* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Connective tissue protein
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
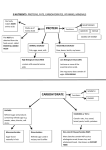
MEAT HYGEINE Dr. Auday S.K AL-Jubori Lecture ( 2 ) Anatomy, Meat Composition and Quality Anatomy :- Cells are the basic building blocks of all living matter. Billions of different types of cells from the tissues of the body; each type is distinct in shape and function . In complex organisms, cells are specialized in form and function. There is also differentiation of cells between different types of organism in the animal kingdom, Which acts as a basis for their classification. There are four main types of tissues in animal bodies:1- Epithelial tissues . Are found on external and internal surfaces and also form specialized structures such as the liver . 2- Muscular tissues . Constituting the flesh of animals, are of three main types :a- Voluntary muscles . Include striped or striated muscles . b- Involuntary muscles . Include unstriped or unstriated or smooth muscles . c- Cardiac muscles . Include a special form of striated muscle found only in the heart. 3- Connective tissues . Include the skeleton, which gives rigidity to the body. Blood is a specialized form of connective tissue although it is sometimes classified alone. 4- Nervous tissues . Is the most specialized of all the tissues. It transmits the nerve impulses of both sensation and movement. 1 Butcher meat:- Is a valuable part of the human diet because :1- It's the most concentrated and easily assimilable of nitrogenous food, and is a good source of first-class protein. i.e. it contains the amino acids essential for human life. 2- It's stimulating to metabolism because of its high protein content, i.e. it assists the body in the production of heat and energy. 3- It's satisfying, for the presence of fat in the diet delays emptying of the stomach ( meat contains fat and therefore remains in the stomach for some hours and allays hunger ). 4- After suitable treatment , which includes the processes of ripening and cooking, meat acquires a palatable flavor, acts as a stimulant to gastric secretion and is readily digested. The approximate composition of lean bovine muscle . Immediately after onset of rigor mortis is given :Water 75.0 % , Protein 19.0 % , Lipids ( fats and oils ) 2.5 % , Carbohydrates ( Glycogen ) 1.2 % , Non – protein nitrogen 1.65 % , Minerals 0.65 and Vitamins minute quantities .( small percentage ) . Note : The best type of meat when the percentage of unsaturated fatty acids high and the percentage of saturated low and the meat have large amount of protein . and this include types of white meat( poultry and fishes ) and same types of red meat i.e. meat of goats, deer, rabbits . 1 – Protein . Protein is the most important muscle constituent and is made up of myofibrillar , sacroplasmic and connective tissue proteins . a- Myofibrillar protein . Gives rigidity to the muscle and forms about-thirds of the total protein, the most important types being myosin and actin . 2 b- Sacroplasmic protein . Are the water-soluble proteins of the fluid cytoplasm of the muscle cells and include myoglobin muscle pigment , hemoglobin blood pigments and soluble glycolytic enzymes . c- Connective tissue protein . Along with the body segments of the body, form it's supporting mechanism . They include collagen, which is insoluble in water and salt and can be converted in to gelatin on heating , elastin, at ough yellow connective tissue, and reticulin, another form of connective tissue not converted to gelatin on heating. 2 – Lipids . The lipids are mostly composed of triglycerides, which are fats and oils, both of which are insoluble in water but soluble in ( ethyl and ether ). The lipids also include phospholipids, saturated, monounsaturated and poly unsaturated fatty acids and other fat-soluble substances, including cholesterol, the level of latter in carcass meat being relatively low, al though much higher in liver . Marked differences in teak muscular lipid level occur in the different species of meat animals. The quantity of fat in all meat animals is very much lower than it's used to be, because fat is an expensive tissue to produce and is not desired by the consumer. Differences in breed, sex, age, and level of nutrition also vary the fat content in meat. 3 – Carbohydrate . Carbohydrate is present mainly as glycogen ( animal starch ), which has major influence on muscle changes after death ( slaughter of animal meat ) . Glycogen also occurs in the liver and is especially abundant in horse meat and in the fetus. It's level in the animal body does not vary as much as does fat although older animals in general have lower reserves of glycogen. 3 4 – Non-protein nitrogen . Non-protein nitrogen is mainly represented by free amino acids, creatine, nucleotides, inosine, monophsphate and carnosine ( a lipetide ), some of which, notably the free amino acids and nucleotides, give meat it's flavor on cooking. Same suget ( e.g. glucose ), lipids ( e.g. certain lower fatty acids ), nitrogen – containing compounds termed pyrazines, and oxygen – and sulphur – containing compounds also contribute to the flavor of meat . 5 – Minerals . The inorganic minerals or ( Ash ) of muscle constitute a little less than 1% of the content, the main elements being in order importance sulpher , potassium , phosphours , sodium , chlorine, magnesium , calcium , iron , copper, chromium , selenium , cobalt ( as vitamin B12 ) and zinc . 6 – Vitamins . Vitamins occur in the form of water- soluble B vitamins thiamin ( vitamin B1), riboflavin ( vitamin B2 ), nicotinic acid ( nicin ), pyridoxine ( vitamin B6 ), panthathenic acid, biotin, folic acid ( pteroylmonoglutamic acid ) and vitamin B12 ( cyanocobalamin ), along with some vitamin A ( lipid – soluble ) and vitamin C ( water- soluble ascorbic acid ). Meat is our most important source of vitamin B12, which is not found in vegetable foods. This vitamin is essential for cell division and nuclear maturation as well as the formation of red blood cells. Deficiencies of Vitamin B12 often occur in man and animals, causing pernicious anaemia in the for mer and anorexia ( lack of appetite ), loss of condition and growth, muscular weakness and fertility in the latter. The important sources of vitamins B in pork, lamb and liver . Meat have vitamin A the important source of it in liver. The level of vitamins in meat is reduced by cooking, the amount depending on the temperature and time employed. 4 7 – Reducing bodies . Rrducing bodies which possess an enzyme action with marked oxidizing properties are present in meat, their action is manifested typically in carcass affected with icterus, for the yellow coloration of the tissues caused by the presence of the bile pigment bilirubin may often disappear if the icteric carcass is detained for 24 hours . 5