* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Investigation of the Surgical patient
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
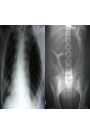
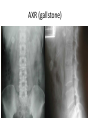
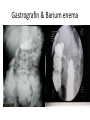
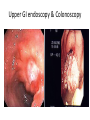
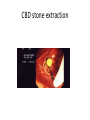
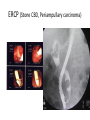
Investigation of the Surgical patient M K ALAM MS;FRCS Objectives At the end of this presentation students will be able to: Identify the need for establishing diagnosis. Describe the whole spectrum of available investigations. Choose relevant investigations and justify their use. Understand the side effects and complications of some investigation. Identify need for assessing physiological status. Understand the need for screening common asymptomatic disorders. Diagnosis • History • Clinical examination • Investigations: -Support clinical suspicion -Refute clinical suspicion -Risk to patient -Cost Other aims of investigation • Assess physiological impairment for risk to surgical treatment. Example: Cardiac, renal respiratory diseases • Screen for common asymptomatic disorders. Example: Diabetes, coronary artery disorders, hypertension Hematological investigations • FBC or CBC: Anemia (low Hb.), MCV, MCHC (normocytic, microcytic), leukocytosis (infection) • Platelet count: Thrombocytopenia ( drug- heparin, ITP, autoimmune), Thrombocytosis ( post-splenectomy) • Coagulation profile: PT, INR, APTT (disordered in patients of jaundice, bleeding, anticoagulant, antiplatelet medications) Biochemical tests • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Na: 135-146 mmol/L ( water overload, NG asp., sepsis, vomiting) K: 3.5- 5.5 mmol/L (changes- vulnerable to arrhythmias) Urea: 2.6- 6.7 mmol/L ( dehydration, renal insufficiency) Creatinine: 60-120 mmol/L (marker of renal disease) Glucose: 3.9-5.6 mmol/L ( diabetes) Total protein: 62-80 G/L Albumin: 35-50G/L (nutritional assessment) Bilirubin <17 mmol/L (jaundice) ALP: 25-120 U/L AST: 10-40 U/L ALT: 5-30U/L LDH: 49-195U/L Creatinine phosphokinase: 24-195 U/L Amylase <100 u/L Microbiological investigations • Urine (UTI), sputum, stool • Hepatitis screening (B, C) • Antibiotic sensitivity Tumour markers • • • • • • PSA- Prostate CEA- Colorectal α- fetoprotein (AFP)- Hepatocellular β-hCG- Testicular, gestational CA 19-9- Colorectal, pancreas CA 125 - Ovarian Imaging studies • Plain x-ray- CXR, AXR, tomograms Side effects: Induction of malignancy, genetic mutation. AXR (gallstone) Imaging studies • Contrast studies- gastrografin swallow, barium meal, barium enema. • Visualize GI tract • Single contrast, double contrast • Inferior to endoscopy • Contraindicated if bowel perforation suspected Gastrografin & Barium enema Imaging studies • CT scan (oral, iv contrast): Widely used for abdomen, chest , brain, vascular and urinary tract. (anaphylactic reaction, renal injury, radiation) • Ultrasound: Safe, low cost. Operator dependent. Investigation of first choice for biliary disease and gynaecology. • MRI: Good images of soft tissue (better than CT), blood vessel (MRI angiogram). No radiation, no known deleterious effect. Slow and expensive. • Isotope scan: More information about function than structure. I131,Tc99, I123, Ga67, Th201- incorporated into other molecule to localize target organ. Detected by gamma camera. Bone metastasis, renal function, foci of infection, GI bleeding, infarction of myocardium, sentinel node detection • PET scan: Expensive. Brain physiology, tumour detection , cardiac physiology. Intestinal ischemia Intussusception Lower GI bleeding Scan Meckel's scan Endoscopy • Precise diagnosis of GI, pancreatico-biliary, bronchus, urinary tract pathology. • Perform cytology/ biopsy. • Minimally invasive therapy- laparoscopy, arthroscopy, ERCP. • Disadvantages: Unpleasant, uncomfortable (sedation/ anesthesia) • Complications: Infection, perforation, aspiration, bleeding, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory arrest Upper GI endoscopy & Colonoscopy CBD stone extraction ERCP (Stone CBD, Periampullary carcinoma) Tissue sampling • Body fluids- pleura, peritoneum, sputum , urine. • Smears, brush cytology • FNAC ( insitu vs invasive, follicular adenoma vs carcinoma) • Core biopsy • Open biopsy • Frozen section biopsy: (biopsy frozen in liquid nitrogen, sliced, stained and reported in minutes) Function tests • Cardiac evaluation: ECG, Thallium scan, echocardiography • Respiratory function: ABG ( risk pCO2 > 45 mmHg) FVC & FEV1 ( risk- < 70% of predicted) • Renal function • Endocrine function Screening • Screening for malignant disease.(FOB, mammography, PSA) • Screening for surgical disease ( abdominal aortic aneurysm) Thank you!

























![NEC-255 PYRUVIC ACID, SODIUM SALT, [1- C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016736441_1-fc3f1c8fad455fdc5c1e9e44060828a8-150x150.png)
