* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War Looms
Spain during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
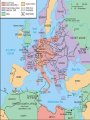
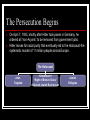
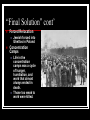
World War Looms Why might the Unites States try to remain neutral? Examine the Issues How might involvement in a large scale war influence the United States? How can neutral countries participate in the affairs of warring countries? Dictators Threaten World Peace Main Idea The rise of rulers with total power in Europe and Asia led to World War II. Why it Matter Today Dictators of the 1930’s and 1940’s changed the course of history, making world leaders especially watchful for the actions of dictators today. Nationalism Grips Europe and Asia The postwar years also brought the rise of powerful dictators driven by the belief in nationalism-the loyalty to one’s country above all else-and dreams of territorial expansion. Failures of World Peace Treaty of Versailles caused anger and resentment Stalin Transforms the Soviet Union Joseph Stalin- “Man of Steel” Made the Soviet Union a communist state #1 goal was control both agriculture and industry He abolished all privately owned farms He transformed the Soviet Union from the a rural nation to an industrial power. 1928- He outlined his “5 year plan” All economic activity was controlled by the government Stalin was responsible for some 8 million deaths The Rise of Facism in Italy Benito Mussolini Facist Party- stressed nationalism and placed the interests of the state above those of individuals. Facists believed in a single strong leader. 1922- marched on Rome w/the “Black Shirts” Il Duce- “the leader” The Nazis Take Over Germany Adolf Hitler Der Fuher “the leader” Mein Kampf-”My Struggle” Unify all Set forth the basic beliefs of Nazism that later became the plan of action for the Nazi Party. Nazism- extreme nationalism German-speaking people Racial Purification Lebensraum- “living space” Storm Troopers or Brown Shirts Third Reich “Thousand Year Reich” Militarist Gain Control in Japan Aggression in Europe and Asia Japan launches a surprise at China and seize control of Manchuria in 1931 Japan leaves the League of Nations Hitler builds up army and invades the Rhineland Mussolini invades Ethiopia Civil War Breaks Out in Spain Gen. Francisco Franco rebelled against the Spanish republic 3,000 Americans-Abraham Lincoln Battalion Civil War in Spain. Franco backed by Hitler & Mussolini Rome-Berlin Axis signed The United States Responds Cautiously Most Americans were alarmed by the international conflicts of the mid thirties but believed that the United States should not get involved. 1928-Kellog-Briand Pact 62 countries signed saying they would not use war as an “instrument of national policy.” America Clings to Isolationism Senator Gerald Nye (Nye Committee)-banks & manufacturers made money during the war. Neutrality Acts: 1st two- outlawed arms sales to nations at war 3rd- banned the sale of arms to nations at civil war. Neutrality Breaks Down Japan launched an attack on China in July 1937. Roosevelt finds a way around the Neutrality Acts Send arms to China Organization Information Russia Type of Government Leader Actions Taken Totalitarian Communism Joseph Stalin “man of steel” 1. 2. Industrial power Gov. Control Italy Germany Japan Fascism Nazism Militarism (Third Reich) Nationalism Benito Mussolini “Il Duce” Adolf Hitler “Der Fuher” 1. 2. State power “Black Shirts” 1. 2. “Racial purificat ion” Mein Kampf Hideki Tojo 1. 2. Left League of Nations Invaded Manchur ia December 8, 1941 Dictators Threaten World Peace What were Stalin’s goals and what steps did he take to achieve them? To make the Soviet Union socialist by ending private enterprise; to transform it into a great industrial power by building state-owned factories and power plants. How did Germany’s and Italy’s involvement affect the outcome of the Spanish Civil War? Hitler and Mussolini’s military support helped Franco take power in Spain. War In Europe Main Idea Using the sudden mass attack called blitzkrieg, Germany invaded and quickly conquered many European countries. Why it Matter Today Hitler’s actions started World War II and still serve as a warning to be vigilant about totalitarian government Austria and Czechoslovakia Fall Hitler declared that to grow, Germany needed the land of its neighbors. His plan was to absorb Austria and Czechoslovakia into the Third Reich. Union with Austria March 12, 1938-German troops marched into Austria unopposed. Bargaining for the Sudetenland Western part of Czechoslovakia Hitler invites Edouard Daladier & Neville Chamberlain to Munich Hitler says the annexation of the Sudetenland will be his “last territorial demand” Sept. 30, 1938- Munich Agreement Appeasement- giving up principles to pacify an aggressor. The German Offensive Begins Hitler warned he was not finished expanding the Third Reich. March 15, 1939- German troops poured into what was left of Czechoslovakia. Then later into Poland. German Offensive Soviets Declare Neutrality Blitzkrieg in Poland The Phony War Nonaggression Pact w/the Soviet Union Lighting War Britain & France Declare War Sitzkrieg Hitler attacks Norway, Denmark Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg France and Britain Fight On France’s Maginot Line proved to be ineffective; the German army threatened to bypass the line during its invasion of Belgium. The Fall of France Germans