* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ohm`s Law
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
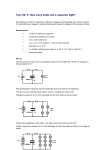
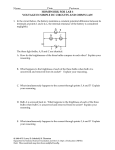
Demonstration: Ohms Law for Serial and Parallel Circuits Leonard Freise Bruce Dillon Lane Matheson Objective: Introduce a visual demonstration of Ohm’s Law. Lights Batteries Parallel Series Equipment: 2 –Lights Power Source Wires with Alligator clamps Multimeter Discussion: Demonstrate set-up of a circuit with one light bulb. Ask students to notice the brightness of the bulb. Place a second bulb in parallel with the first one. Note that the brightness of the bulbs stays the same, but the current increases. Next, rearrange the bulbs in series. Note that the brightness of the bulbs decreases compared to before, but the current is the same as when there was only one bulb in the circuit. The light bulb is an example of a resistor. The resistance of any material is measured by the relationship R = V/I where V is the potential difference measured in volts and I is the current measured in amps. Resistance is measured in Ohms, , which is equivalent to volts/amps. For many materials, the resistance is constant over a wide range of voltages and currents. Light bulbs are designed to have increasing resistance as voltage is increased, so the light bulbs will not demonstrate the concept of constant resistance. The exercise that accompanies this demo uses resistors instead of bulbs to allow students to verify Ohm’s Law. Questions: 1. What would you expect to happen to the brightness of the bulbs if we placed a. Three bulbs in parallel? b. Three bulbs in series? 2. What would you expect to happen to the current if we placed a. Three bulbs in parallel? b. Three bulbs in series?