* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometric Similarities
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
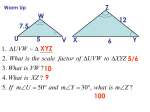
Geometric Similarities Math 416 Geometric Similarities Time Frame 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Similarity Correspondence Proportionality (SSS) (Side-side-side) Proportionality (SAS) (side-angle-side) Similarity Postulates Deductions Dimensions Three Dimensions Similarity Correspondence Similarity – Two shapes are said to be similar if they have the same angles and their sides are proportional Note – we see shape by angles & we see size with side length Consider A 8 100 Similar & Why? D 95 24 X 16 100 15 W 95 10 85 80 B 5 80 32 C Y 85 20 Z Proportionality (SSS) We say the two shapes are similar because their angles are the same and their sides are proportional We can note corresponding points AX DW BY CZ Angles We note corresponding angles < ADC = < XWZ (95°) < DCB = < WZY (85°) < CBA = < ZYX (80°) < BAD = < YXW (100°) Notes Hence we would say ADCB XWZY Hence we note corresponding angles < ADC = < XWZ < DCB = < WZY < CBA = < ZYX < BAD = < YXW Proportionality Next is proportionality which we will state as a fraction AD=8 DC=16 CB=32 BA=24 XW 5 WZ 10 ZY 20 YX 15 What is the proportion (not in a fraction)? 8/5 which is reduced to 1.6 Question #1 Identify the similar figures and state the similarity relationship, side proportion and angle equality A BIG T MED MED B Z BIG SMALL C SMALL C Notes for Solution By observing you need to establish the relationship. Look at angles or side lengths Important: An important trick when comparing angles and sides is that the biggest angles is always across the biggest side, the smallest from the smallest and medium from the medium. Solution #1 Triangle ABC ˜ TCZ AB = BC = CA TC CZ ZT < ABC = < TCZ < BCA = <CZT < CAB = <ZTC Important Note Make sure the middle angle letters are all different because the middle letter is the actual angle that you are looking at. AC = CA < ACB = < BCA Both the above are the same Question #2 R K MED MED SMALL Q SMALL T MED MED L X With isosceles (or equilateral triangles) you may get two (or three) different answers). However, you are only required to provide one. Solution a for #2 The question is to identify similar figures and state the similarity relationship, side proportion and graph equality. QKT ˜ RXL QK = KT = QT RX XL RL < QKT = < RXL < KTQ = < XLR < TQK = < LRX Solution b for #2 You can also have another solution Triangle QKT is still congruent to RLX QK = KT = QT RL LX RX < QKT = < RLX < KTQ = < LXR < TQK = XRL More Notes There are other ways of establishing similarity in triangles At this point we will abandon reality for simple effective but not accurate drawings of triangles… (it is not to scale). Please complete #1 a – o For Question #3, again, state similarity relationship, side proportion and angle equality. Question #3 T A 18 B 21 35 Q 45 30 R 27 C If the three sides are proportional to the corresponding three sides in the other triangle, the two will be similar. Solution Notes You need to check… SMALL with SMALL MEDIUM with MEDIUM BIG with BIG Solution #3 ABC ˜ QRT Small Small Med Med Big 18 = 21 = 27 30 0.6 35 Big 45 = 0.6 = 0.6; YES SIMILAR Proportionality SAS We can also show similarity in triangles if we can find two set corresponding sides proportional and the contained angles equal; we can determine similarity X A 18 14° 15 42 14° Y B C 35 Z Question #4 Show if the triangle is similar Solution… since <BAC = <XYZ = 14° 18 = 42 15 35 = 6/5 6/5 BAC ˜ XYZ Notice BAC = Small, Angle, Big & compared to Small, Angle, Big Triangle Similarity Postulates There are three main postulates we use to state similarity SSS all corresponding sides proportional SAS two sets of corresponding sides and the contained angle are equal AA two angles (the third is automatically equal since in a triangle, the interior angle must add up to 180°) are equal Example #1 Why are the following statements true? QPT ˜ ZXA X AA Q 84° 42° 54° P 84° 54° T A Z Example #2 Why are the following statements true? M SAS KTR ˜ PMN R 18 27 51° T 24 K N 51° 16 P Solution: since 24/16 = 27/18 Example #3 K A 16 B 12 24 C 32 T 6 9 Since 16 = 24 = 32 6 9 12 8/3 = 8/3 = 8/3 SSS P Parallel Lines Facts: If two tranversals intersect three parallel lines, the segments between the lines are proportional a c b d Therefore, a = c b d Notes Also note that… C B A • • BC = 1 • AC 2 Parallel and the Triangle If a parallel line to a side of a triangle intersects the other two sides it creates two similar triangles A B C Therefore, ABE ˜ ACD E D Question #1 3 4 9 x 3= 9 4 x 3x = 36 Find x x = 12 Question #2 A We note BE // CD Thus, x B 40 C 50 ABE ˜ ACD AB = BE = AE E AC CD AD x = 50 = AE 150 D x+40 150 AD Question #2 Sol’n Con’t We only need x = 50 x+40 150 150x = 50(x+40) 150x = 50x + 2000 100x = 2000 x = 20 Proportion Ratio Consider 1 10 1 10 Dimensions SIDE SMALL BIG RATIO SIDE 1D 1 10 1:10 or 1/10 AREA 2D 1 100 1:100 OR 1/100 Dimensions In general in 1D if a:b then in 2D a2 : b2 Ex. In 1D if 5:3 then in 2D? In 2D then 25:9 You can go backwards by using square root Ex. In 2D if 36:49 then in 1D 6:7 3D or Volume Consider 1 5 1 1 5 5 3D or Volume Side 1D Small Big Ratio 1 5 1:5 or 1/5 125 1:125 or 1/125 Volume 3D 1 3D or Volume In general in 1D if a:b then in 3D… Then in 3D a3 : b3 Ex. In 1D if 6:7 then in 3D In 3d 216:343 You can go backwards by using the cube root Ex. In 3D if 27:8 then in 1D In 1D 3:2 Practice Complete the following 1 D Length 2 D Area 3 D Volume 2:9 4:81 8:729 2:11 4:121 8:1331 5:3 25:9 125:27 3D Question #1 Two spheres have a volume ratio of 64:125. If the radius of the large one is 11cm, what is the radius of the small one? 3D Ratio 64:125 Big Small 1D Ratio 4:5 r 11 x 5x = 44 x = 8.8 Thus 4 = x 5 11 3D Question #2 V=? V=200m3 A Base = 100m2 A base = 16 m2 Question #2 Solution Big Small Area of Base 100 16 Volume 200 x Thus 200 = 1000 x 64 1000x = 12800 x = 12.8 1 Ratio 10 / 4 2 Ratio 100/16 3 Ratio 1000/64