trapped almost 400,000 British & French soldiers as they fled to the beach of Dunkirk. Italy enters the war on the side of Germany and attacks France from the south. France surrenders- June 22, 1940 Charles de Gaulle- French general flees to England and sets up a government-in-exile The Battle of Britain Summer of 1940- Luftwaffe begins to bomb Britain Destroy the Royal Air Force (RAF) 1,000 planes every night for 2 months bomb London. New technology helped Britain curb the bombing- the Radar Battle of Britain Why were the Germans defeated ? The Germans fought too far away from their bases so that refueling and rearming were impossible. The German fighters had a very limited time which they could spend over Britain before their fuel got too low. British fighters could land, refuel and rearm and be in the air again very quickly. The change of targets was crucial. It is now believed that Fighter Command was perhaps only 24 hours away from defeat when the attack on the cities occurred. The breathing space this gave Fighter Command was crucial. Radar War in Europe Review Why was the blitzkrieg effective? It surprised the enemy and then crushed it with overwhelming force. What terms of surrender did Hitler demand of the French after the fall of France in 1940? What was General Charles de Gaulle’s reaction? German occupation of northern France and the establishment of a Nazi-controlled puppet government in southern France; de Gaulle fled to England and set up a government-in-exile. The Holocaust Main Idea During the Holocaust, the Nazis systematically executed 6 million Jews and 5 million other “nonAryans” Why it Matters Today After the atrocities of the Holocaust, agencies formed to publicize human rights. These agencies have remained a force in today’s world. The Persecution Begins On April 7, 1933, shortly after Hitler took power in Germany, he ordered all “non-Aryans” to be removed from government jobs. Hitler moves for racial purity that eventually led to the Holocaust-the systematic murder of 11 million people across Europe. The Holocaust Jews Targeted Kristallnacht “Night of Broken Glass” Attacked Jewish Businesses Jewish Refugees Jews arrested during Kristallnacht Hitler’s “Final Solution” Obsessed with a desire to rid Europe of its Jews, Hitler imposed what he called the “Final Solution”-a policy of genocide, the deliberate and systematic killing of an entire population. The Condemned Jews Gypsies-whom the Nazis believed to be an “inferior race” Freemasons- charged as supporters of the “Jewish Conspiracy” Jehovah’s Witnesses- who refused to join the army or salute Hitler Homosexuals, people w/mental illnesses, the disable “Final Solution” cont’ Forced Relocation Jewish forced into Ghettos in Poland Concentration Camps Life in the concentration camps was a cycle of hunger, humiliation, and work that almost always ended in death. Those too weak to work were killed. The Final Stage The Final Solution reached its final stage in early 1942. The 3rd phase would add murder by poison gas. Mass Extermination The German built 6 death camps in Poland. Chambers could kill 12,000 people a day. An estimated 6 million Jews died in the death camps. Auschwitz Death Camps Dachau Treblinka The Holocaust Review What groups did Nazis deem unfit to belong to the Aryan “master race?” Jews, Gypsies, homosexuals, people with mental or physical disabilities, Poles, Ukrainians, and Russians. How did some Europeans show their resistance to Nazi persecution of the Jews? Some people risked death by hiding Jews in their homes or helping them to escape to neutral countries. America Moves Toward War Main Idea In response to the fighting in Europe, the United States provided economic and military aid to help the Allies achieve victory. Why it Matters Today The military capability of the U.S. became a deciding factor WWII and in world affairs ever since. The United States Musters Its Forces As German tanks thundered across Poland, Roosevelt issued an official proclamation of neutrality. U.S. Musters Forces U.S. Neutrality The Axis Threat Building U.S. Defense “Cash-&-Carry” Tripartite Act German, Italy, Japan Selective Training & Service Act The Great Arsenal of Democracy Not long after the election, President Roosevelt told his radio audience during a fireside chat that it would be impossible to negotiate a peace with Hitler. Lend-Lease Act Great Arsenal German Wolf Packs Supporting Stalin FDR Plans for War With the army provided for, Roosevelt began planning for the war he was certain would come. The Atlantic Charter Great Britain and U.S pledged: collective security, disarmament, self-determination, economic cooperation, and freedom of the seas. Shoot on Sight U-boat attacks “When you see a rattlesnake poised to strike, you crush him” Full-scale war seemed inevitable. Japan Attacks the United States Japan Attacks Japan in the Pacific Peace Talks Hideki Tojo Japan in Indochina U.S. oil embargo Hirohito negotiates Tojo plans attack Dec. 6, 1941 U.S. Issues warning Attack on Pearl Harbor Reaction to Pearl Harbor Dec. 7, 1941 2,403 killed 1,178 wounded “A day that will live In infamy” Congress declares war America Moves Toward War Review What congressional measures paved the way for the U.S. entry into World War II? Increased defense spending, peacetime draft, Lend-Lease Act, and an end to the ban against arming merchant ships. Why did the United States enter World War II? Because the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor.