* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macrocytic Anemia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
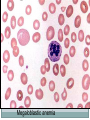
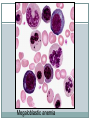
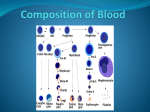
Macrocytic Anemia CLINICAL PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT SCU Normal blood cells Complete Blood Count (CBC) Normal red blood cells Definition An (without) -emia (blood): a reduction below normal in hemoglobin or red blood cell number Symptoms and signs of Anemia None if mild Fatigue Breathlessness Dizzines Pale Skin & mucous membranes Jaundice ( if hemolytic) Tachycardia Differential Diagnosis Using MCV Macrocytic anemias (MCV = 150 fl): > normal cells Normocytic (MCV = 80-96 fl): cells are normal in volume Microcytic anemias (MCV = 50 fl): cells are < normal Macrocytic anemia Defined as MCV > 100 femtoliters Identified by peripheral blood smear or automated RBC indices Smear is more sensitive in detecting early macrocytic changes and small numbers of macrocytes Cell morphology can aid in determining etiology of macrocytosis Common Causes of Macrocytosis cause % of cases Alcohol abuse 36% B12 or Folate deficiency 21% Chemotherapy or drugs 11% Hemolysis or bleeding 7% Liver disease 6% Primary bone marrow disorders 5% Hypothyroidism 5% Others 12% Megaloblastic Anemia Defective DNA synthesis leads to nuclear/cytoplasmic asynchrony B12/folate deficiency Macrocytic anemia with hypersegmented neutrophils Megaloblastic Anemia retarded DNA synthesis unimpaired RNA synthesis BIG cells! immature nucleus mature cytoplasm How is B12 involved? B12 (and folate) are required for DNA synthesis. • Slowed DNA synthesis means big, immature nucleus • Cytoplasm (with RNA in it) matures just fine B12 is also required for conversion of homocysteine to methionine • ↑ homocysteine = atherosclerosis! • ↓ methionine = subacute combined degeneration Megaloblastic anemia Megaloblastic anemia Reticulocyte Count (In the Diagnosis of Anemia) Useful in determining response and potential of bone marrow. Reticulocytes are non-nucleated RBCs that still contain RNA. Visualized by staining with supravital dyes, including new methylene blue or brilliant cresyl blue; RNA is precipitated as dye-protein complex. Normal range is 0.5-2.0% of all erythrocytes. If bone marrow responding to anemia, should see increases in retic count. Newborns have higher retic count than adults until second or third week of life. Retics Slide Thank You