* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quadratics
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
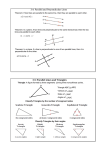
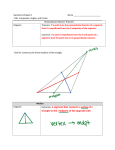
Properties and Attributes of Triangle By: Ou Suk Kwon • Perpendicular Bisector is a line that pass through a vertex of one angle of triangle passing through the line that is in the opposite side, this line must pass through the midpoint and should be perpendicular. • Perpendicular Bisector Theorem tells us if a point is on the perpendicular bisector segment, then it is equidistant from the endpoints of the segments. • Its converse says if equidistant from the endpoints of a segment, then it is one the perpendicular bisector of the segment. 1) AD perpendicular BC DB=DC Conclusion: AB=AC 2) BF perpendicular AC AF=CF Conclusion: BA=BC 3) CE perpendicular AB AE=BE Conclusion: CA=CB 1) AB=AC Conclusion: AD perpendicular BC BD=CD 2) BA=BC Conclusion: BF perpendicular AC AF=CF 3) CA=CB Conclusion: CE perpendicular AB AE=BE • Angle bisector is when you are bisecting each angles of the triangle. You use them when you are finding incenter of the triangle. • Angle bisector theorem tells us if a point is on the bisector of an angle, then it is equidistant from the sides of the angle. • And its converse tells us that if a point in the interior of an angle is equidistant from the sides of the angle, then it is on the bisector of the angle. 1) BAD=CAD Conclusion: BD=CD XWD=YWD Conclusion: XD=YD XWD=YWD Conclusion: XD=YD 1) XD=YD Conclusion: XWD= YWD XD=YD Conclusion: XWD=YWD 2) XD=YD Conclusion: XWD=YWD • Concurrent means that something is meeting, intersecting or converging with something else. The theorem is a point is on the perpendicular segment iff it is equidistant to all vertices. The circumcenter of a triangle is always equidistant from the vertices of the triangle. • Circumcenter is the point where all the perpendicular bisector segments meets. • The angle bisectors of a triangle intersect at a point that is equidistant from the sides of the triangle. That is why you can make a circle in side of that triangle and the radius will be same. • Incenter is the point that is intersected by all three angle bisectors. It is equidistance from each sides. • Median is the segment that goes from the vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. • A centroid is a point where all the medians meet. Something very special about centroid is that each line is divided into one side that is one-third and the other side is two-thirds, also centroid is the center of gravity when you are building something. Altitude is a perpendicular segment that pass through the vertex and the side of the opposite side to that vertex. And simply orthocenter is the point where every altitudes meet. • Mid segment of the triangle is the segment that has two endpoints of the mid points of 2 sides of the triangle. • The segment joining the midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side, and is half the length of the third side. • The Theorem tells us that the midsegment of a triangle will be parallel to a side of triangle and also will be ½ of it. • The relationship between opposite angles and segments is that the side that is the longest in the triangle will have the biggest angle facing it. The angle that is facing the shortest side will be the smallest angle in the triangle. • We use Angle-Side Relationships to find the biggest and smallest angles just by knowing the measurement of sides, or opposite way. • An exterior angle is always bigger than the 2 non-adjacent angles in the inside of a triangle. Examples The sum of any 2 sides of the triangle will be always greater then the 3rd side. 1)AB+AC > BC AB+BC>AC 3) BA+VX>AC 2) BA+CA>BC AC+BC>AC Indirect proofs 1.Change the statement as the opposite(false) 2.Use the new statement as the given 3.Solve 4.When you can’t solve any more write a contradiction. • You just have to follow this steps to prove any statement using indirect proofs. Examples • Triangle has 2 obtuse angles • So first change the statement to opposite, which is triangle has 2 obtuse angles (given). • Then <1+<2+<3=180 (triangle) sum theorem • Obtuse angle= 90>x (def of obtuse angle) • When we have 2 angles that are obtuse we will get more then 180 in all the triangle (contradiction) Example • The women was in the bathroom, and at the same time she was blamed that she Stoll pancakes from monkeys that are in the jungle, people saw her entering to bathroom. • So here we change it to opposite she is guilty because she steal monkey’s pancake in jungle(given) • She can’t be in 2 places at the same time (contradiction) Example • Triangle can’t have angles that are more than 180 • Triangle has angles that are more than 180 (given) • <1+<2+<3=180 (def of triangle) • If one angle has more than 180, other 2 angles won’t have here own angles, (contradiction) Hinge theorem • If 2sides of a triangle are congruent to other two sides, then if one of the included angle of the triangles is bigger, then the opposite side is also bigger than the other. • Its converse says, if 2sides of a triangle are congruent to other two sides, then if one of the third side of the triangles is bigger than the other, then the opposite angle is also bigger than the other. Examples Given: AC=DF CB=FE Conclusion AB=DE Given: AC=DF CB=FE Conclusion AB=DE Given: AC=DF CB=FE Conclusion AB=DE Converse examples 1<2 C<D F<C • Hypotenuse is length of leg times √2. • Both legs are congruent. • So something very special about this theorem is that the triangle’s legs will be the same size but the hypotenuse will be length times √2 Examples 15 X root2 X= 4 X root2 X= 4root2 16/root2 Which is 8root2 30-60-90 Theorem • In the triangle that has 3 angles of 30 60 and 90 the Hypotenuse will be always double of the base and the 3rd side will be always base X root3 Examples X= 16/2 = 8 Y= 8 X root3 8root3 X= 60/2 = 30 X=12/root3 4root3 y= 4root3 X 2 8root3 _____(0-10 pts.) Describe what a perpendicular bisector is. Explain the perpendicular bisector theorem and its converse. Give 3 examples of each. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe what an angle bisector is. Explain the angle bisector theorem and its converse. Give at least 3 examples of each. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe what concurrent means. Explain the concurrency of Perpendicular bisectors of a triangle theorem. Explain what a circumcenter is. Give at least 3 examples of each. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe the concurrency of angle bisectors of a triangle theorem. Explain what an incenter is. Give at least 3 examples of each. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe what a median is. Explain what a centroid is. Explain the concurrency of medians of a triangle theorem. Give at least 3 examples of each. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe what an altitude of a triangle is. Explain what an orthocenter is. Explain the concurrency of altitudes of a triangle theorem. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe what a midsegment is. Explain the midsegment theorem. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe the relationship between the longer and shorter sides of a triangle and their opposite angles. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe the exterior angle inequality. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe the triangle inequality. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe how to write an indirect proof. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe the hinge theorem and its converse. Give at least 3 examples. _____(0-10 pts.) Describe the special relationships in the special right triangles (30-60-90 and 45-45-90). Give at least 3