* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intracanal Medication
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
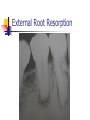
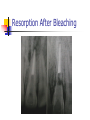
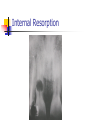
Intracanal Medication Dr syed Abrar Ali Assistant Professor Operative Dentistry Introduction An agent used as an adjunt to cleaning and shaping for prevention or treatment of apical periodontitis. Functions of Intracanal Medicaments Primary function Disinfection Secondary Functions Induction of hard tissue formation Pain control Control of exudation or bleeding Control of inflammatory root resorption Primary function Disinfection Antimicrobial Agents Antibiotics Sulpha preparations Penicillins Metronidazole Terracycline Clindamycin Antimicrobial Agents Disinfectants Aldehydes Halogens Phenols Chlorhexdine Calcium Hydroxide CaOH with antimicrobial additives Concept Of Predictable Disinfection In Endodontics Mechanical instrumentation Antibacterial effect of irrigation Effect of antibacterial dressing Single visit issue Microbes Of The Pulp With apical periodontitis Retreatment cases Fusobacterium, prevotella, pophyromonas, peptostreptococcus, veillonella, spirochetes Enterococci esp. E. Fecalis, Yeasts Actinomyces Secondary Functions Induction Of Hard Tissue Formation Also called root end closure or apexification Calcium hydroxide, MTA Barrier allows mechanical compression of root filling Secondary Functions Pain Of Endodontic Origin Interappointment dressing to combat infection Ledermix Corticosteroids NSAIDS Secondary Functions Exudation And Bleeding Exudation Sign of infection Large apical formen Over-instrumented canal Bleeding Calcium Hydroxide Formacresol Secondary Functions Root Resorption After infection and trauma Several types CaOH, Ledermix, Calcitonin External Root Resorption Resorption After Bleaching Internal Resorption Tissue Toxicity and Biological Considerations Aldehydes and phenols Tissue damage Interfere with healing or serve as locus for bacterial colonization to creat a lesion that never existed Suggested Clinical Procedure Mechanical reduction of bacteria Application of medicament Irrigation Dressing Temporary filling Suggested Reading Harty’s Chapter 7