* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Abroad - Weber State University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
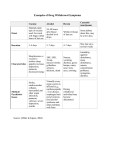
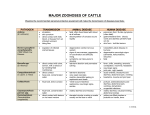
Study Abroad Keeping students healthy throughout the experience Lisa Trujillo, MS, RRT Study Abroad Locations United States Central America South America European Countries China Africa Japan Basic First Aid Lacerations Bleeding Protect yourself FIRST! Infection control Sprains – Soft Tissue Injuries Ice – 20 min at a time, 30 min between, not directly on skin Support – splint or brace, elastic bandage wrap – not too tight Rest – elevation will help reduce swelling Anti-inflammatory medication Fractures Splint, ice, support, elevate Medical care First Aid Kit Kit should include: *CPR mouth shield *Exam gloves *Cold pack Alcohol wipes and antiseptic hand cleaner Gauze, bandages and adhesive tape Insect repellant/bite treatment Antibiotic ointment/hydrogen peroxide Pain killer – acetaminophen and/or ibuprofen *For Program Directors Physical Illnesses Dehydration Causes Diarrhea, vomiting, fever, sweating, lack of fluid intake, hot weather Symptoms Dry mouth, sleepiness, thirst, decreased urine output, dry skin, headache, constipation, dizziness or lightheadedness Extreme symptoms include lack of sweating, sunken eyes, rapid heartbeat, rapid breathing, fever, dry skin that lacks elasticity Treatment Oral rehydration with water or sports drinks that contain electrolytes Physical Illnesses (cont.) Altitude Sickness Acute mountain sickness – most common 20% of people experience mild symptoms between 6300 and 9700 feet Dizziness, headache, nausea, difficulty sleeping 2-3 days to resolve – may consider dropping elevation until symptoms subside Faster and higher climb = greater risk of illness High-altitude pulmonary edema Rarely occurs below 10,000 feet Includes difficulty breathing, tightness in chest, fatigue and coughing Requires prompt medical attention High-altitude cerebral edema Mostly occurs above 10,000 feet Includes confusion, difficulty with balance and coordination, and hallucinations Medical emergency requiring immediate medical attention Changes in Diet Can lead to change in GI function Diarrhea Constipation Food allergies Vegetarian Food Borne Illnesses Gastrointestinal Illnesses Diarrhea Nausea/Vomiting Mental Health New experiences for many students Culture shock Emotional experiences Extremes of any kind Debriefing on a daily basis recommended Journaling Contact with family where possible Know about pre-existing mental health concerns Jet Lag Problems it may cause Activity delay Reduced coping ability Decreased resistance to illness How to prevent or limit effects Sleep aids OTC Rx No napping during the day Tropical Diseases Malaria – Mosquito-borne parasite Endemic to many countries (Subsaharan Africa, India, Haiti) Can be fatal Be sure you are recommending the proper antimalarial medication Some prophylactic antimalarial meds are ineffective on resistant strains of malaria Signs and symptoms Moderate to severe shaking chills High fever Profuse sweating a body temp falls Headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Prevention – Anti-malarial medication, mosquito repellant, long sleeves in evenings, bed nets and avoiding areas with standing water Tropical Diseases (cont.) Dengue Fever – Mosquito-borne virus Endemic to Southeast Asia and Western Pacific Islands but can occur in Latin America and the Caribbean Cases may range from mild to severe hemorrhagic fever Signs and symptoms Fever up to 106 F (41 C) Headaches, muscle and joint pain, pain behind the eyes Widespread rash, nausea and vomiting, minor bleeding mouth of mouth and nose No specific treatment (virus) Hydration, pain and fever reducers, - avoid aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen Prevention is encouraged through mosquito repellant and protective clothing OTC Meds Medications to consider Imodium Pepto Bismol Anti-nausea meds Stool softeners Cold medicine – Nyquil/Dayquil Allergy medications Ibuprofen / Acetaminophen Sleep aid – Melatonin, Nytol, etc. Vitamins Electrolyte supplements – drink mix Students should discuss any new medication, even OTC meds, with their physician. Rx Meds Medications to consider Lomotil – stops peristalsis in the GI tract Ciproflaxin – broad spectrum antibiotic for GI bacteria Zofran – anti-nausea Ambien – sleep aid Levaquin – upper respiratory infection Mefloquine – antimalarial for chloroquine resistant areas Prescription medications may be suggested to students depending on the travel destination and risk of illness Travelers must keep meds in the original packaging Prescription meds are only to be used by the patient they are prescribed to Hospitals and Medical Facilities Know where medical facilities are in your area What are the medical response procedures 911…?? How to call for help Travel Insurance vs. Trip Insurance Trip costs Medical expenses Some hospitals will require payment then reimbursement is provided by insurance company Questions…??