* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 25 Lesson 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
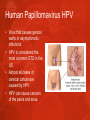
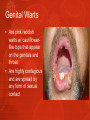
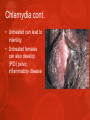
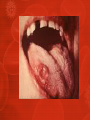
Ch. 25 Lesson 2 Common STIs STDs • The CDC reports that STDs account for more than 85% of the most common communicable diseases in the US • The primary means of transmission of STDs is sexual activity. • Teens who choose abstinence from sexual activity greatly reduce their risk of contracting STDs. Human Papillomavirus HPV • Virus that causes genital warts or asymptomatic infections • HPV is considered the most common STD in the US. • Almost all cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV • HPV can cause cancers of the penis and anus. Genital Warts • Are pink reddish warts w/ cauliflowerlike tops that appear on the genitals and throat • Are highly contagious and are spread by any form of sexual contact Chlamydia • Is a bacterial infection that affects the reproductive organs • 40% of cases are reported in teens 15 to 19 yrs old • It’s asymptomatic • Males may experience discharge from the penis and burning upon urination • Females may experience vaginal discharge, burning urination or abdominal pain Chlamydia cont. • Untreated can lead to infertility • Untreated females can also develop (PID) pelvic inflammatory disease Genital Herpes • Caused by the herpes simplex. There are two types… • Type 1 usually caused by cold sores • Type 2 caused by genital sores • Both can infect the mouth and genitals • About 20% of the total adolescent population is infected with the virus Genital Herpes continued • Most of those infected are asymptomatic and are not aware they have it. • Most have blister-like sores that occur periodically • Meds can relieve symptoms, but cannot cure • Can be fatal for infants who contract it from their mothers Gonorrhea • A bacterial STD that usually affects mucous membranes • The highest rates of gonorrhea are found in females from 15-19 yrs old and males from 20-24 yrs old. • Symptoms include a discharge from the penis/vagina and painful urination • Approximately 50% of females infected have no symptoms Gonorrhea continued • Can lead to infertility • Can spread to the bloodstream and cause permanent damage to the joints. • Females can pass the infection to their babies during childbirth and contract eye infections that cause blindness. Trichomoniasis • Caused by microscopic protozoan that results in infections of the vagina, uretha, and bladder. • About 5 million new cases every year • Usually no symptoms occur, however the disease may result in vaginitis-an inflammation of the vagina with discharge, odor, irritation, and itching Syphilis • An STD that attacks many parts of the body and is caused by a small bacterium called a spirochete. • The first sign of the infection is a painless reddish sore, called a chancre. • If not treated it spreads to other parts of the body. Syphilis continued • The disease can damage internal organs (heart, liver, nervous system, and kidneys) • If left untreated, the person is at risk of paralysis, convulsions, and heart disease. • An infant with syphilis may have a damaged nervous system and can die from the effects. Other Common STD’s • • • • • Chancroid (bacteria) Bacterial Vaginosis Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Pubic lice Seeking Treatment • Being embarrassed should not stop a person from seeking treatment from a private physician or health clinic • By law, information about these diseases is kept confidential • Only health care professionals can prescribe treatment and antibiotics • Ultimately it is the responsibility of any person infected with an STD to notify anyone they have had sexual contact with. Lesson 2 Review Questions 1. Which STDs might not present noticeable symptoms? 2. Analyze and explain the harmful effects of two common STDs on fetuses and infants. 3. Where can a person go for treatment of an STD? Review Questions continued… 4. Describe the symptoms of gonorrhea & genital herpes for males and females> 5. Public policies enable health officials to locate & contact sexual partners of people who have been diagnosed with an STD. How do these policies help with the prevention and treatment of STDs?