* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.6b student activity #1
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
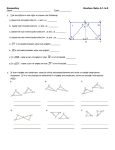
GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B INSTRUCTIONAL LESSON & ASSESSMENT For this TEKS students should be able to compare and classify shapes using geometric vocabulary and properties. Focus for this lesson is the use of properties to classify quadrilaterals. A review of properties and and classification of triangles is included in Instructional/Student Activity #2. BEFORE THE LESSON: 1. Make teacher transparencies. 2. Make one copy per student of page 3 – Quadrilaterals. 3. Make copies of Student Activity sheets, Open-Ended and Mini-Assessment. 4. Materials for Instructional/Student Activity #2: 1 set of Geometry Go Fishing Cards per group of 4 students (copy on cardstock, laminate, and cut apart), Student Activity #2, 1 Geometry Go-Fishing Properties Chart per group of 4 students (copy the Quadrilaterals chart on one side of cardstock and the Triangles chart of the other side of the cardstock, then laminate), 1 Number cube per group of 4 students MATH BACKGROUND Understanding how to classify quadrilaterals A polygon is a closed plane figure formed from line segments that meet only at their endpoints. A quadrilateral is a 4-sided polygon. The sum of the measures of the four angles of any quadrilateral is 360 . Students in Grade 7 should be familiar with the attributes and classification of the following quadrilaterals. Type Example Parallelogram Consecutive Angles Properties Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Rectangle Adjacent Sides Rhombus Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Square Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Trapezoid Exactly one pair of opposite sides is parallel. Exactly two pairs of consecutive angles are supplementary. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 1 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITY #1 QUADRILATERALS A quadrilateral is a polygon. A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by line segments that meet only at their endpoints. A quadrilateral has four sides which are line segments. Some quadrilaterals have special traits, so they have special names: trapezoid, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, and square. The sum of the measures of the four angles of any quadrilateral is 360. . TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 2 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. Students in Grade 7 should be familiar with the attributes and classification of the following quadrilaterals. Quadrilaterals Type Example Parallelogram Consecutive Angles Rectangle Adjacent Sides Properties Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Rhombus Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Square Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Exactly one pair of opposite sides is parallel. Exactly two pairs of consecutive angles are Trapezoid supplementary. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 3 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B STUDENT ACTIVITY #1 QUADRILATERALS A polygon is a ____________ ____________ figure formed from _________ _____________ that meet only at their ___________________. A quadrilateral is a ____-sided _________________. Parallelogram A parallelogram is a _______________________. In a parallelogram both pairs of __________________ sides are ________________. In a parallelogram both pairs of __________________ sides are ________________. In a parallelogram _____________________ angles are _______________________. In a parallelogram _______ angles are supplementary. Sketch two examples of parallelograms in the space below. Rectangle A rectangle is a _______________________. In a rectangle both pairs of __________________ sides are ________________. In a rectangle both pairs of __________________ sides are ________________. In a rectangle both pairs of __________________ sides are perpendicular. In a rectangle all ______________ angles are ______________________. Sketch two examples of rectangles in the space below. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 4 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. Rhombus A rhombus is a _______________________. In a rhombus both pairs of __________________ sides are ________________. In a rhombus _____________ sides are ________________. In a rhombus both ___________ of __________________angles are ___________________. In a rhombus _______________________ angles are __________________________. Sketch two examples of rhombuses in the space below. Square A square is a _______________________. In a square both pairs of __________________ sides are ________________. In a square ___________ sides are ________________. In a square all pairs of adjacent sides are ________________________. In a square all ___________ are __________ angles. Sketch two examples of squares in the space below. Trapezoid A trapezoid is a _______________________. In a trapezoid exactly _______ pair of _________________ sides is ________________. In a trapezoid exactly _______ pairs of ________________ angles are _____________________. Sketch two examples of trapezoids in the space below. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 5 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITY #2 MATERIALS: 1 set of Geometry Go Fishing Cards per group of 4 students (copy one side of each page on cardstock and copy Geometry Go-Fishing logo on the opposite side, laminate, and cut apart), Student Activity #2, 1 Geometry Go-Fishing Properties Chart per group of 4 students (copy the Quadrilaterals chart on one side of cardstock and the Triangles chart on the other side of the cardstock, then laminate), 1 Number cube per group of 4 students PROCEDURE: Organize students into groups of 4. Give each group of 4 one set of Geometry Go Fishing Cards, Properties Chart and number cube. Students place the set of cards facedown in a stack in the center of their work area. Students play Geometry Go Fishing as outlined in Student Activity #2. Ask the following questions after you have distributed the Geometry Go-Fishing Cards and the Properties chart and before students begin playing the game: What are some properties to look for in triangles and quadrilaterals? Listen for the following as you roam the room: Do students use correct geometric vocabulary to ask for cards during the game? Do students ask for correct properties or figures when they ask for cards? Do students recognize that specific properties may belong to more than one figure? Do students verbalize a variety of geometric terms? Do students analyze each shape with accurate vocabulary? Do students formulate good questions when asking for a card during the game? Look for the following as you roam the room: Do the students correctly match properties and figures? Do the students correctly name the figures? Do the students interact with group members to agree or disagree with card matches? Answers to these questions can be used to support decisions related to further whole class instruction or group and individual student instruction during tutorial settings. . TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 6 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. GEOMETRY GO-FISHING CARDS (Copy on cardstock, copy TEKSING TOWARD TAKS logo on back, laminate, and cut apart along the dashed lines. Make one set of cards per group of 4 students.) Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 7 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. All sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Exactly one pair of opposite sides is parallel. Exactly two pairs of consecutive angles are supplementary. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 8 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. No sides are congruent. No angles are congruent. At least 2 congruent sides. Exactly one angle is a right angle. Two angles, called the base angles are congruent. All three sides are congruent. All three angles are congruent. The acute angles are complementary. The side opposite the right angle, called the hypotenuse, is the longest side. All three angles are acute. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 9 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. Exactly one angle is an obtuse angle. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 10 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. The sum of the measures of the angles is 180 . o The sum of the measures of the angles is 180 . o The sum of the measures of the angles is 180 . o TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 The sum of the measures of the angles is 180 . o 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 11 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. Parallelogram Parallelogram Rectangle Rectangle Rhombus Rhombus Square Square Trapezoid Scalene Triangle TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 12 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. Isosceles Triangle Equilateral Triangle Right Triangle Acute Triangle Obtuse Triangle The sum of the measures of the angles is 360 . o The sum of the measures of the angles is 360 . o TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 The sum of the measures of the angles is 360 . o 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 13 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 T E K SING TO WA RD TA K S M a t h em a t ic s Geometry Go-Fishing TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 14 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. GEOMETRY GO-FISHING PROPERTIES CHART QUADRILATERALS Figure Example Parallelogram Consecutive Angles Properties Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. Both pairs of opposite sides are congruent. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Rectangle Adjacent Sides Rhombus Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Square Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. All sides are congruent. All pairs of adjacent sides are perpendicular. All angles are right angles. Trapezoid Exactly one pair of opposite sides is parallel. Exactly two pairs of consecutive angles are supplementary. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 15 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. GEOMETRY GO-FISHING PROPERTIES CHART TRIANGLES Type Example Properties No sides are congruent. No angles are congruent. Scalene triangle Congruent sides At least 2 congruent sides. Two angles, called the base angles are congruent. Isosceles triangle Congruent angles All three sides are congruent. All three angles are congruent. Equilateral triangle Right triangle Exactly one angle is a right angle. The acute angles are complementary. The side opposite the right angle, called the hypotenuse, is the longest side Acute triangle All three angles are acute. Exactly one angle is an obtuse angle. Obtuse triangle TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 16 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B STUDENT ACTIVITY #2 Geometry Go-Fishing MATERIALS: 1 set of Geometry Go Fishing Cards per group of 4 students Student Activity #2 1 Geometry Go-Fishing Properties Chart per group of 4 1 Number cube per group of 4 students GOAL: To make books of Geometry cards. Each book must have 4 cards: a figure card, a name card that matches the figure, and two property cards that match the figure. The winner of the game will be the player with the most books at the end of the game. BEGIN: Place the Geometry-Go-Fishing Property Chart in the center of the table. Shuffle the cards and deal 6 cards to each player. Place the remaining cards face down in the middle of the table (the TESKING TOWARD TAKS side up) for the DRAW PILE. Each player rolls the number cube. The player with the largest number is Player 1. If there is a tie for the largest number, roll again. Player 2 is to the left of Player 1. Player 3 is to the left of Player 2, and Player 4 is to the left of Player 3. RULES: Player 1 looks at his/her hand of cards and secretly identifies a card needed to complete a book. Player 1 asks any player for the card, saying, “Do you have the ______ card?” If the player has that card, the player says, “Yes, I do” and gives the card to Player 1. Player 1 continues asking for cards and collecting cards until another player answers, “No, I don’t, Geometry Go-Fishing.” Player 1 then draws a card from the top of the DRAW PILE. Player 2 now begins his/her turn and follows the same rules as Player 1. The game continues to the next player at the end of each player’s turn. If any player makes a book of 4 cards at any time, he says “Geometry Book” and lays the 4 cards out for the rest of the players to see. If all players agree the book is correct, the player places the four cards in a stack on the table in front of him. If the players agree the books is not correct, the player returns the cards to his hand. Players may use the Geometry Go-Fishing Properties Chart at any time during the game or to confirm a “Geometry Book” is correct. When the DRAW PILE is empty, play continues, but without the draw from the pile rule. The game ends when any player has 6 Geometry Books. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 17 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. o. 7.6B STUDENT ACTIVITY #3 Look at these plane figures. Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 Which figure appear does not appear to have both pairs of opposite sides parallel and all pairs of consecutive angles supplementary? Figure 1 appears to be a ____________________________. In a _________________________ both pairs of opposite sides are __________________, and all pairs of consecutive angles are ____________________________. Figure 2 appears to be a ____________________________. In a ____________________________both pairs of opposite sides are __________________, and all pairs of consecutive angles are ____________________________. Figure 3 appears to be a __________________. In a __________________both pairs of opposite sides are __________________, and all pairs of consecutive angles are ____________________________. Figure 4 appears to be a ____________________________. In a ____________________________only _______pair of opposite sides is parallel, and only two pairs of consecutive angles are ____________________________. Only the sides and angles in Figure _______ meet the requirements. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 18 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B OPEN ENDED #1 Classify the following quadrilaterals according to the given information. 7 140 40 1 7 40 2 7 3 140 7 150 30 30 4 5 150 1. What mathematical concepts and vocabulary do I need to know to be able to work this problem? 2. Will the Grade 7 Mathematics Formula Chart be helpful on this problem? Why or why not? 3. Arrowhead markings that are identical on the sides on a pair of sides of a polygon indicate the sides are parallel. Add any additional arrowhead markings that would be appropriate to the figures above. 4. What problem-solving strategy or strategies will I use to help solve this problem? 5. Extension (7.9A): If the perimeter of a rhombus is 48 units, find the length of a side of the rhombus. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 19 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 7.6B OPEN ENDED #1 Classify the following quadrilaterals according to given information. 