* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
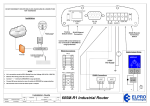
CSE401n:Computer Networks Lecture 16 Wireless Link & LANs WS: ch-14 KR: 5.7 1 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs 802.11b operate at 2.4 GHz, 11 Mbps widely deployed 802.11a 5-6 GHz range up to 54 Mbps 802.11g 2.4 GHz up to 54 Mbps All have base-station and ad-hoc network versions All use CSMA/CA for multiple access 2 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN IEEE 802.11 standard: unlicensed frequency spectrum: 900Mhz, 2.4Ghz, 5.1Ghz, 5.7Ghz and 802.11b 802.11a 3 Frequency Band 4 5 IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Basic Service Set (BSS) (a.k.a. “cell”) contains: wireless station (WS) access point (AP): base station BSS’s combined to form distribution system (DS) Two operation modes: Infrastructure mode • everything through AP Peer-to-peer mode • called ad hoc network 6 IEEE 802.11 Architecture Distribution system (DS) Access point (AP) Basic service set (BSS) Stations competing for access to shared wireless medium Isolated or connected to backbone DS through AP Extended service set (ESS) Two or more basic service sets interconnected by DS 7 Ad Hoc Network approach No AP No connection to the outside world Wireless hosts communicate with each other Applications: “laptop” meeting in conference room, car 8 Distribution of Messages Within a DS Distribution service Used to exchange MAC frames from station in one BSS to station in another BSS Integration service Transfer of data between station on IEEE 802.11 LAN and station on integrated IEEE 802.x LAN 9 Transition Types Based On Mobility No transition Stationary or moves only within BSS BSS transition Station moving from one BSS to another BSS in same ESS ESS transition Station moving from BSS in one ESS to BSS within another ESS 10 Association-Related Services Association Establishes initial association between station and AP Reassociation Enables transfer of association from one AP to another, allowing station to move from one BSS to another Disassociation Association termination notice from station or AP 11 Access and Privacy Services Authentication Establishes identity of stations to each other Deathentication Invoked when existing authentication is terminated Privacy Prevents message contents from being read by unintended recipient 12 802.11 – Traffic and Access Methods Two types of traffic services Asynchronous Data Service (mandatory) • exchange of data packets based on “best-effort” Time-Bounded Service (optional) Two types of coordination function DCF (Distributed Coordination Function) PCF (Point Coordination Function) Access methods (why not CSMA/CD?) DCF-CSMA/CA (collision avoidance) • collision avoidance via randomized back-off mechanism (if sense busy, random backoff even if no collision) • ACK packet for acknowledgements (not for broadcasts) DCF-RTS/CTS • avoids hidden terminal problem PCF • access point polls 7.12.1 13 IEEE 802.11 Medium Access Control MAC layer covers three functional areas: Reliable data delivery Access control Security 14 Reliable Data Delivery More efficient to deal with errors at the MAC level than higher layer (such as TCP) Frame exchange protocol Source station transmits data Destination responds with acknowledgment (ACK) If source doesn’t receive ACK, it retransmits frame Four frame exchange Source issues request to send (RTS) Destination responds with clear to send (CTS) Source transmits data Destination responds with ACK 15 The Hidden Terminal Problem A B C A is sending to B, but C cannot receive from A Friis Law (power decay proportional to distance square) Therefore C sends to B, without detecting the transmission from A to B In summary, A is “hidden” for C Implication: How to do carrier sense and collision detection? 