* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diabetes and You
Chromium(III) picolinate wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Oral rehydration therapy wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Thrifty gene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
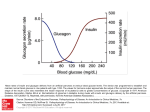
For Better Living Sandra Kelly Cain Diabetes and You Diabetes is the leading cause of premature deaths and the sixth leading cause of all deaths in the United States. Not managed properly, diabetes can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, nerve damage, amputations and even death. Unfortunately, about 7 million people in the United States have diabetes and don’t even know it. The most common type of diabetes, adult-onset, usually begins when persons are in their mid 50's. Minor changes in your lifestyle can reduce your chances of getting this disease. Diabetes is a disorder in which the body does not use the sugars in food the usual way. Normally, some of the food you digest is changed into glucose or sugar, which your body uses for fuel. Your blood carries glucose to the cells where a hormone called insulin allows it to enter the cells. Diabetics produce too little insulin or sometimes none at all or their bodies cannot properly use the insulin. This causes high levels of glucose to build up in the blood. If left untreated, these high levels of glucose can lead to serious complications. What are the types of Diabetes? There are 3 type of diabetes: Type I, Type II and Gestational. Type I is the most severe form and usually occurs around age 11 or 12. It is often called juvenile-onset or insulin-dependent diabetes. Type II is the most common form of diabetes. In many cases, Type II can be controlled with diet and exercise. Type II diabetics are usually older adults who are overweight and have a blood relative with diabetes. The third type, Gestational Diabetes, occurs in some pregnant women and usually disappears after childbirth. Warning Signs of Diabetes If you have any of the following problems on a regular basis, you should contact your doctor. You may need to be tested. Type I: abdominal thirst, frequent urination, weakness, excessive hunger, rapid , unexplained weight loss, poor growth, flushed skin, fruity breath, nausea and vomiting. Type II: Any of the Type I signs plus the following: tingling or numbness, itchy skin, frequent infections, slow healing, drowsiness, blurred vision, overweight. If you have diabetes, the American Diabetic Association recommends the following: 1. Eat a variety of foods. No single food provides all the nutrients needed by your body. 2. Maintain a healthy weight. Let your doctor help determine a healthy weight for you. Weight loss reduces the risk of developing diabetes. Losing as little as 10 extra pounds can make a difference in your blood glucose, cholesterol and fat levels. 3. Choose a diet low in fat, saturated fat and cholesterol. Fat in your diet should be no more than 30% of your total calories. Saturated fat should be no more than 10% of your total calories. Cholesterol should be no more than 300 milligrams per day. 4. Increase your intake of fiber foods. Research shows that dietary fiber reduces a diabetic’s need for insulin, improves glucose control, lowers cholesterol and fat levels and even helps lose weight. Water-soluble fiber has a stabilizing effect on blood sugar levels. Sources of watersoluble fiber include oat products, peas, beans, pasta, brown rice, cracked wheat and fruit. 5. Control your sugar consumption. Your doctor should be involved in setting an amount of sugar for you. 6. Use salt in moderation. You need less than 1,000 milligrams of sodium per 1,000 calories and should not consume more than 3,000 milligrams per day. To reduce sodium, cut back on salt when cooking as well as at the table. 7. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Alcohol blocks the production of glucose and enhances the effects of insulin. There is no cure for diabetes. However, you can manage or delay diabetes through diet, exercise, weight control and if necessary, medication. Source: North Carolina Cooperative Extension Herb Rubbed Pork Roast 1 1/2 teaspoon salt 1 1/2 teaspoons celery salt 1 teaspoon onion powder 1 teaspoon garlic powder 1 teaspoon paprika 1 teaspoon pepper 1/2 teaspoon dill weed 1/2 teaspoon dried rosemary, crushed 1/2 teaspoon rubbed sage 1 boneless rolled pork loin roast, 4 pounds In a small bowl, combine the seasonings. Rub over roast. Place on a rack in a shallow roasting pan coated with nonstick cooking spray. Bake, uncovered, at 350 degrees for 1 3/4 - 2 hours or until a meat thermometer reads 160 degrees. Let stand for 10 minutes before slicing.