* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IEEE Communications-2017 - Levine Lectronics and Lectric
Parallel port wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Serial port wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
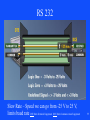
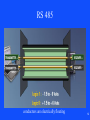
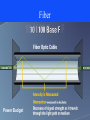
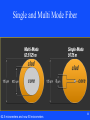
Advances in Communications & Reliability of Power and Control Systems Presented by John S. Levine, P.E. Levine Lectronics and Lectric, Inc. 770 565-1556 [email protected] 1 Are you frustrated? • Ever had problems getting on the network? • Ever had problems getting on the web? • How can a person with an Apple Computer send you an email when you use Microsoft Outlook? • Why can’t I talk to these relays? 2 • All these questions will hopefully be answered and more because: This is all part of Communications! 3 Overview of Topics to be covered • Basics • Ethernet • Protocols • HMI 4 Basics • • • • • • • Introduction Parallel Serial Parity Error Network Standards OSI Model 5 Introduction 6 Formatting Word – Could be 16,32, or 64 bits Group Address Description Current 0300 0301 0302 030D 030E 030F Phase A Current Phase B Current Phase C Current Phase A Differential Phase B Differential Phase C Differential 7 Parallel 8 Serial Baud Rate – A measure of how fast serial data is moving between devices per second. 2 common levels are 19, 200 BPS and 9,600 BPS and now 115,200 BPS 9 Serial Communications • Physical Layer – RS 232 – RS 485 – USB 10 RS 232 Slew Rate – Speed we can go from -25 V to 25 V, limits baud rate DTE Data Terminal Equipment DCE Data Communication Equipment 11 RS 485 conductors are electrically floating 12 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Port • Up to 127 devices can connect to the host, either directly or by way of USB hubs. • Individual USB cables can run as long as 5 meters; with hubs, devices can be up to 30 meters away from the host. • With USB 2.,the bus has a maximum data rate of 480 Mb per second. • With USB 3.,the bus has a maximum data rate of 4.80 Gb per second. (Plan to go to 10 GB) • A USB cable has two wires for power (+5 volts and ground) and a twisted pair of wires to carry the data. • On the power wires, the computer can supply up to 500 milliamps of power at 5 volts. Type A Type B Type C 13 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Port 14 IEEE 1394 Interface • The IEEE 1394 interface is a serial bus interface standard for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer, frequently used in a personal computer (and digital audio and digital video). The interface is also known by the brand names of FireWire (Apple Inc.), i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx (Texas Instruments). Though not as widely used, the 1394 standard also defines a backplane interface. • Firewire 400-Speeds from 100, 200, or 400 Mbits/s half-duplex • Firewire S3200-Speeds up to 3200 Mbits/s half-duplex 15 Network 16 Network 17 Network Topologies • The network topology defines the way in which computers, printers, IEDs and other devices are connected • A network topology describes the layout of the wire and devices as well as the paths used by data transmissions. • Commonly, referred to as a linear bus, all the devices on a bus topology are connected by one single cable. 18 PRP Parallel Redundant Protocol 19 20 Standards 21 2008 Proposed IEEE C37-2 Revision presented at Georgia Tech Relay Conference Copy at www. L-3.com/IEEE 22 OSI Model 23 Developed in 1978, the Open System Interconnection has 7 layers each performing part of the communications. 1) The physical level controls the physical connections between devices, network topology, voltage levels to define 0’s and 1’s.RS232, RS485, and USB are 3 examples 2) Data link level provides framing 3) Network determines optima routing – IP of TCP/IP is based on this 4) Transport level guarantees delivery and is error free – the TCP of TCP / IP (Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) is at transport level 5) Session mechanism for the establishment of a communications session between applications 6) Presentation – correct translation of data 7) Application – provides the facilities or interface to allow the application protocols or drivers such as Modbus or DNP 24 Ethernet • • • • Introduction 10/100/1000 Base T Hubs and Switches Fiber 25 Introduction 26 Ethernet in Devices Relays do not use DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 27 10/100 Base T Max distance 100 meters or 328 feet 28 10/100/1000 Base T Cat 5 Cable Cat 5e Cable Cat 6 Cable (up to 250 Mhz) Cat 6A (Augmented-up to 500 Mhz) 29 Power over Ethernet (PoE)How does it work? Note: RJ45 Socket Pin-out RJ45 Connector Pin-out Source - http://pinouts.ru/Net/poe_pinout.shtml Which pin-out to use is determined by an interrogation between the switch and the end device. All wiring is STANDARD EtherNet. Fiber Power Budget 31 Single and Multi Mode Fiber 32 Single and Multi Mode Fiber 62.5 micrometers and now 50 micrometers 33 Common Fiber Connectors ST-Straight tip LC-Lucent Connector SC-Subscriber Connector Primary Ethernet Port Redundant Ethernet Port 34 Traditional Switchyard Construction Traditional Breaker Wiring Traditional Cable Trench Thousands of Copper Wires from Switchyard Labor Intensive Copper Wiring on Relay Panels Hard Fiber Eliminating Complexity Eliminates 33 of breaker terminations 40 less cabling with no terminations required Eliminate 90 of control building terminations 1,000’s of wires replaced with few communication cables 36 Hubs and Switches 37 Managed Switches • Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): a set of protocols for managing network performance, finding and solving network problems, and planning for network growth • Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP): configures broadcast message behavior • Virtual LAN (VLAN): a network of computers that behave as if they are connected to the same wire even though they may actually be physically located on different segments of a LAN • Quality of service (QoS): Allows prioritization of packets to occur or improve performance for key channels • Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP): algorithm to prevent wiring topology mistakes or create redundancy in a network 38 Industrial Switches for the Plant Floor 39 Hubs and Switches 40 Wireless • This is where the future is. Products are now being designed with Wireless build into the device. • Regulated and unregulated frequencies – 900 Mhz – 2400 Mhz – 1800 / 3650 / 5800 Mhz • Different speeds depending on the application • As the Frequency goes up, the distance goes down 41 42 Router • Definition from Wikipedia - A router is a computer networking device that forwards data packets across a network toward their destinations, through a process known as routing. Routing occurs at Layer 3 (the network layer i.e. Internet Protocol (IP) of the OSI seven-layer protocol stack. Wikipedia and Linux are written collaboratively by volunteers and are “open source” and free. 43 Other Computer Networking Devices • Gateway: device sitting at a network node for interfacing with another network that uses different protocols. Works on OSI layers 4 to 7. • Bridge: a device that connects multiple network segments along the data link layer. Works on OSI layer 2. • Repeater: device to amplify or regenerate digital signals received while setting them from one part of a network into another. Works on OSI layer 1. 44 Other Terms • PRP – Parallel Redundancy Protocol – Two completely separate Lans going to the same device • Bandwidth – max data transfer rate • Server - computer programs running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients“ • VPN – Virtual Private Network • RSTP - Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol – determines the path the message will take between 2 nodes 45 Other Terms • IRIG-B – Time code accurate to 10 ms • SNTP – Simple Network Time Protocol – typically 1 to 2 ms • PTP (Precision time Protocol) time distribution technologies sub-microsecond accuracy (GE MultiSync 100) • QoS- Quality of Service – Overall performance of the network 46 Proxy, Firewall, and Port • Proxy: computer network service which allows clients to make indirect network connections to other network services • RADIUS Server: Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service is a client/server protocol and software that enables remote access servers to communicate with a central serverto authenticate dial-in users and authorize their access to the requested system or service. 