* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Information Age Enterprise - L1 - The University of Texas at Dallas
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Business model wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Supply chain management wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
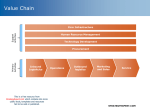
Role of IT in a Business Firm Varghese Jacob & Sumit Sarkar University of Texas at Dallas Goal Understand contexts that can be used to identify the role and impact IT can have on your business. “We have a philosophy where we look for productivity and process enhancements wherever we can. To a great degree that dictates the technology solution rather than the other way around” Cassese VP of business technology and marketing research, Pfizer Context Decision-making Competitive Value chain Environment Decision Making Decision ? Decision Process A university professor, who was previously a sailor, was aware that ships are addressed as "she" and "her". He often wondered what gender should be used to address computers. To answer the question, he set up two groups of computer experts. The first was comprised of women, the second of men. Each group was asked to recommend whether computers should be referred to in the masculine or feminine gender. They were asked to give 4 supporting reasons. The women reported that computers should be referred to in the masculine gender, because: 1. To get their attention, you have to turn them on 2. They have a lot of data, but are still clueless 3. They are supposed to help us solve problems, but half the time they are the problem. 4. As soon as you commit to one, you realize that if you had waited a little longer you could have had a better model The men concluded that computers should be referred to in the feminine gender, because: 1. No one but the Creator understands their internal logic 2. The native language they use to communicate with other computers is incomprehensible to everyone else 3. Even your smallest mistakes are stored in long-term memory for later retrieval. 4. As soon as you commit to one, you find yourself spending half your paycheck on accessories for it. Simon’s Model of Decision Making The Process Intelligence Activity Design Activity Choice Review How can IT be used to support the decision process? Competitive Strategies How can a firm perform above-average in the long run? Fundamental basis for sustainable competitive advantage (Michael E. Porter) • Low Cost • Differentiation • Focus > > Cost Differentiation Porter’s Five Competitive Forces New Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Competitors Substitute Products/Services Bargaining Power of Customers Competitors Value proposition Cost leadership Differentiation Focus (cost or differentiation) Branding First mover advantage Bargaining Power Buyers have bargaining power where • Multiple potential suppliers • Buyer accounts for large proportion of the seller's business Seller can gain bargaining power by • Introducing switching costs • Reduces the number of possible suppliers (how?) New Entrants Establish barriers to entry • High entry cost (up-front investments) • Economies of scale • Economies of scope • Branding • Switching cost in monopolistic competition (lock-in) • Risk of retaliation Substitutes Threats of substitute products countered by • introducing switching cost • providing a higher level of service >convenience (e.g., one-stop shopping) >after-sales service • offering low price >volume discounts Does IT play a role in above? • Can IT build (lower) barriers to entry? • Can IT build in Switching costs? • Can IT change the basis of competition? • Can IT change the balance of power in supplier relationships? Example Kalamazzo, Michigan a city with 125,000 has two hospitals, Borgess MedicalCenter and Bronson Methodist Hospital. Both of which are competing for the same patient pool. Both of them want to increase its inpatient pool. Borgess Medical Center asked themselves How can we get an increasing share of a decreasing market? Who is the hospital’s customer? Physician or patient? Borgess Medical Center came to the conclusion that physicians are the customers. Goal how does one increase customer loyalty? Borgress’s solution Gave each physician a computer and software free in their offices at no cost. Software included patient billing, appointment scheduling etc. PC connects to the hospitals system for scheduling admissions and operating rooms. PC for access to results of lab tests. Physician referral service. Result 18% increase operating revenues. 5% increase in admissions when there is decline elsewhere. The Value Chain What is the value chain? What is its significance? What is the role of IT within the value chain? SUPPORT ACTIVITIES The Value Chain FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROCUREMENT PRIMARY ACTIVITIES MARGIN INBOUND LOGISTICS OUTBOUND LOGISTICS OPERATIONS SERVICE SALES & MARKETING Source: Porter, Michael E. Competitive Advantage: Creating and sustaining superior performance The Value System Supplier Value Chain Upstream Value Firm Value Chain Buyer Value Chain Channel Value Chain Downstream Value Source: Porter, Michael E. Competitive Advantage: Creating and sustaining superior performance Inbound Logistics Receiving raw materials Inbound inspection Material handling and inventory control systems Raw material warehousing activities Operations Develop and Maintain Facilities Schedule Operations Assemble Parts Manufacture Products/Deliver Services Efficiency of plant layout and work-flow design Maintain Inventory Outbound Logistics Finished goods warehousing activities Process customer orders Schedule deliveries Distribution (& Shipping) of finished goods and services Marketing and Sales Market Research • Identify new products & services • Identify customers • Understand customer needs • Forecasting Develop & Maintain Markets • Sales promotion and advertising • Pricing strategies • Evaluate alternative distribution channels • Motivate and evaluate sales force Customer Service Provide replacement parts Repair services Handle warranty and guarantee policies Customer education and training Solicit customer feedback for product improvement Human Resource Management Recruiting, hiring, training, and promotion of employees Reward systems for motivating and challenging employees Ensure work environment to minimize absenteeism and keep turnover at desirable level Technology Development Improve products and processes • R&D • Improved maintenance, packaging, testing, material handling, work flow Procurement Develop sources of inputs Procure raw materials Procure plant, machinery, and buildings Evaluate lease vs. purchase decisions Facilitate long-term relationships with reliable suppliers Firm Infrastructure Strategic planning Accounting and finance Legal and environmental Total quality management Coordination and integration of all activities in the value chain Linkages in the Value Chain Functions are inter-related • Improving raw material quality may reduce manufacturing costs Linkages can be to external entities SUPPORT ACTIVITIES Cost Maps FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE (3%) HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (7%) TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT (5%) PROCUREMENT (4%) PRIMARY ACTIVITIES MARGIN INBOUND LOGISTICS (8%) OUTBOUND LOGISTICS (9%) OPERATIONS (43%) SERVICE (8%) SALES & MARKETING (13%) Source: Porter, Michael E. Competitive Advantage: Creating and sustaining superior performance Porter and Millar’s Five-Step Process Assess information intensity Determine the role of IT Identify and Rank ways in which IT can provide competitive advantage Can IT help spawn new businesses Develop a plan for taking advantage of IT Exercise • Groups that end with even numbers should consider Amazon and groups that end with odd numbers should consider Barnes and Noble (brick and mortar version). Address the following issues within the context of the value chain: > > > > What is the product being sold? Describe what the primary value activities mean as it pertains to your organization, e.g.what does inbound logistics mean for your business? Identify the specific activities that you would need to perform within the generic primary activities of the value chain. In your opinion which of the primary activities have the highest percentage cost and what would be its cost drivers? Which of the secondary activities would have the highest percentage cost? Identify three IT implementations that could reduce the cost or provide additional value.