* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DW Geometry Assessment - Crook County School District #1
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
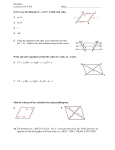
District Assessment Crook County School District #1 Geometry - Fall Exam (revised 2015) Student’s Name: __________________________________ Grade Level: _____ 1. (Standard G-SRT.B.5) If the measure of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is 120˚, how many sides does the polygon have? 3. Period: ___________ (Standard G-CO.A.1) “Two lines in a plane always intersect in exactly one point.” Which of the following best describes a counterexample to the assertion above? A. 3 B. 4 A. Coplanar lines C. 5 B. parallel lines D. 6 C. perpendicular lines D. A conditional statement is shown below. If a quadrilateral has perpendicular diagonals, then it is a rhombus. (Standards G-CO.C.11, G-SRT.B5) 2. Which of the following is a counter example to the statement above? A. intersecting lines In the diagram below, 1 4 4. (Standards G-CO.C.9, G-CO.C.10) l 1 2 3 C. m 4 t Which of the following conclusions does not have to be true? B. D. A. 3 and 4 are supplementary angles B. Line l is parallel to line m. C. 1 3 D. 2 3 5. (Standard G-SRT.B.5) Given: TRAP is an isosceles trapeziod with diagonals RP and TA . Which of the following must be true? 8. (Standard G-SRT.B.5) In the figure below, AC DF and A D . C A. RP TA B B. RP || TA C. RP A F TA D. RP bisects TA E 6. (Standard G-SRT.B.5) Which figure can serve as a counterexample to the conjecture below? If one pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral is parallel, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. A. B. C. D. rectangle Rhombus Square trapeziod Which additional information would be enough to prove that ABD DEF ? A. AB DE B. AB BC C. BC EF D. BC DE 7. (Standard G-CO.C.11) What values of a and b make quadrilateral MNOP a parallelogram? N D 21 9. (Standard G.CO.C.10) What is the m WZX ? O 1320 V 3a – 2b 13 W M P Z 4a + b 0 52 Y A. a = 1, b = 5 X B. a = 5, b = 1 C. a = 11 34 ,b= 7 7 A. 800 B. 900 C. 1000 D. a = 11 34 ,b= 7 7 D. 1100 10. (Standard G.CO.D.12) Marsha is using a straightedge and compass to do the construction shown below. 12. (Standard G.CO.D.12) Given: angle A What is the first step in constructing the angle bisector of angle A? B P l Which best describes the construction Marsha is doing? A. a line through P parallel to line l B. a line through P intersecting line l C. a line through P congruent to line l D. a line through P perpendicular to line l 11. (Standards G-SRT.B.5) What is m 1 ? D C A A. Draw ray AD B. Draw a line segment connecting points B and C. C. From points B and C, draw eual arcs that intersect at D. D. From point A, draw an arc that intersects the sides of the angle at points B and C. 13. (Standard G-CO.C.11) If ABCD is a parallelogram, what is the length of segment BD? 36° B C 88° 5 7 E 6 A 1 D A. 10 B. 11 A. 34° C. 12 B. 56° D. 14 C. 64° D. 92° 14. (Standard G-SRT.B.5) The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is the same as the sum of its exterior angles. What type of polygon is it? 17. (Standard G-CO.C.10) Two angles of a triangle have measures of 55° and 65°. Which of the following could not be a measure of an exterior angle of the triangle? A. quadrilateral A. 115° B. hexagon B. 120° C. octagon C. 125° D. decagon D. 130° 15. (Standard G-CO.C.11) In Parallelogram FGHI, diagonals IG and FH are drawn and intersect at point M. Which of the following statements must be true? 18. (Standard G-CO.C.10) What is m x ? B x A. ∆FGI must be an obtuse triangle. B. ∆HIG must be an acute triangle. C. ∆FMG must be congruent to ∆HMG. D. ∆GMH must be congruent to ∆IMF. 16. (Standard G-CO.C.11) Quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram. If adjacent angles are congruent, which statement must be true? A. Quadrilateral ABCD is a square. A 60° 25° C A. 35° B. 60° C. 85° D. 95° 19. (Standard G-CO.C.11) In the figure below, AB || CD . B. Quadirlateral ABCD is a rhombus. A D (x + 40)° (x – 40)° C. Quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle. D. Quadrilateral ABCD is an isosceles trapeziod. B What is the value of x ? A. 40 B. 50 C. 80 D. 90 C 20. (Standard G-SRT.B.5) For the quadrilateral shown below, what is ma mc ? C c° B 95° 32° 22. (Standard G-CO.C.11) In the figure below, n is a whole number. What is the smallest possible value for n? D a° A. 53° n A n B. 137° 15 C. 180° A. 1 D. 233° B. 7 C. 8 21. (Standard G-CO.C.9) In the accompanying diagram, parallel lines l and m are cut by transversal t. D. 14 23. (Standard G-CO.C.11) Parallelogram ABCD is shown below. t 1 A l 2 B m E Which statement about angles 1 and 2 must be true? A. 1 2 D C B. 1 is the complement of 2 . Which pair of triangles can be established to be congruent to prove that DAB BCD ? C. 1 is the supplement of 2 . A. ∆ADC and ∆BCD D. 1 and 2 are right angles. B. ∆AED and ∆BEC C. ∆DAB and ∆BCD D. ∆DEC and ∆BEA (G-CO.D.12, G-CO.C.9) 24. A 500 B 1300 1300 D C Is ABCD a parallelogram? (Figure is not drawn to scale.) Explain your reasoning. You cannot answer, “Because it looks like one or because it doesn’t look like one.” (G-SRT.B.5) 25. BD is the perpendicular bisector of AC . Is ABD CBD ? Why or why not? Explain your reasoning. B A C D