47 Proxy, Firewall, and Port • Firewall: a piece of hardware or software put on the network to prevent some communications forbidden by the network policy • Computer port (hardware) - a physical interface between a computer and other computers or devices (COM1) • Computer port (software) - a virtual data connection between computer programs possibly through a computer network 48 Firewalls From a Linksys router 49 Relays at L-3 Wan I.P 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145 96.87.252.145:5 18 Firewall Technolog Port y LAN IP 503 Relays 192.168.1.241 503 Relays none 503 Relays none 503 Relays none 504 Relays 192.168.1.242 505 Relays 192.168.1.243 508 Relays 192.168.1.246 509 Relays 192.168.1.247 511 Relays 192.168.1.249 513 Relays 192.168.1.210 514 Relays 192.168.1.211 515 Relays 192.168.1.212 516 Relays 192.168.1.249 LAN Port 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 502 Slave Address 1 45 89 242 243 254 254 254 254 254 254 254 517 Relays 192.168.10.238 502 1 518 Relays 192.168.10.238 502 1 Device Multinet PQM II 745 489 469 760 369 350 850 Rack T35 Rack B90 Rack M60 Rack PQM II Rack EPM 7000 Web EPM 7000 Serial to Ethernet Converters 51 Serial to Ethernet Converters 52 Adding Devices to a Network • Static IP address 3.94.244.1 for device • Subnet 255.255.255.0 for network – Go to Network and Sharing Center – Change adapter settings – Right click for properties 53 Adding Devices to a Network DNS - Domain Name System, Internet system to translate names into IP addresses IP v4 and IP v6 (8 groups of 4 hex digits 0db8:2001:85a3:0000:0000:8a2a:0370:7334) 54 Checking IP Address 55 Checking IP Address 56 Other useful Dos Command • • • • ipconfig /release ipconfig /renew ipconfig /all (gives you IP and MAC address) ping –t – Control C to stop the ping • • • • tracert exit You can hit F3 to go to the previous dos command Or you can hit the up arrow to go back to previous dos commands 57 ping 58 tracert • Black list and White list • Gray list 59 Useful Internet Sites and Programs • www.Dnsstuff.com - can use to find if a web site is getting blocked or who owns it. • www.Speakeasy.net/speedtest/ - Can use for a speed test • www.Spinrite.com – Can use to check for leaks in your firewall • http://www.kloth.net/services/nslookup.php get the IP address for a I.P. name. • www.whatismyip.com – your WAN IP • Wireshark - http://www.wireshark.org/ 60 61 Wireshark 62 Protocols • • • • • • • • • • • Modbus Modbus Plus DNP DeviceNet and EtherNet/IP Profibus and Profinet Direct I/O IEC 61850 Hart BACnet EtherCat Protocol Converters 63 Modbus • Can be communicated via RS 232, RS485, 10/100 Base T, and 10/100 Base F • Is half-duplex serial in all configurations • Uses a master and slaves • Data is stored in registers 64 Modbus Plus • Proprietary protocol • Can be communicated via RS485 or ethernet. Uses a peer-to-peer token exchange type network. MultiMaster. • Global data can be sent with the token. • 64 nodes per network, can Bridge networks. • Speeds up to 1 MB • Up to 1800 meters with repeaters 65 Digital Network Protocol (DNP 3) • • • • • • • • Developed by GE Harris – can time stamp data Scalable Has Client (computer) and server (device) Also called Master and Slave Can poll for change Can set up for Unsolicited messaging from server Can provide only changed values. Can Prioritize messages 66 Digital Network Protocol (DNP 3) 67 DeviceNet (serial) EtherNet/IP (Ethernet Industrial Protocol) • • • • • • Based on the Controller Area Network protocol (CAN) Managed by the Open DeviceNet Vendors Association Bus Topology at 24 VDC Baud rates of 125, 250, and 500 Kbps Can have up to 64 nodes on a single local network DeviceNet uses abstract OOT (Object-Oriented Technique) – – – – objects class instances attributes 68 DeviceNet 69 Profibus (serial) Profinet (ethernet) • Profibus (Process Field Bus) • Profibus-DP (Decentralized Periphery) • Profibus -FMS (Fieldbus Message Specification) • Profibus -PA (Process Automation) • Profinet – Ethernet based Field network 70 Profibus 71 Profibus 72 Profibus 73 IEC 61850 • Designed as a universal plug and play between manufactures • Uses descriptions instead of registers • Generic Object Oriented Substation Event – Messaging (GOOSE Messaging) • Ethernet is required as part of IEC 61850 The phrase “sixty-one-eight-fifty” has become a designator for the