* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Excretory Route
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
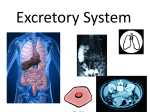
Route of the Excretory System Route of the Excretory System The excretory system removes wastes put into the blood by cells. The kidney, liver, and skin all play a role in removing wastes from the blood. The ureters, bladder, and urethra collect, hold and direct these blood wastes out of the body. The excretory system removes wastes put into the blood by cells. The kidney, liver, and skin all play a role in removing wastes from the blood. The ureters, bladder, and urethra collect, hold and direct these blood wastes out of the body. Body cells produce wastes when they produce energy. Cells combine the simple sugar glucose and oxygen to get energy. Cells often make glucose for this process from the amino acids making up the proteins we eat. The process that cells use to make glucose from amino acids leaves behind ammonia. Ammonia is also produced by bacteria in the gut. Ammonia is toxic to cells, so it is carried away by the blood. Body cells produce wastes when they produce energy. Cells combine the simple sugar glucose and oxygen to get energy. Cells often make glucose for this process from the amino acids making up the proteins we eat. The process that cells use to make glucose from amino acids leaves behind ammonia. Ammonia is also produced by bacteria in the gut. Ammonia is toxic to cells, so it is carried away by the blood. Blood containing ammonia enters the liver. The liver is the largest solid organ of the body. It is located below the lungs and above the small intestines. One of the liver’s function is to detoxify substances. The cells in the liver take in the ammonia from the blood and change it into urea. Urea is less toxic, but it is still a waste product of metabolism. Urea leaves the liver cells and is also carried away by the blood. Blood containing ammonia enters the liver. The liver is the largest solid organ of the body. It is located below the lungs and above the small intestines. One of the liver’s function is to detoxify substances. The cells in the liver take in the ammonia from the blood and change it into urea. Urea is less toxic, but it is still a waste product of metabolism. Urea leaves the liver cells and is also carried away by the blood. Blood containing urea enters the kidneys through an artery. The body contains two large bean shaped kidneys in the lower back. The kidneys contain over a million filtering units called nephrons. The arteries that brings blood into each kidney branches into small vessels that lead to each nephron. Urea is removed from the blood in round globular structures of the nephrons. Tubes leaving each nephron collect the urea and water removed by the nephron. These tubes join making bigger tubes and all connect to a large central space. The large central space connects to a tube called the ureter. Blood containing urea enters the kidneys through an artery. The body contains two large bean shaped kidneys in the lower back. The kidneys contain over a million filtering units called nephrons. The arteries that brings blood into each kidney branches into small vessels that lead to each nephron. Urea is removed from the blood in round globular structures of the nephrons. Tubes leaving each nephron collect the urea and water removed by the nephron. These tubes join making bigger tubes and all connect to a large central space. The large central space connects to a tube called the ureter. The rest of the excretory system functions to collect, store and eliminate urine. Urine is urea and water other wastes filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. Ureters are tubes that bring urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder is located in the pelvis and stores urine until it is eliminated. The urethra is the tube urine travels through from the bladder to exit the body. The rest of the excretory system functions to collect, store and eliminate urine. Urine is urea and water other wastes filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. Ureters are tubes that bring urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder is located in the pelvis and stores urine until it is eliminated. The urethra is the tube urine travels through from the bladder to exit the body. Limited amounts of urea are also eliminated by the skin in the sweat. This occurs through sweat glands in the skin. The skin of the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and foreheads have the highest concentration of sweat glands. The skin is the largest and heaviest organ of the body. Limited amounts of urea are also eliminated by the skin in the sweat. This occurs through sweat glands in the skin. The skin of the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and foreheads have the highest concentration of sweat glands. The skin is the largest and heaviest organ of the body.