* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Bonds
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
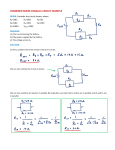
Current Electricity What Happened Here?? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0OK0VKz9mkc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TIy3GqS-cd8 Electric Current – The rate that electric charges move through a conductor. Unit is Ampere. 1 Amp = 1 Coulomb 1 Second Forget the Coulomb, I just need a regular COMB! Electrical Resistance The tendency of a material to resist the flow of electrons*. * Caused by collisions (and friction) of charges and atoms of the conductor. A light bulb is a resistor. It changes electrical energy into light and thermal energy Electrical Resistor – Device designed to slow the movement of electrical current. Ohm’s Law The ratio of voltage across a conductor to the current it carries. Resistance (R) = Voltage (V) Current (I) Measured in Ohms. 1 Ohm (Ω) = 1 Volt 1 Ampere Georg Ohm (1787 – 1854) No e for me just G-E-O-R-G! V I R 1. If the current through a certain resistor is 6.2 Amps and the voltage across the resistor is 110V, what is the resistance? 2. If the Voltage across a flashlight bulb is 3V and the bulbs resistance is 6Ω, what is the current through the bulb? Electrical Circuit An assembly of electrical devices connected so that it provides a predictable, controlled path for the electrical current. Series Circuit – A circuit that forms a single path for electrical current. Parallel Circuit A circuit consisting of devices connected at common points that provide two or more paths for electrical current. Schematic Diagram A diagram that uses standard symbols to represent components of an electrical circuit. Schematic Diagram What type of circuit? In a Series Circuit; • The current is the equal throughout the circuit. • The equivalent resistance is the sum of the individual resistors. REq = R1 + R2 + R3 • The total voltage is the sum of the voltage drops across each resistor. For the following circuit determine; • The current • The equivalent resistance. • The voltage drop across each resistor. In a Parallel Circuit; • The total current is the sum of the currents through each path. • The equivalent resistance is the sum of the individual resistances. 1 = 1 1 1 REq R1 + R2 + R3 • The voltage is the same for each resistor. For the following circuit determine; • The total current • The equivalent resistance. • The voltage drop across each resistor. In a Series-Parallel Circuit; 1. Draw a schematic. 2. Calculate the equivalent resistance for parallel resistors. 3. Re-draw schematic. 4. Calculate the new equivalent resistance for series resistors. 5. Find the total current. 6. Go backwards to find voltage drops and currents across individual resistors. Circuits - Combine equivalent resistance for resistors R3 + R4. R34 = R3 + R4 = 5 Ω + 15 Ω = 20 Ω - Re-draw schematic. Calculate the new equivalent resistance for parallel resistors. - 1 = 1 + 1 = 15Ω REq 60Ω 20Ω - Re-draw schematic. - Calculate the new equivalent resistance for series resistors. Req = 25 Ω + 15 Ω + 20 Ω = 60Ω - Find total current and voltage drops across individual resistors. I = 120V = 2 Amps 60Ω - Finally, calculate the current through each parallel resistor (using the voltage for each section) I = 30V = 0.5 Amps 60Ω I = 30V = 1.5 Amps 20Ω etc…