* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ethernet - Inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Registered jack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
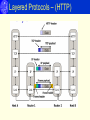
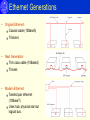
Ethernet Kenneth Castelino Network Architecture - Protocols • • • • • Physical: Actual signal transmission Data-Link: Framing / Error Detection Network: Routing / Addressing Transport: Congestion / Flow Control Application: Specific to user needs Layered Protocols – (HTTP) Data Link Layer - Ethernet • Invented in 1973 @ Xerox. (IEEE 802.3) • Originally a LAN technology – extended to MAN / WAN. • Same frame format, different wiring schemes, data rates across generations. • Most common version (10BaseT) – 1990. Ethernet Generations • Original Ethernet: Coaxial cable (10Base5) Thicknet. • Next Generation: Thin coax cable (10Base2) Thinnet. • Modern Ethernet: Twisted pair ethernet (10BaseT) Uses hub: physical star but logical bus. Ethernet Components • NIC – Network Interface Card Integrated Tx/Rx – direct interface to medium. • MAU – Media Attachment Unit Attaches network interface to the medium (integrated into NIC). • AUI – Attachment Unit Interface Decouple physical layer -reuse MAC design with different media. • MII – Media Independent Interface Like AUI for gigabit / faster ethernets. Ethernet Addressing • 48-bit address • Address assigned when NIC card is manufactured. • Packets can be sent to Single address – Unicast All stations on network – Broadcast (address = all 1s.) Subset of stations – Multicast • Broadcast (address = all 1s.) All receivers accepts unicast / broadcats. • Half addresses reserved for multicast (247) NIC can accepts zero or more multicasts. Ethernet Frame Sender adds: Senders address is source Recepients addreess in destination Type of data in frame type Error check data (CRC) Receiver NIC: Gets transmitted frame. Examines address and either accepts or rejects. Passes frame to system software. Media Access Control - MAC • Shared medium – stations take turns at sharing the medium. • Media access control ensures fairness. CSMA / CD • Carrier Sense: wait till medium is idle before sending frame. • Multiple Access: multiple computers use the same shared media. Each uses same access algorithm. • Collision Detection: Listen to medium – detect if another station’s signal interferes – back off and try again later. CSMA / CD • If collision occurs: wait a random time t1 - 0< t1<d. D depends on transmission speed – time for frame width or 512 bits. • If second collision occurs, wait a random time t2 - 0< t2<2d. Double range for each succesive collision. Exponential backoff • No acknowledgement like TCP. • CSMA/CA used in wireless networks where not all stations receive message. • Both sides send small message followed by data: X is about to send to Y Y is about to receive from X Data frame sent from X to Y. Recent Developments • 100Base-FX LED light source / MMF / 2 km max distance. Modal dispersion – limited bandwidth • 100Base-SX (IEEE 802.3z) Short wavelength laser (850 nm) Max distance = 5 km. • 100Base-LX Long wavelength laser (1310 nm) Max distance = 5 km. Beyond Gigabit Ethernet • 10 Gb/s Ethernet No CSMS/CD, same frame format. • Applications Upgrade LANs / Backbone. MAN applications. References [1] I.P. Kaminow, Tingye Li, Ed., “Optical Fiber Telecommunications IV”, Chapter 11, Academic Press, 2002. [2] John Chuang, SIMS 250 , UC Berkeley, Fall 2001.