7 40 140 1 7 2 7 140 40 7 3 30 150 4 30 TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 5 150 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 20 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. NAME___________________ DATE___________ SCORE ___/5 7.6B Mini Assessment 1. If AB is parallel to DC and AD is parallel to BC , which of the following best describes quadrilateral ABCD? A 4. B C D A Square B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Parallelogram 5. 2. Which of the following statements will be true for all trapezoids? A The figure must have two congruent sides. B The figure will have exactly two parallel sides. C The figure must have two right angles. D The figure might have all four sides congruent. Which of the following statements will not be true for all rectangles? A All four angles are right angles. B Opposite sides are congruent. C Adjacent sides are perpendicular. D All four sides are congruent. Which of the following statements will not be true for all rhombuses? A All four angles are right angles. B All four sides are congruent. C Consecutive angles are supplementary. D Opposite angles are congruent. 3. Which of the following statements will be true for all squares? A The figure may have only two congruent sides. B The figure must have only two right angles. C The figure will have exactly two parallel sides. D The figure will have all four sides congruent. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 21 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify shapes including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and circles. NAME___________________ DATE___________ SCORE ___/5 7.6B Homework #1 1. Complete the following statements about the attributes of a rectangle. Sketch a rectangle. A rectangle will have 4 _______angles. A rectangle will have 2 pairs of __________ and __________ sides. Adjacent sides of a rectangle will be _________________. A rectangle’s angles will have a sum of ___________degrees. If the rectangle has 4 congruent sides, then it is called a ____________. The diagonals of a rectangle will be ____________. Sketch: 2. Complete the following statements about the attributes of a trapezoid. Sketch a trapezoid. A trapezoid will have exactly 2 pairs of _______angles. A trapezoid will have exactly 1 pair of __________ sides. A trapezoid’s angles will have a sum of ___________degrees. Sketch: 3. Complete the following statements about the attributes of a parallelogram. Sketch a parallelogram. A parallelogram will have 2 pairs of _______ angles. Consecutive angles will be ________________. A parallelogram will have 2 pair of __________ and _________sides. A parallelogram’s angles will have a sum of ___________degrees. If the parallelogram has four congruent sides, then it is called a ________. Sketch: 4. A rectangle has _______lines of symmetry. Sketch a rectangle and its lines of symmetry. 5. Draw and label a rectangle and one of its diagonals. Make a statement about the angles created when the diagonal was drawn. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 22 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify shapes including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and circles. NAME___________________ DATE___________ SCORE ___/5 7.6B Homework #2 1. Complete the following statements about the attributes of a square. A square has 4 _______angles. A square has 2 sets of ________ sides. The angles of a square have a sum of ___________degrees. A square will have _______congruent sides. Adjacent sides of a square will be _____________ Sketch a square. Sketch: 2. Complete the following statements about the attributes of a rhombus. Sketch a rhombus. A rhombus has 2 pairs of _______ angles. Consecutive angles are ______________. A rhombus has 2 pairs of __________ sides. The angles of a rhombus have a sum of ___________degrees. A rhombus has __________congruent sides. Sketch: 3. Following is a list of attributes. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. 4 right angles 4 congruent sides 2 pairs of parallel sides Exactly 1 set of parallel sides Exactly 2 pairs of supplementary angles Adjacent sides are perpendicular Sum of the measures of the angles is 360 degrees Write the letters of the attributes that belong to each of the following quadrilaterals on the lines. Square: ________________ Parallelogram: ________________ Rectangle: ________________ Rhombus: ________________ Trapezoid: ________________ TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 23 GRADE 7 MATHEMATICS (7.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student compares and classifies shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties. The student is expected to: (B) use properties to classify triangles and quadrilaterals. 4. Look at the markings on the quadrilaterals below. If the same type of arrows ( ) are on two different sides of a quadrilateral, it indicates the sides are parallel. Label each quadrilateral as a parallelogram, rectangle, square, rhombus, or trapezoid. 5. A 2-dimensional figure is a quadrilateral with 4 congruent sides. Is the quadrilateral a square? Can the figure be classified as any other type of quadrilateral? Explain your answer. TEKSING TOWARD TAKS 2005 6 Weeks 2 - Lesson 7 Page 24