next generation substation secondary system with a higher degree of integration, reduced cost, greater flexibility, communication networks replacing hard-wired connections, plug-and-play functionality, reduced construction and commissioning time, and other advantages 76 IEC 61860 77 78 IEC 61850 Applications • Breaker Failure Initiate to Other Breaker • Broadcast a Trip Message to All Feeder Breakers – (Bus Differential) • • • • • • • High Speed Bus Transfer (M-T-M) Switching Set Groups Upstream Relay Tripping & Blocking Bus Protection Relay Voting Reclose Initiation Load Shedding – KW or KVA Load Shedding – Underfrequency Load Shedding • Transfer Tripping • Remote Start/Stop Commands 79 Hart • HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) Protocol is the global standard for sending and receiving digital information across analog wires between smart devices and control or monitoring system. 80 BACnet • BACnet (Building Automation and Control) was developed in 1987 by a group of HVAC and Building Automation professionals as a standard, open protocol specifically for the building automation industry. It is an ASHRAE, ANSI, and ISO standard protocol. • Protocol – The BACnet protocol defines a number of services that are used to communicate between building devices. The protocol services include Who-Is, I-Am, Who-Has, I-Have, which are used for Device and Object discovery. Services such as Read-Property and Write-Property are used for data sharing. The BACnet protocol defines a number of Objects that are acted upon by the services. The objects include Analog Input, Analog Output, Analog Value, Binary Input, Binary Output, Binary Value, Multi-State Input, Multi-State Output, Calendar, EventEnrollment, File, Notification-Class, Group, Loop, Program, Schedule, Command, and Device. 81 EtherCat • EtherCat is an Ethernet based fieldbus system designed for extremely fast data update times in the range of < 100 µs. • The Standard Ethernet packet or frame is no longer received, interpreted, and copied as process data at every node. The EtherCAT slave devices read the data addressed to them while the telegram passes through the device, processing data "on the fly". Similarly, input data are inserted while the telegram passes through. A frame is not completely received before being processed; instead processing starts as soon as possible. Sending also is conducted with a minimum delay of small bit times. 82 Protocol or Gateway Converters 83 Universal Gateway There are Universal Gateways and controllers that collects metering, status, event, and fault report data from serial or LAN based Intelligent substation devices. The Gateways summarizes data from the substation devices and makes it available locally/remotely through a standard secure web browser (HTTPS). 84 Human Machine Interface (HMI) • • • • • Overview Plug and Play One-Line Viewer Annunciator OPC / DDE Server 85 HMI Overview • SCADA – Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition • RTU – Remote Terminal Unit • It is now extremely easy and cost effective to view your devices without having to be in front of the relays. 86 Plug and Play Viewpoint Monitoring 87 Dashboard 88 One-Line Viewer 89 One-Line Editor 90 Annunciator 91 Automatic Event and Waveform Retrieval 92 Trending Reports 93 Comtrade Files 94 OPC • The OPC Foundation is an industry consortium that creates and maintains standards for open connectivity of industrial automation devices and systems. The OPC standards specify the communication of industrial process data, alarms and events, historical data and batch process data between sensors, instruments, controllers, software systems and notification devices. 95 DDE • Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE) is a technology for communication between multiple applications under Microsoft Windows and OS/2. • Microsoft Excel has a DDE server – you can open a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet and fill it with data, by opening a DDE conversation with Excel and sending it DDE commands. 96 OPC / DDE Server 97 Sources of Information • http://www.gegridsolutions.com/resources.htm – GE Multilin Communications Training CD • • • • http://www.wikipedia.org/ http://www.profibus.com/wbt/en/wbt1/ http://www.odva.org/ http://www.dnp.org/ 98 Website: www.L-3.com 99 Thank You 100