* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Introduction. 2. The history. 3. Economic, political and social
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
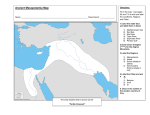
1. Introduction. 2. The history. 3. Economic, political and social organization. 4. The writing. 5. The city. 6. The king Hammurabi. 7. The principals gods. 1. Introduction The Mesopotamic empire was between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates. They are born in Armenian in the lake Van. These rivers are navigable, near the Persian Gulf. The Mesopotamic culture is a very ancient culture of approximately 5000 years to A. C. All this culture principally divided in four states: Assyria, Mesopotamia, Caldea and The Elam. ! Assyria: in the most top part of the river Tigris, in a mountainous place. ! Mesopotamia: between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates, is the most fertile zone. ! Caldea: in the south of Mesopotamia, very fertile region and his capital was Babylonia. ! The Elam: was in the east of the Tigris river. The peoples that were living this region were the Sumerian to the north of the Euphrates, they were a mixture of Caucasian and Negroid, their race has not been determined. His attributes the cuneiform writing to them. The most important cities were: Ur, Lagash and Larsa. The Sumerian were not of Semitic origin and not of Indo-European origin. The downtown of the Sumerian cities was the temple, called "Ziggurat". They were polytheistic, they practised the agriculture. They invented the vehicle with wheels, they were living in cities and separated states. They were governed by a king called "Patesi". 2. The History In the Mesopotamic Empire there were two towns: Asirians and Caldeans: -Assyrians: warriors. -The Caldean people: peaceful character, art and culture. Both were Semites. In the town of the Caldeos there was a very important personage called Hammurabi, king of Babylonia. Later there came the Assyrians with their kings His capital was Nineveh. Later the decadence comes and the second empire will be Assyrian. The warriors Assyrians were terrible with the peoples that were conquering, Persian and Caldeans fought against the Assyrians and they conquer them. Later the second empire comes king Nabucodonosor. Caldeos, with the 3. Economic, political and social organization. 1. Social and political organization: ! The King: he had military powers. ! The Governors: they governed the territories of the kingdom. They were generals and judges at the same time. ! The aristocracy: they were priests and traders. ! The peasants: the people who work the land. 2. Economical organization: The Assyrians and the Caldeans practised the agriculture taking advantage of the waters currents of the rivers, they had cattle and many horses. They knew the art, were imposing taxes on the conquered villages.. 4.The writing The writing in Mesopotamia is the oldest in the world. They writing in splints of clay, this writing is call cuneiform. At the beginning was a ideographic writing later started to represent the sound. The Mesopotamic alphabet. A Babylonian text. 5.The City Cities in this area had three parts, the down town of city with temples , suburbs with farm animals, and the commercial area. The temples were very important in this early culture. Much of the social, economic and political activities of the cities would downtown around the temple area. Temples in the cities were called ziggurats, which comes from a word meaning summit or mountain top. The temples were built on the top of step pyramids. The ziggurat of Ur. The downtown of Babylon. The temple of Babylon. The palace of Korsabad. 6.The king Hammurabi Hammurabi was the king of the city-state of Babylon, he made Babylon one of the great cities of the ancient world. In 1792 b.C. Hammurabi proclaimed king of Babylon. He recorded a system of laws called the Code of Hammurabi. This code had 282 laws were writing in stone and placed in a public location. Some of Hammurabi's laws were based on the principle "An eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth." This means that anyone who commits a crime should be punished in the same manner as that crime. If someone put out another person's eye, their eye would be put out in return. Hammurabi's Code may seem cruel today. 7.The principals Gods ! Anu: he was the god of the sky, he change the seasons. ! Enlil: he was the god of the wind and the agriculture. ! Ninhursag: she was the goddess of the wild life and the birth rate. ! Enki: was the goddess of the water, god of knowledge and magic. ! Marduk: he prevented the Flood, like Noe in the Bible. ! Ereshkigal and Nergal: they live in the underground ! Ishtar: The goddess of the war. Statue of Ishtar the goddess of the war. Bibliography The mesoptamic writing history. http://redescolar.ilce.edu.mx/redescolar/proyectos/histor ia_escritura/ses2mesopo.htm Universal history of Mesopotamia. http://icarito.tercera.cl/icarito/2001/822/pag7.htm The history of Mesopotamia and the King Hammurabi http://www.artehistoria.com/frames.htm?http://www.art ehistoria.com/historia/contextos/205.htm The cities. http://www.historylink101.com/lessons/farmcity/mes1.htm