16 The Exposed Terminal Problem A B C D B is sending to A, C intends to send to D C senses an “in-use” medium, thus C waits But A is outside the radio range of C, therefore waiting is not necessary In summary, C is “exposed” to B Implication: false carrier sense 17 Basic Solution: RTS-CTS Short signaling packets RTS (request to send) and CTS (clear to send) Contain sender address, receiver address, transmission duration Example: solve the hidden terminal problem A RTS CTS B CTS C D 18 Access Control 19 Medium Access Control Logic 20 Interframe Space (IFS) Values Short IFS (SIFS) Shortest IFS Used for immediate response actions Point coordination function IFS (PIFS) Midlength IFS Used by centralized controller in PCF scheme when using polls Distributed coordination function IFS (DIFS) Longest IFS Used as minimum delay of asynchronous frames contending for access 21 IFS Usage SIFS Acknowledgment (ACK) Clear to send (CTS) Poll response PIFS Used by centralized controller in issuing polls Takes precedence over normal contention traffic DIFS Used for all ordinary asynchronous traffic 22 802.11 – Inter Frame Spacing Defined different inter frame spacing SIFS (Short Inter Frame Spacing) highest priority, for ACK, CTS, polling response PIFS (PCF IFS) medium priority, for time-bounded service using PCF DIFS (DCF, Distributed Coordination Function IFS) lowest priority, for asynchronous data service DIFS DIFS medium busy PIFS SIFS contention next frame t direct access if medium is free DIFS 23 802.11 – RTS/CTS + ACK Sender sends RTS with NAV (Network allocation Vector, i.e. reservation parameter that determines amount of time the data packet needs the medium) after waiting for DIFS Receiver acknowledges via CTS after SIFS (if ready to receive) CTS reserves channel for sender, notifying possibly hidden stations Sender can now send data at once, acknowledgement via ACK Other stations store NAV distributed via RTS and CTS DIFS sender data RTS SIFS receiver other stations CTS SIFS SIFS NAV (RTS) NAV (CTS) defer access ACK DIFS new contention data t 24 802.11 Collision Avoidance: RTS-CTS + ACK DIFS: Distributed Inter-Frame Spacing SIFS: Short Inter-Frame Spacing 25 802.11: PCF for Polling PIFS point coordinator D D SIFS U polled wireless stations NAV SIFS NAV medium busy contention free period contention period t D: downstream poll, or data from point coordinator U: data from polled wireless station 26 MAC Frame Format 27 MAC Frame Fields Frame Control – frame type, control information Duration/connection ID – channel allocation time Addresses – context dependant, types include source and destination Sequence control – numbering and reassembly Frame body – MSDU or fragment of MSDU Frame check sequence – 32-bit CRC 28 Frame Control Fields Protocol version – 802.11 version Type – control, management, or data Subtype – identifies function of frame To DS – 1 if destined for DS From DS – 1 if leaving DS More fragments – 1 if fragments follow Retry – 1 if retransmission of previous frame 29 Frame Control Fields Power management – 1 if transmitting station is in sleep mode More data – Indicates that station has more data to send WEP – 1 if wired equivalent protocol is implemented Order – 1 if any data frame is sent using the Strictly Ordered service 30 Control Frame Subtypes Power save – poll (PS-Poll) Request to send (RTS) Clear to send (CTS) Acknowledgment Contention-free (CF)-end CF-end + CF-ack 31 Data Frame Subtypes Data-carrying frames Data Data + CF-Ack Data + CF-Poll Data + CF-Ack + CF-Poll Other subtypes (don’t carry user data) Null Function CF-Ack CF-Poll CF-Ack + CF-Poll 32 Management Frame Subtypes Association request Association response Reassociation request Reassociation response Probe request Probe response Beacon 33 Management Frame Subtypes Announcement traffic indication message Dissociation Authentication Deauthentication 34 Wired Equivalent Privacy 35 Authentication Open system authentication Exchange of identities, no security benefits Shared Key authentication Shared Key assures authentication 36 IEEE 802.11 802.11a 802.11b 802.11 Standard approved Sep. 1999 Sep. 1999 July 1997 Available bandwidth 300 MHZ 83.5 MHZ 83.5 MHZ Unlicensed freq. 5.15-5.35G of operation 5.725-5.825G 2.4-2.4835G 2.4-2.4835G No. of nonoverlapping Ch. 4 3 3 Rate per channel 6,9,12,18,24,36, 48,54 Mbps 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps 1,2 Mbps Range 225 feet 225 feet ?? Modulation OFDM DSSS DSSS, FHSS DSSS: direct sequence spread spectrum FHSS: frequency hopping spread spectrum OFDM: orthogonal frequency division multiplexing 37