent. Mechanism Of Action Improves target cell responsiveness to insulin without increasing insulin secretion reduces peripheral resistance. Decreases liver glucose output Helps to increase skeletal muscle, liver and adipose tissue uptake of glucose Adverse Side Effects Headache & Pain Dizziness Hepatotoxicity Nausea & Vomiting Rhinitis Diarrhea Medical Uses Used to regulate blood glucose levels - euglycemia The Insulins To Encourage Glucose Transport Into The Cell To Reduce The Possibility Of Hyperglycemia Porcine, Bovine, Humulin Short Acting : 2-4 Hrs Regular, Semilente, Regular Iletin Intermediate Acting : 12-20 Hrs NPH, Lente, Lente Iletin I Long Acting : 24-36 Hrs Ultralente Iletin I, Ultralente Mechanism Of Action Binding Of Insulin To Cell Receptors Causes : Glucose Transporters To Be Made In Greater Numbers - Up Regulation Glucose Transporters Migrate To The Cell Membrane And Bring Glucose Into The Cell Medical Uses Essential For Type I Diabetics Must Have To Control Blood Sugar May Be Used In Type II Diabetics If Sulfonylureas and Biguanides Do Not Keep Blood Sugar In Control Adverse Reactions Hypoglycemia Sweating Dizziness Palpitations Tremor Hunger Tingling In Extremities Lightheadedness Headaches Anxiety Drowsiness Slurred Speech Irritability Unsteady Movement Seizures Lipodystrophy Allergic Reactions Shortness of Breath Skin Rashes At Site of Injection Whole Body Rashes Sweating Tachycardia Wheezing Clinical Considerations Be Familiar With The Signs Of Hypoglycemia Make Sure The Patient Has Not Skipped Meals Know The Patient's Medications Make Sure The Patient Is Hydrated Advise The Patient To Wear Medical ID Tags Teach The Patient To Monitor Their Blood Sugar - Glucometer Exercise Considerations Type I Diabetic Mode : Aerobic Frequency : 7 days/week Duration : 20-30 min/session Intensity : 45%-85% MHR 10 - 14 RPE (Borg) Type II Diabetic Mode : Aerobic Frequency : 5 days/week Duration : 30-60 min/session Intensity : 45%-70% MHR 10 - 14 RPE (Borg) Blood Glucose < 6 mmol/L ( <108 mg/dl) = Eat CHO 6-16 mmol/L (108-288 mg/dl) = Ex. > 16 mmol/L (>288 mg/dl) = See MD Exercise Considerations Avoid Exercising During The Peak Insulin Activity To Avoid Hypoglycemia (Type I) Eat a meal 1-2 hrs. before exercise Eat extra CHO during exercise if longer than 30 minutes Measure blood glucose before, during and after exercise Inject Insulin Into Skinfold of NonExercising Muscle (Abdominal Wall) Drop Insulin Levels 1-2 Units Before Exercise Exercise With A Partner Carry Money While Exercising Wear Good Foot Wear Practice Scrupulous Foot Care Inspect Calluses Look For Red Pressure Areas Look For Blisters & Ulcerations