* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download notes
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rule of marteloio wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
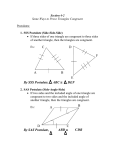
Geometry-Part 7 Triangle Congruency Two triangles are congruent if they have the same angle measures and the same side lengths, but we DON’T need to know ALL of the side lengths and ALL of the angle measures. There are five theorems that we can use to prove two triangles congruent. Side-Side-Side Theorem (SSS) SSS stands for “Side-Side-Side” and states that two triangles are congruent if all three sides of the triangle are congruent. Example: Since all side lengths are congruent, these triangles are congruent by SSS. Side-Angle-Side (SAS) SAS stands for “Side-Angle-Side” and states that two triangles are congruent if two triangles with two known side lengths, and the included angle are congruent. Since two sides and the included angle of both triangle are congruent, the triangles are congruent by SAS. Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) ASA stands for “Angle-Side-Angle” and states that two triangles are congruent if two triangles with two known angle measures and the included side length are congruent. Example: Since two angles and the included side are congruent, these triangles are congruent by ASA. Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) AAS stands for “Angle-Angle-Side” and states that two triangles are congruent if two triangles with two known angle measures and the non-included side length are congruent. Example: Since two angles and the non-included side are congruent, these triangles are congruent by AAS. Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) H-L stands for “Hypotenuse-Leg” and works for right triangles. This states that if we have two right triangles with the same length of hypotenuse and same length for one of the two legs are congruent, then the triangles are congruent. Example: Since the hypotenuse and length of one of the legs of the triangle are congruent, the two triangles are congruent. CAUTION! You cannot use “Angle-Angle-Angle” or “Angle-Side-Side” to prove triangles congruent. Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent (CPCTC) This theorem states that if you can prove two triangles congruent by any of the theorems above, it means that all other corresponding parts of the triangle are congruent. Angle-Angle Similarity (AA~) In triangles, if two pairs of corresponding angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar. NOTE: You cannot prove that the triangles are congruent using this, because you can have two triangles with different side lengths and the same angle measures. Reflexive Property of Congruence A measure is equal to itself. Proof Time! More Proof Time!