* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
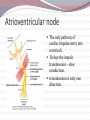
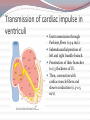
Specialized excitatory and conductive system of the heart Automatic electrical rhythmicity of sinus fibers Mechanism of sinus nodal rhythmicity iK: delayed rectifier current slow voltage-gated K+ channels (activated by depolarization) if: funny current Voltage-gated Na+ channels activated at hyperpolarization beyond -50 mV iCa2+: L-type Ca2+ channel activated at Em higher than 55 mV Transmission of cardiac impulse through atria and internodal pathways Ends of SA nodal fibers connect (gap junctions) direclty with: 1. Surrounding atrial muscle fibers (0.3 m/s) 2. Conduction fibers (1 m/s): Anterior interatrial band Anterior, lateral and posterior internodal pathways Atrioventricular node The only pathway of cardiac impulse entry into ventriculi. Delays the impuls transmission – slow conduction. transmission in only one direction. Transmission of cardiac impulse in ventriculi Fast transmission through Purkinje fibers (1.5-4 m/s). Subendocardial position of left and right bundle branch. Penetration of their branches to 1/3 thickness of LV. Then, connection with cardiac muscle fibers and slower conduction (0.3-0.5 m/s). Sinus node- cardiac pacemaker Discharge rates: SA node: 70-80 /min AV node: 40-60 /min Purkinje fibers: 15-40 /min Abnormal “ectopic” pacemakers increased discharge rate most often in AV-node and Purkinje fibers. Or, blockage in A-V transmission. Stokes-Adams syndrome sudden A-V bundle block synkope Control of heart rhythmicity and impulse conduction Regulation by autonomic nervous system: Parasympathetic innervation Sinus node, AV-node, lesser atria, ventriculi no supresseion of sinus node rhythmicity slows down conduction through AV-node (can cause complete AV-block – ventricular escape) mechanism: hyperpolarization (-65 to-75 mV) Sympathetic innervation whole heart (conduction and contractile fibers) β1-receptors: increase permeability to Ca2+ and Na+ Modulation of pacemaker rhythmicity