* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Animalia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
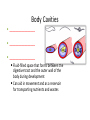
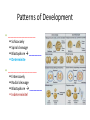
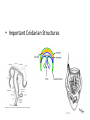
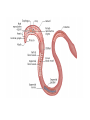
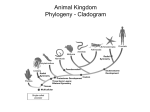
Kingdom Animalia Review of the Six Kingdoms • • • • • • Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia The Nature of Animals • • • • • • • • Multicellular Eukaryotic Lack Cell Walls Heterotrophic Sexual reproduction Movement (some) Specialization (some) Over 1.2 million species know and classified Origin and Classification • From the sea • Colonial Protists (Choanoflagellate) • Phylogeny based on morphology Body Structure Patterns of Symmetry ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Dorsal Ventral Anterior posterior Embryonic Germ Layers • Fundamental tissue types found in the embryo – ________________ • Skin & coverings, nervous system – ________________ • Circulation, muscle, internal organs (bone) – ________________ • Digestive tract or gut • _______________ = 2 germ layers • _______________ = 3 germ layers Body Cavities _________________ _________________ _________________ Fluid-filled space that forms between the digestive tract and the outer wall of the body during development Can aid in movement and as a reservoir for transporting nutrients and wastes Fertilization & Development • Gametes – Egg and sperm • Fertilization – ____________ – Mitosis – Cleavage • • • • _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ • Blastula formation & Stem Cells Patterns of Development ____________________ Schizocoely Spiral cleavage Blastophore _________ Determinite _____________________ Enterocoely Radial cleavage Blastophore _________ Indeterminite! The 9 Major Animal Kingdom Phyla • • • • • • Porifera Cnidaria Ctenophora Platyhelminthes Nematoda Rotifera • • • • • Annelida Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata Chordata Animal Phylogeny Tree Invertebrates • • • • Invertebrate Characteristics All forms of symmetry Segmentation - some Body support - exoskeleton Systems – Respiratory – simple diffusion to gills – Circulatory – open and closed – Digestive – cellular or gut – Excretory – simple diffusion to nephridia – Nervous – none to ___________________ – Reproduction – sexual, budding, and hermaphrodites – Endocrine – hormone regulation – Muscular – none to strong muscles Porifera Subkingdom – ______________ Aquatic sponge Sessile as adults 1 cm-2 m diameter Body Plan – no symmetry Choanocytes _____________________ osculum _____________________ Calcium carbonate Silica Filter feeding Amebocytes Regeneration, budding, hermaphrodites, larva and gemmules Cnidarians Subkingdom __________________ Hydra, jellyfish, coral and sea anemones Radial symmetry Tissues and simple organs Fresh and Ocean environments Medusa & Polyp forms Cnidocyte w/ nematocyst _______________________ Classes: Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa and Anthozoa • Important Cnidarian Structures Ctenophora • • • • • • • Marine Comb jelly Rows of beating cilia along outside Water beats to move _______________ for defense ____________________ Bioluminescence Platyhelminthes _________________________ Three germ layers Bilateral symmetry Acoelomate Cephalization Diffusion Classes Turbellaria Free living ___________________ _ Trematoda flukes Cestoda tapeworms Nematoda ___________________________ • Bilateral symmetry • Free living and parasitic • Pseudocoelomate • ______________ ______________ • Separate sexes • Cuticle • Examples: Ascaris, Hookworm, Trichinella and Pinworms Rotifera • • • • • Free living aquatic Transparent Pseudocoelomate Cilia round the mouth Mouth Anus Mollusca Coelomates Trochophore larva Visceral Mass Mantle cavity Head-foot __________________ Siphons Chromatophores Examples - Clam, snail, slug, octopus Annelida __________________________ Little rings Setae Coelomate Three Classes Oligochaeta earthworm Polychaeta Bristle worms Hirudinea leeches Earthworm Anatomy Arthropoda • • • • • • Bilateral Coelomates Jointed appendages Exoskeleton – chitin Compound eye _____________________ Subphyla – Trilobita – Crustacea – Chelicerata – Uriramia Echinodermata • • • • • • • • Marine Pentaradial symmetry No cephalization ______________________ Tube feet Deuterostome Cardiac and pyloric stomach Examples - Sea star, sand dollar, basket star Invertebrate Chordates Animals _________________________ Deuterostome Chordates must have the following Notochord Stiff, but flexible rod of cells that runs the length of the body near the dorsal ridge Dorsal nerve cord Pharyngeal pouches Post anal tail Examples – lancelet and tunicate